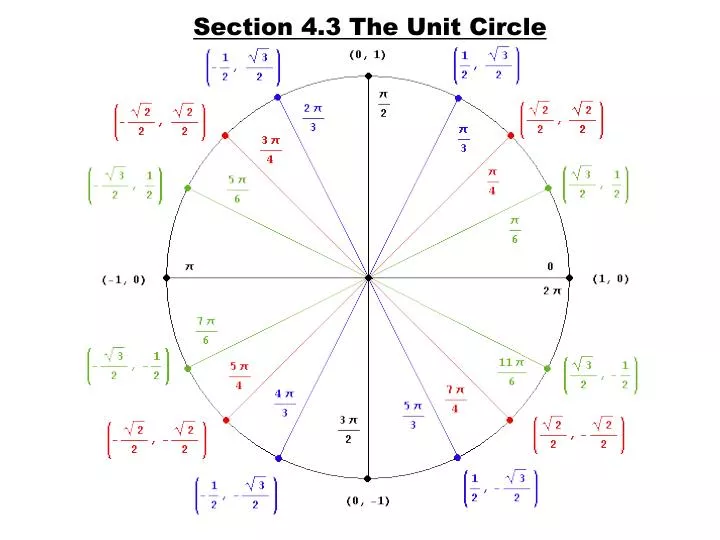
Unit Circle Powerpoint
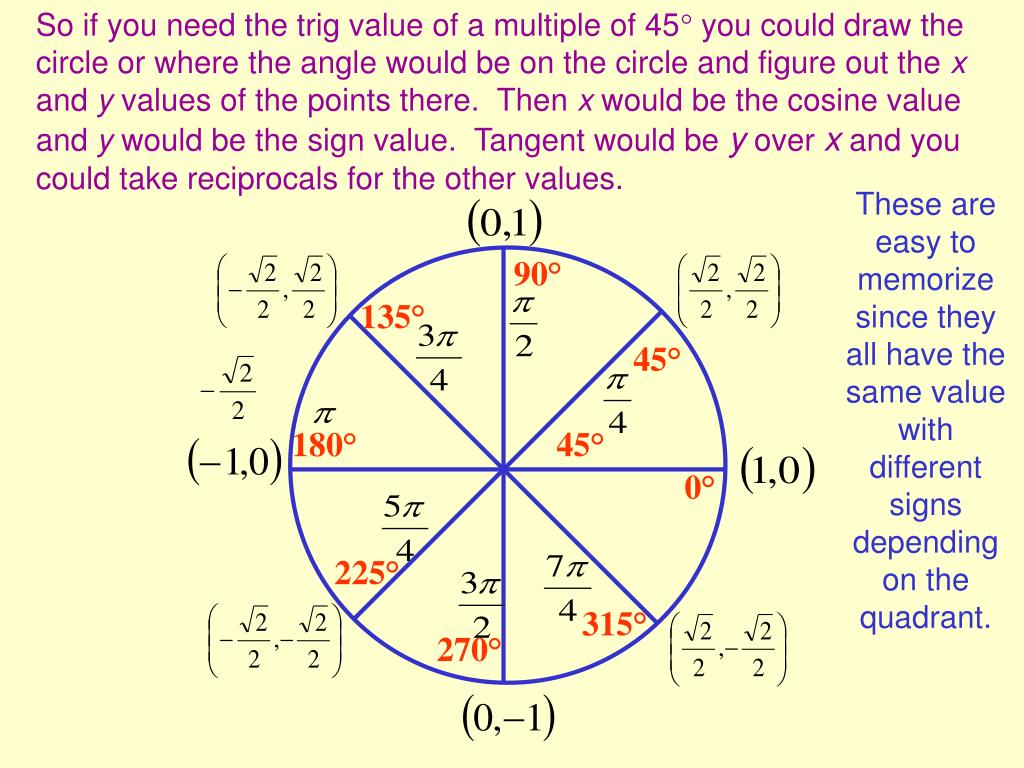
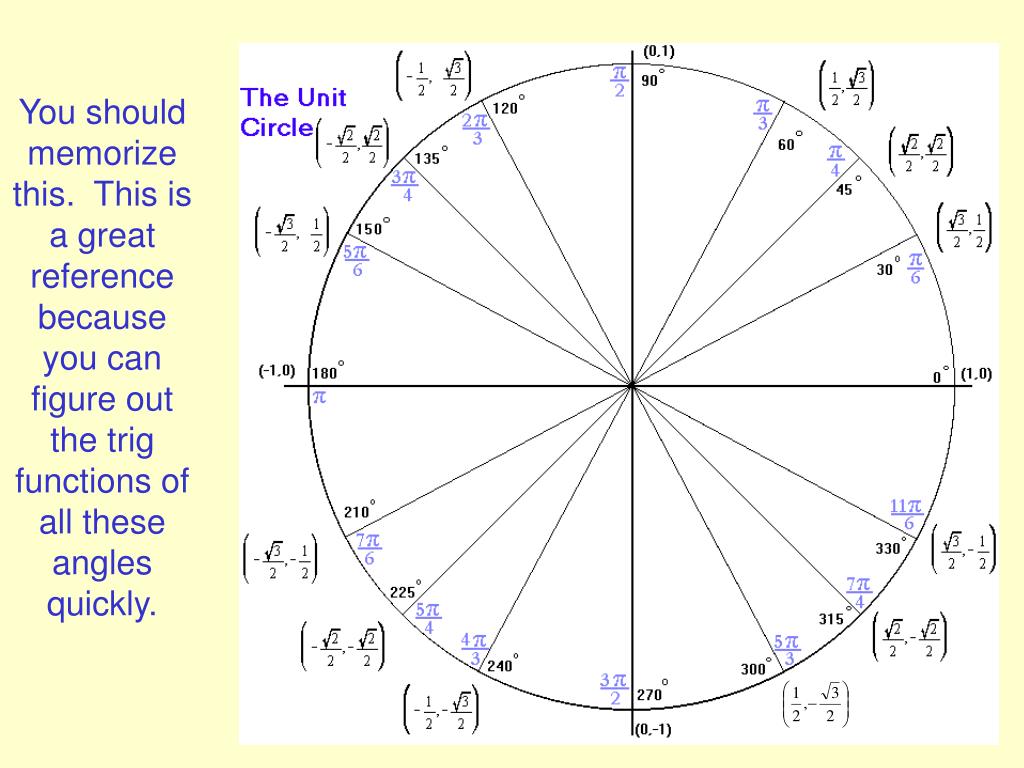
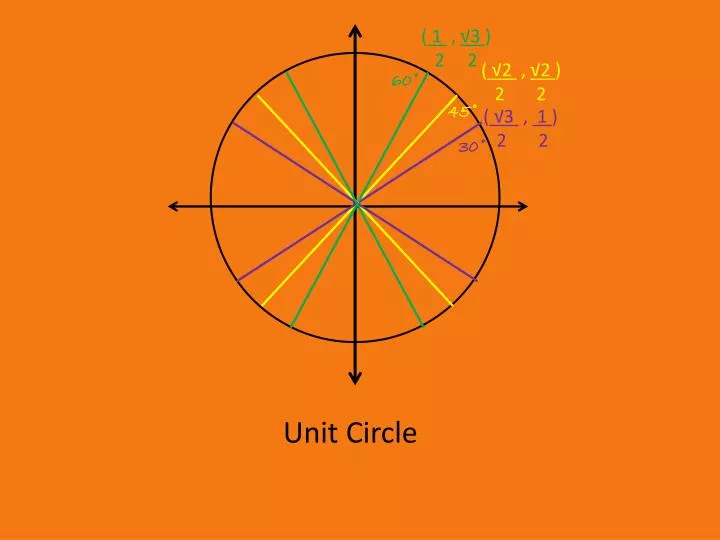
The document discusses the unit circle and angle measure. It defines a unit circle as a circle with radius of 1 centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. Common angles like 30, 45, 60, 90 degrees etc.
are marked on the circle. Radian measure is also discussed and the circumference of a unit circle is 2π. Special right triangles are used to determine the coordinates of points on the unit.

PPT - The Unit Circle PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4973719
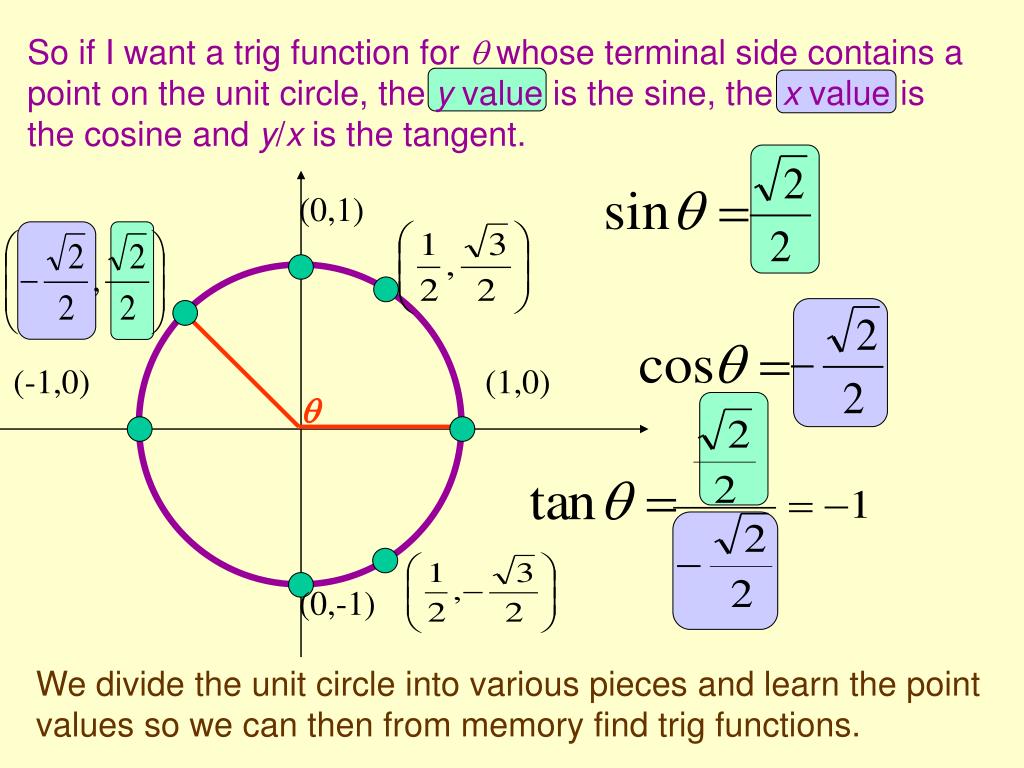
The unit circle and the point P We are going to use the unit circle to define the trigonometric functions in quite a sneaky way. Let P be a point on the circle itself and draw a line from the origin to the point P Let be the angle between the positive x-axis and the line joining P to the origin, as shown in the next slide. Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle.

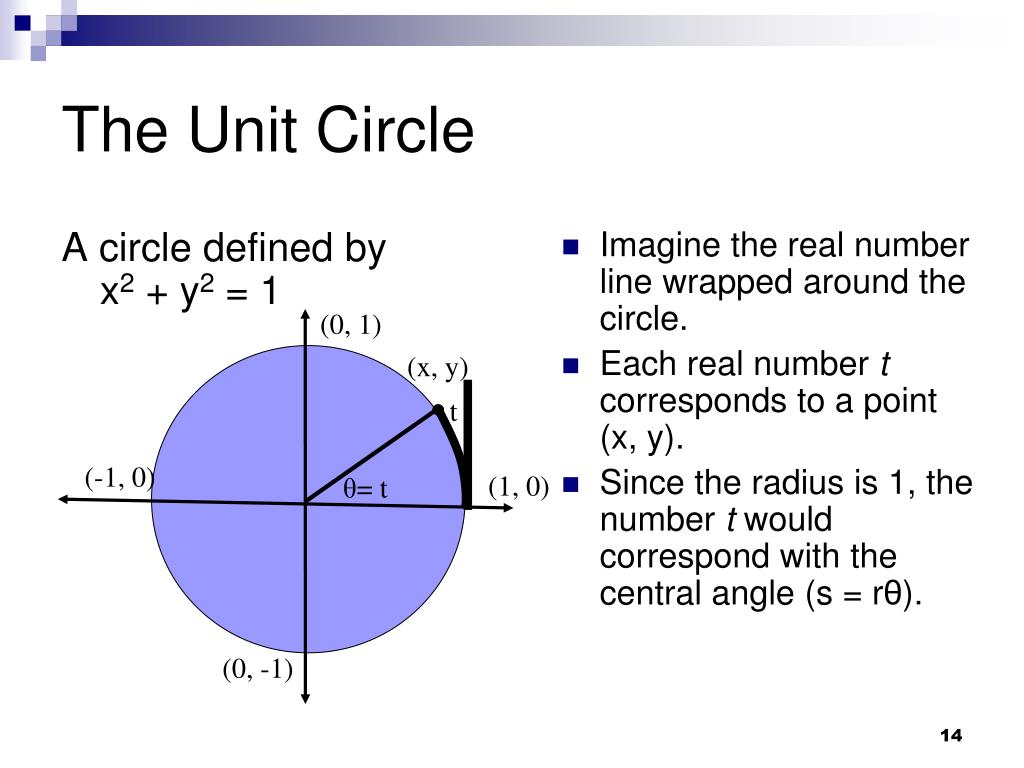
Section 4.2. Objectives. Identify a unit circle and describe its relationship to real numbers.
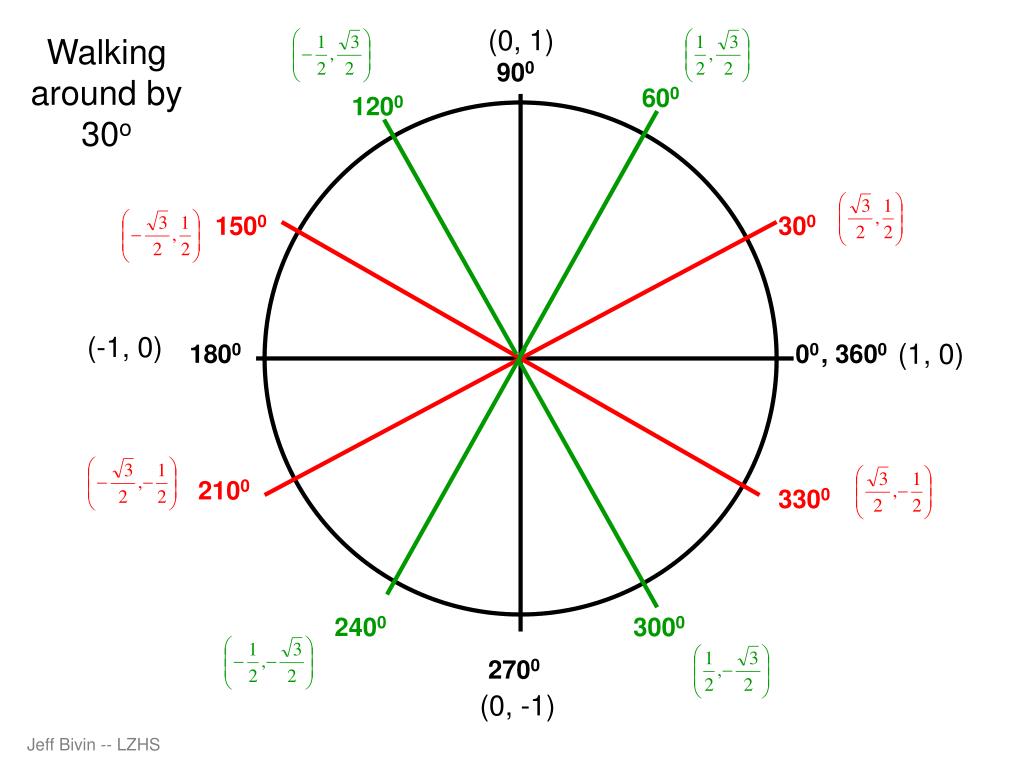
Unit Circle Ppt at Phyllis Fetter blog
Evaluate trigonometric functions using the unit circle. Recognize the domain and range of sine and cosine functions. Explore the unit circle, its properties, and trigonometric functions with this free PowerPoint presentation.

Unit Circle Powerpoint - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt /.pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document discusses trigonometric functions of any angle. It begins by defining an angle and introducing the concepts of coterminal angles, complementary angles, and supplementary angles.
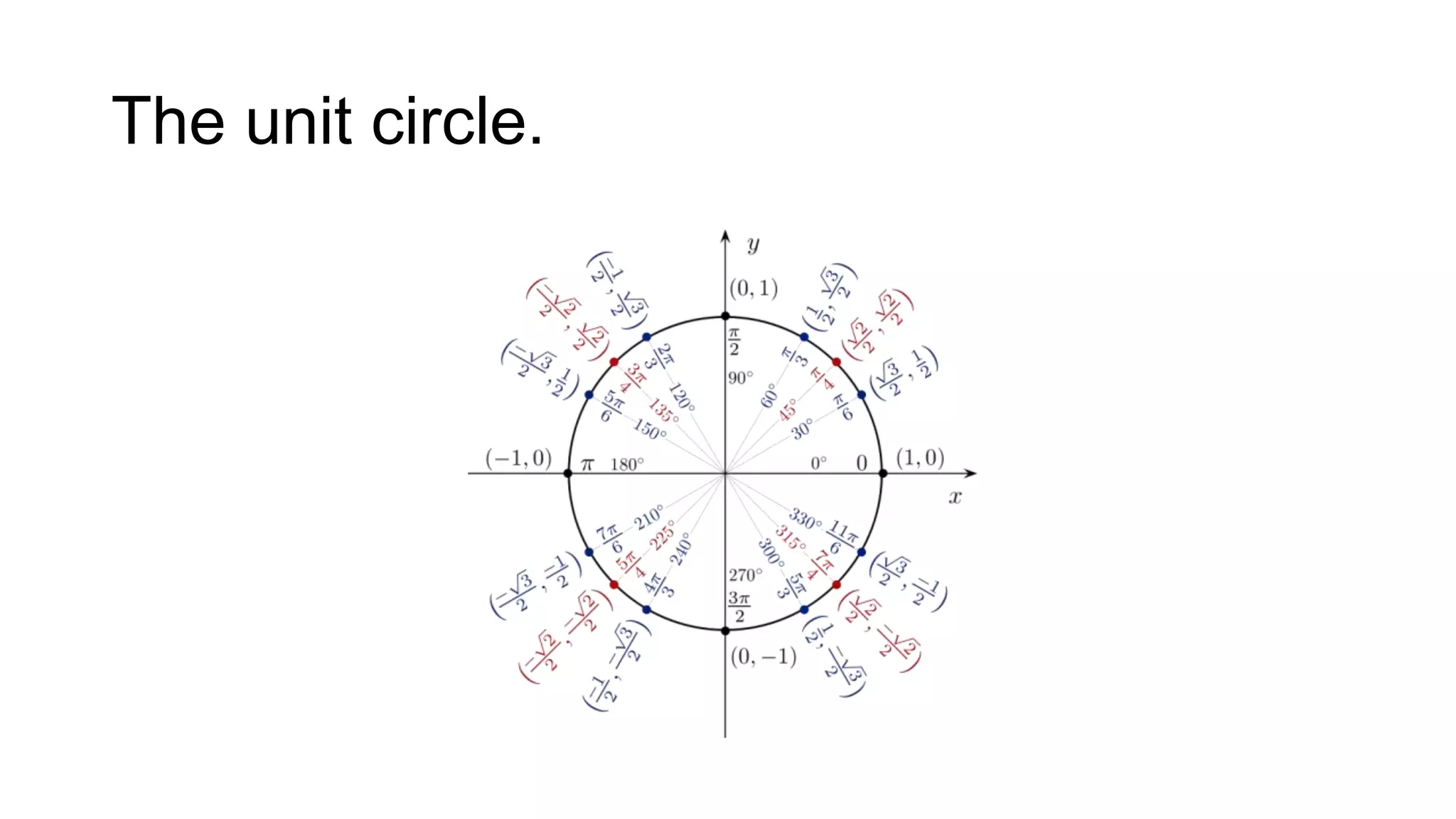
PPT - Unit Circle PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2500424
It then discusses how to determine the six. Unit Circle Powerpoints Our powerpoint presentations for 9th and 10th grade thoroughly explain the unit circle, focusing on how it relates to trigonometric functions, angle calculations, and radian measures, crucial for advanced mathematics study. Teachers, save yourself time creating lessons! This fully editable PowerPoint lesson is professionally designed and teaches Geometry students the important concepts related to the Unit Circle.
The 13-slide lesson is animated for continued student engagement.NOTE! This resource can also be found in t. Given a unit circle, what distinguishes the unit circle from all other circles? Identify the 4 quadrants. What direction do we move in going from the first to the fourth quadrant? How would you describe points on the circumference of the circle? Read the Cartesian coordinates of points in each quadrant.
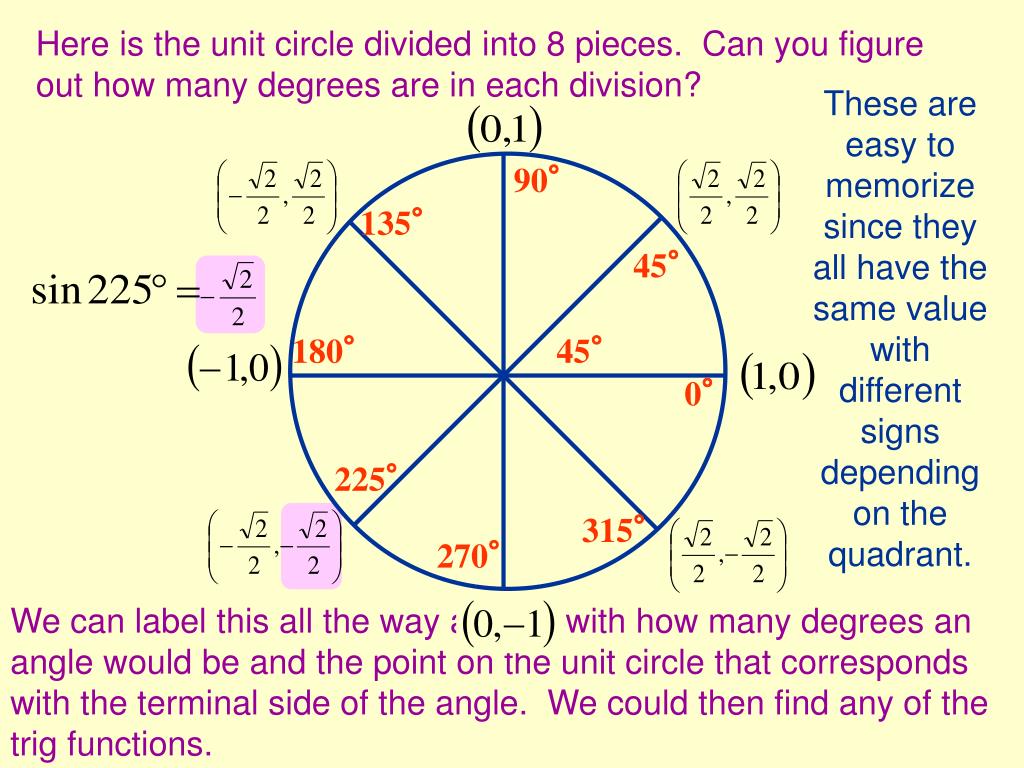
This document section discusses trigonometric functions using the unit circle approach. It defines trigonometric functions of angles based on the coordinates of points on the unit circle. Several examples are worked out, finding exact values of trigonometric functions like cosine, tangent, and sine at specific angles by considering the appropriate points on the unit circle.

It also discusses. The Unit Circle is a circle with a radius of 1. Being so simple, it is a great way to learn and talk about lengths and angles.