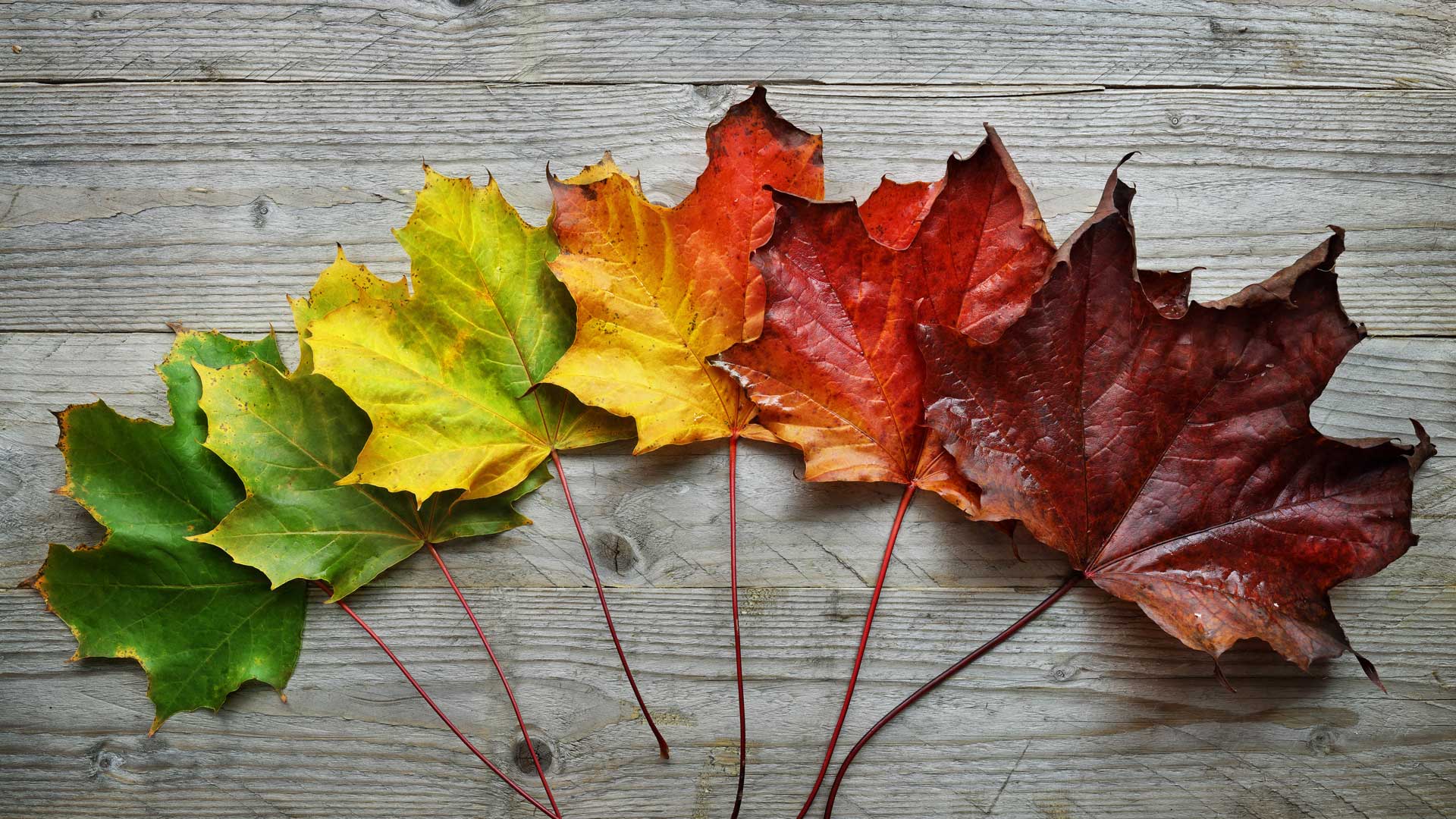
Leaf Color Variation
Based on the PCA model and the metabolic variations during the leaf color change, metabolite comparisons between purple and green leaves were further analyzed to determine the mechanism of leaf. Leaf color variation provides an essential window into a plant's nutritional status. Understanding how specific nutrient deficiencies manifest through changes like chlorosis, reddening, browning, or distorted growth enables timely identification and intervention.

In studies of variegated plants like Silverstripe, leaf color variations are largely due to differences in pigment types, amounts, and distribution [14]. Unlike typical pigment-driven color changes, Silverstripe's white leaves are notably caused by chlorophyll deficiency, offering unique insights into the mechanisms of leaf color variation. We investigated the impact of leaf color variation on herbivory, testing current hypotheses indicating that leaf color could influence herbivory through bottom-up control (by signaling leaf quality and defenses) or top-down control (by attracting predators).
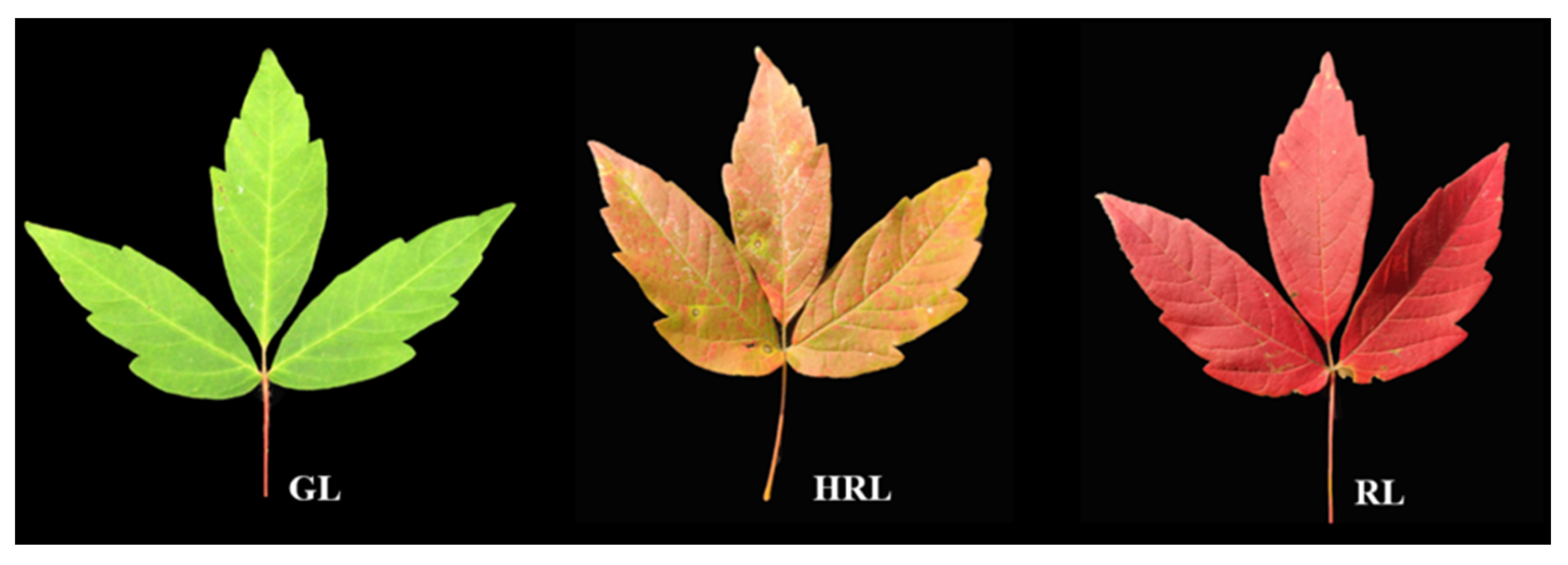

How Do Leaves Change Color
A comprehensive phylogenetic meta-analysis was conducted to assess the effects of leaf color on defense traits, leaf palatability. Autumn in full color. What triggers the color change? What color or colors do each species of trees turn? What causes the variations in color? The factors that influence autumn leaf color are shorter day lengths, weather (primarily cooler temperatures and less moisture) and changing lev.

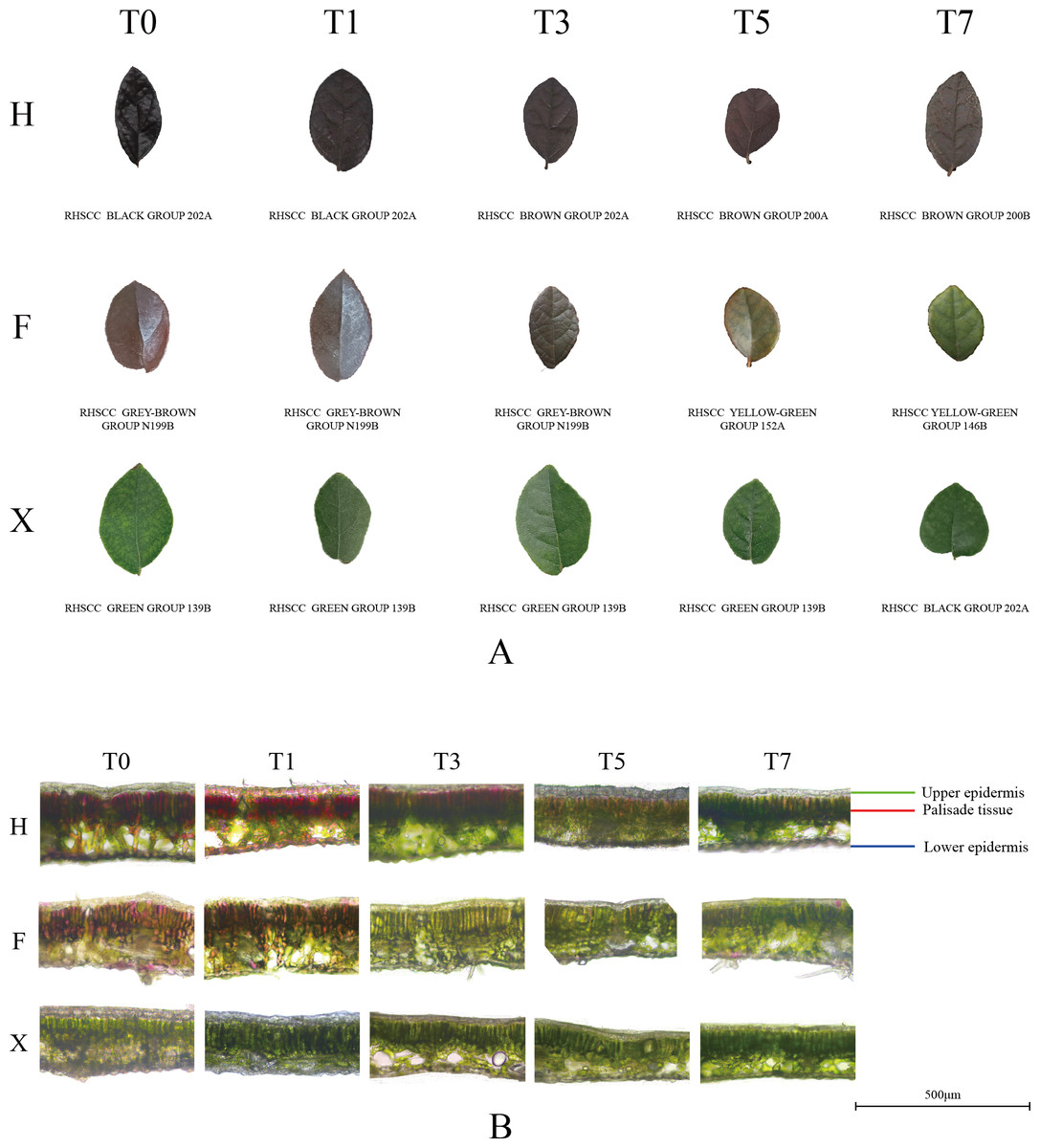
This study aims to elucidate the physiological and molecular mechanisms underlying leaf color change in maple leaves through physiological, transcriptional, and metabolic assays. Data analysis encompasses gene expression levels and metabolite changes in three distinct states of maple leaves: green, half-red, and red. In th study, the leaves in purple, purple-green, and green stages were compared in terms of anatomical, physiological, and molecular.

The sequence of leaves showing color differences between a mature leaf ...
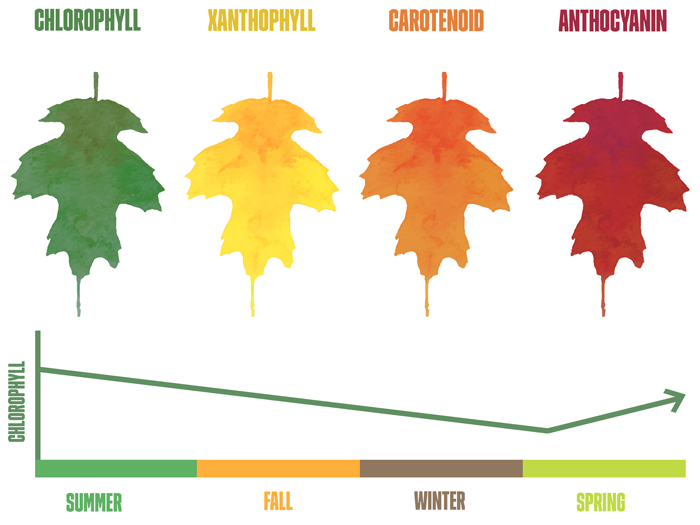
We found that the variation of leaf color from purple to green was mainly determined by the change in pigments distributed in the leaf surface. The color of fall foliage depends on the tree species and the mixture of pigments in the leaf. There are three main pigments that give leaves their color and include chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins.

In spring and summer chlorophyll is the pigment that gives leaves their green color. The Science of Leaf Color Change Leaf Pigments The pigments (chlorophylls, carotenoids and anthocyanins) which, in various combinations, account for the colors produced during autumn. When do leaves reach peak color? The peak dates for fall foliage in the U.S.
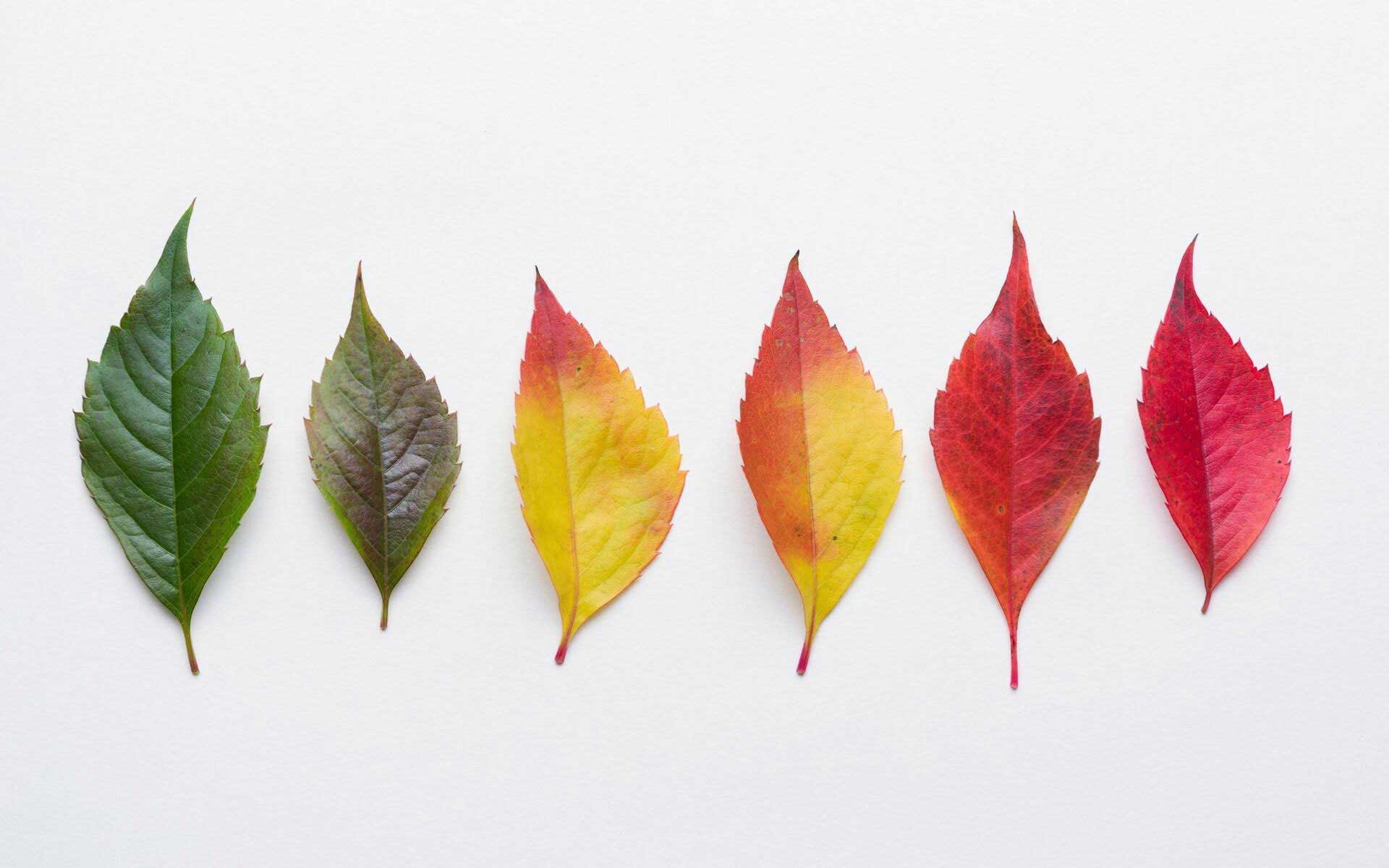

How Do Leaves Get Their Color at Steven Trinkle blog
vary from region to region.