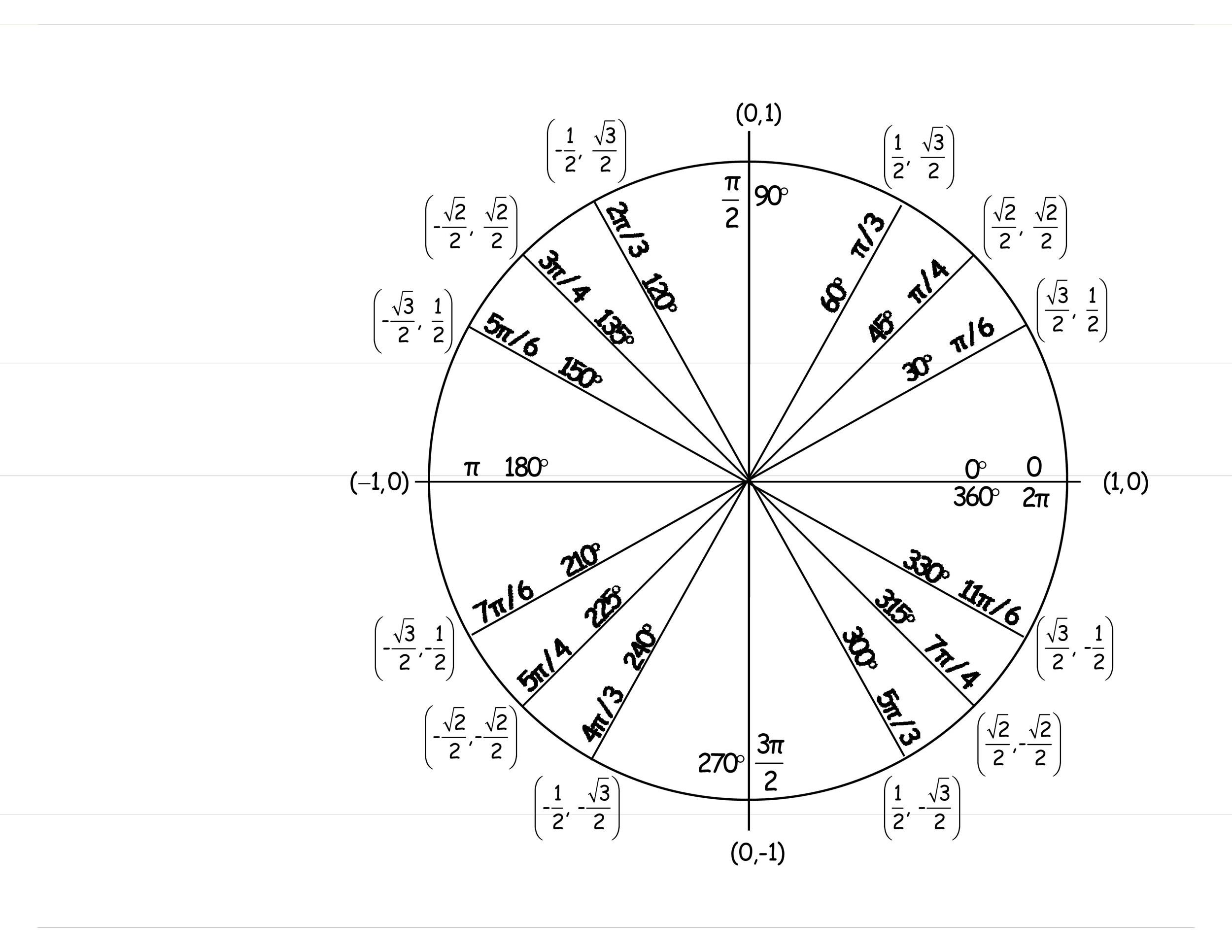
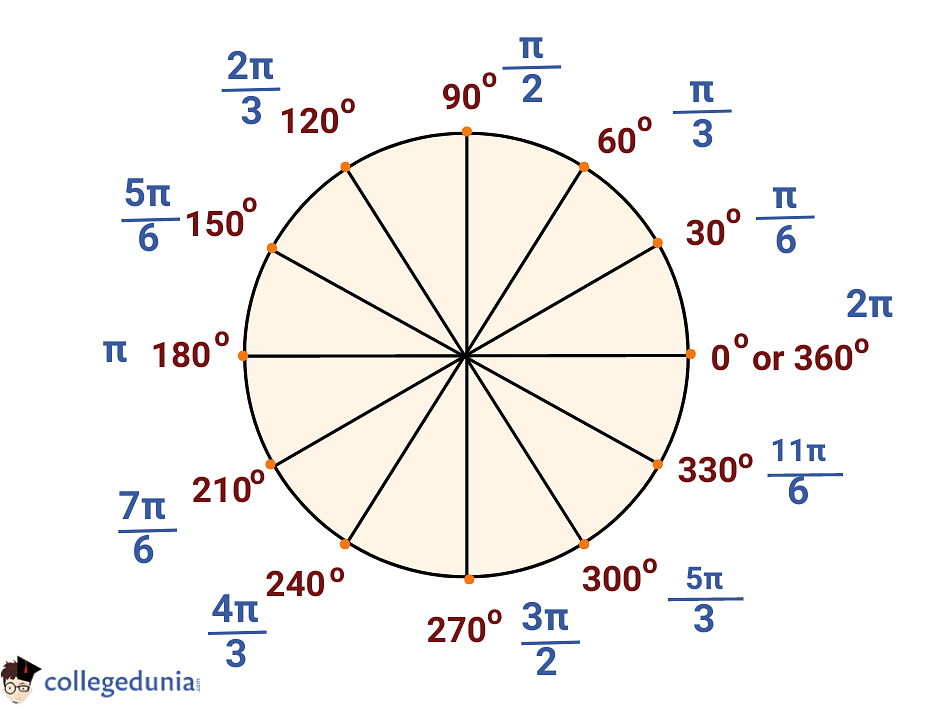
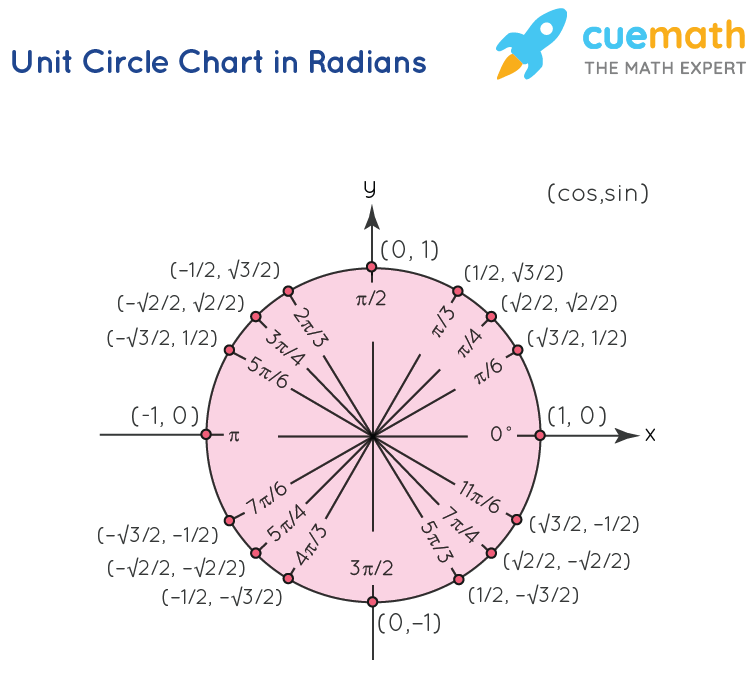
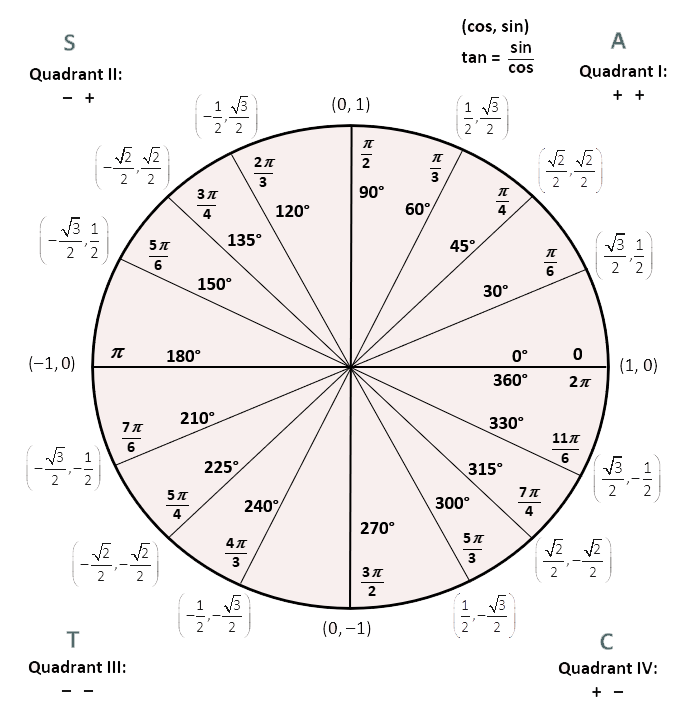
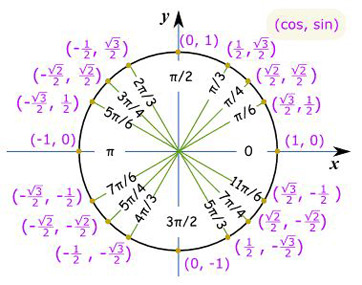
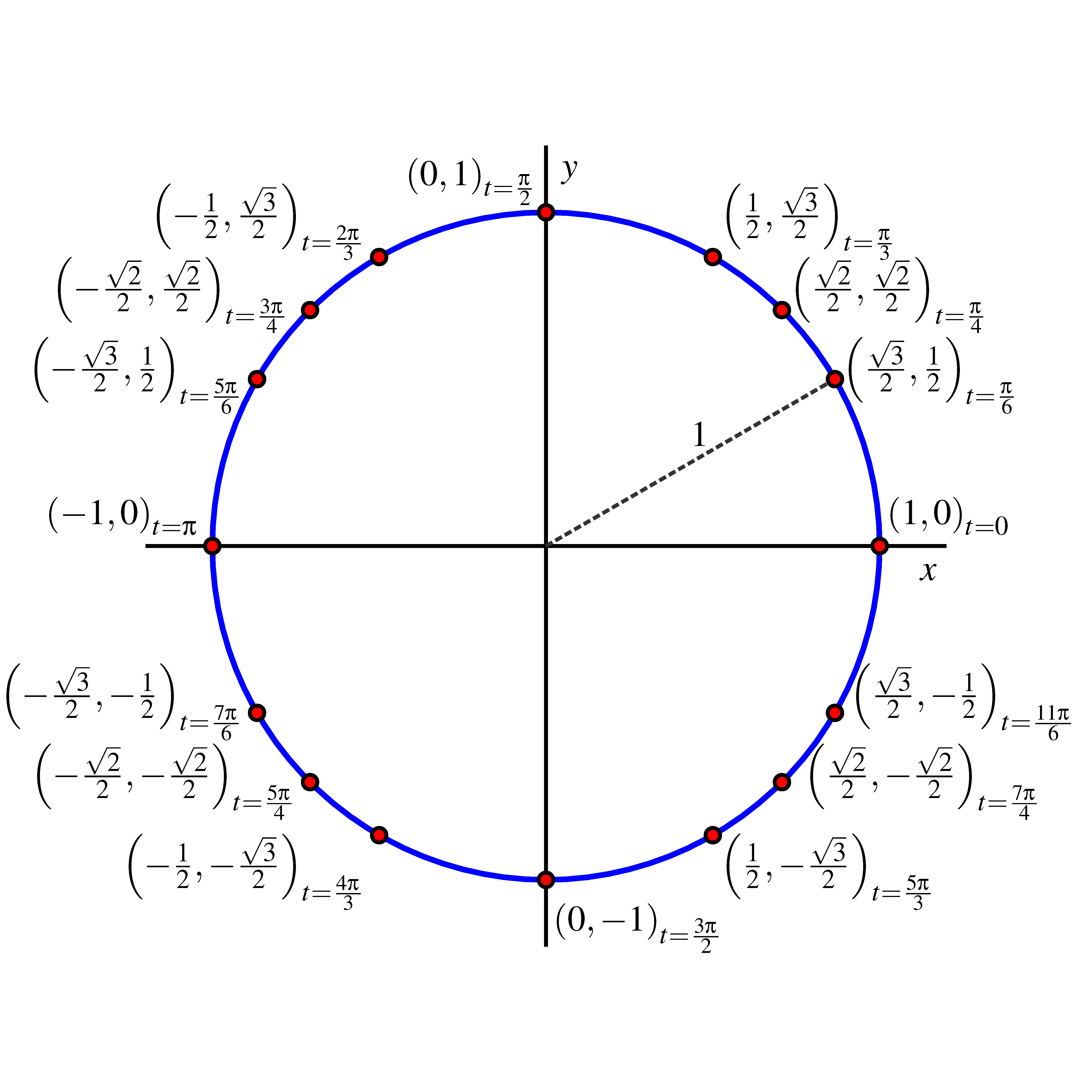
Radian Circle Graph
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Interactive Unit Circle Explore our all-in-one interactive unit circle chart.

Master angles, radians, sine, cosine, and tangent with ease. Our visual tool makes trigonometry simple, providing a complete unit circle table, diagram, and reference for all your needs. What is a unit circle in trigonometry explained with its equation, chart, table, & labeled diagram.
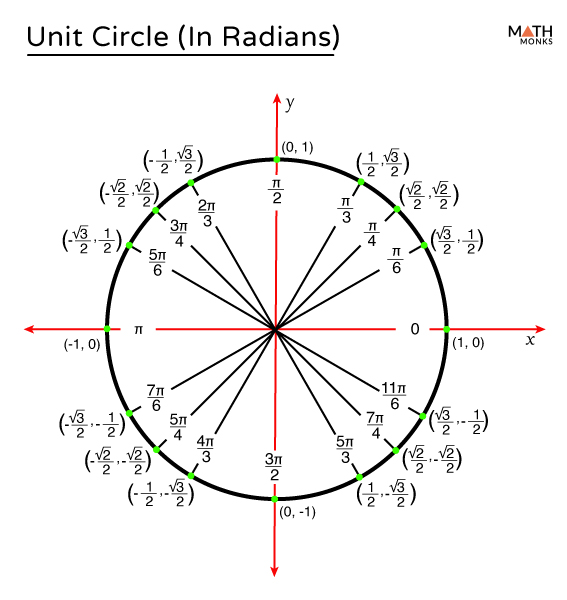
Unit circle radians, Blank unit circle, Circle diagram
The "Unit Circle" is a circle with a radius of 1. Being so simple, it is a great way to learn and talk about lengths and angles. The center is put on a graph where the x axis and y axis cross, so we get this neat arrangement here.

Sine, Cosine and Tangent Since the radius is 1, we can read sine, cosine and tangent just from the x and y coordinates. 2 Now look at the unit circle and find the point \ (P\) designated by that same angle in radians. 3 Measure the horizontal (signed) distance that gives the \ (x\)-coordinate of point \ (P\).
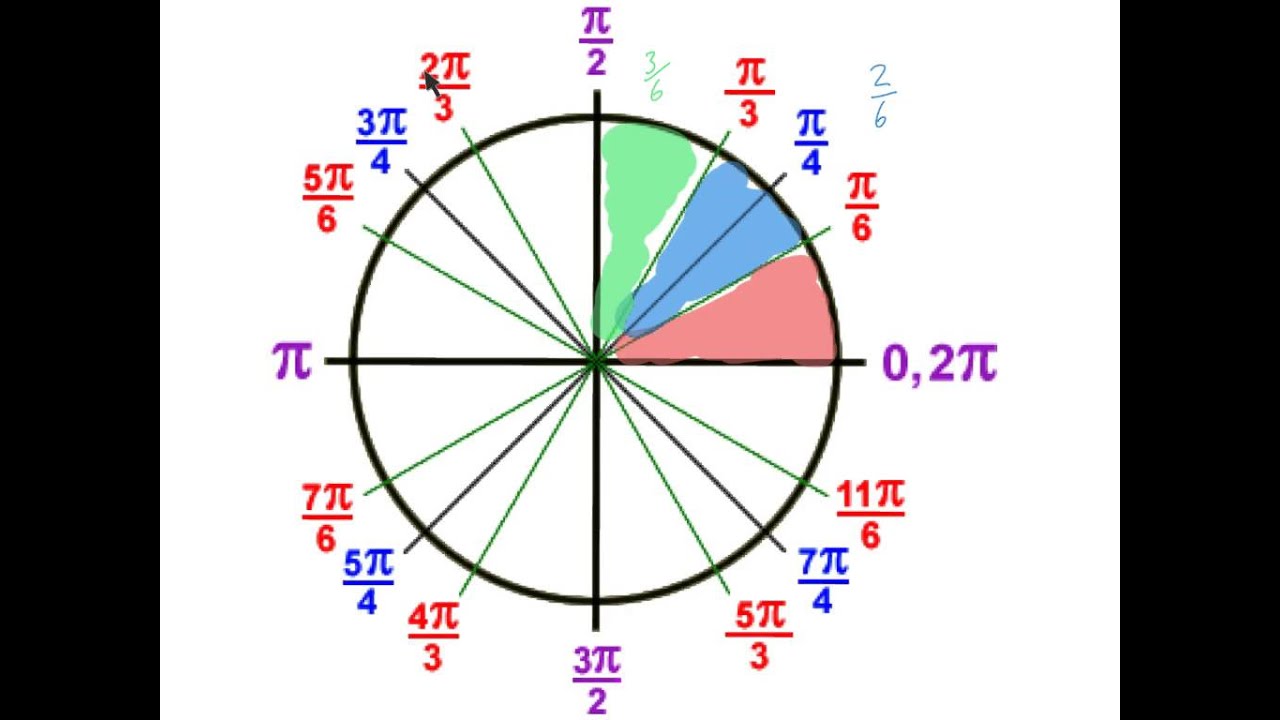
Trigonometry Chart Radians
The ANGLE α is the LENGTH OF THE ARC in the unit circle for the angle α in degrees. Read this sentence until you understand it. It is critical.
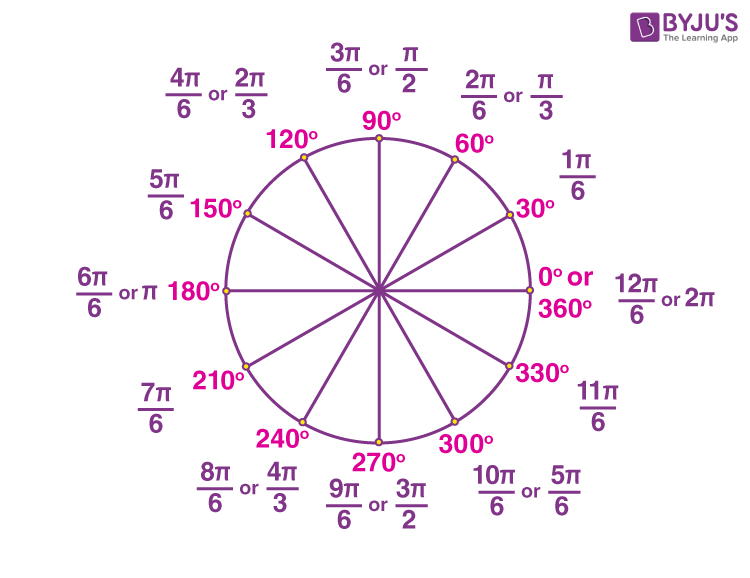
The height of the point is the value of the sine function of the angle α. Rounded to 3 decimal places, how much is α=? What is the α in degrees? Which is on the x. 12 graph and make a dot at the top of it.

Labeling the unit circle using radians | Math, Algebra 2, Circles ...
Note: Since this point is above the x-axis in the unit circle, the corresponding point on the function graph should also be above the x-axis. Transferring the Spaghetti for the Triangle Drawn to the π radians Mark 3 Continue constructing triangles and transferring lengths for all marks on the Unit Circle. Explore the unit circle with our interactive calculator and downloadable chart.
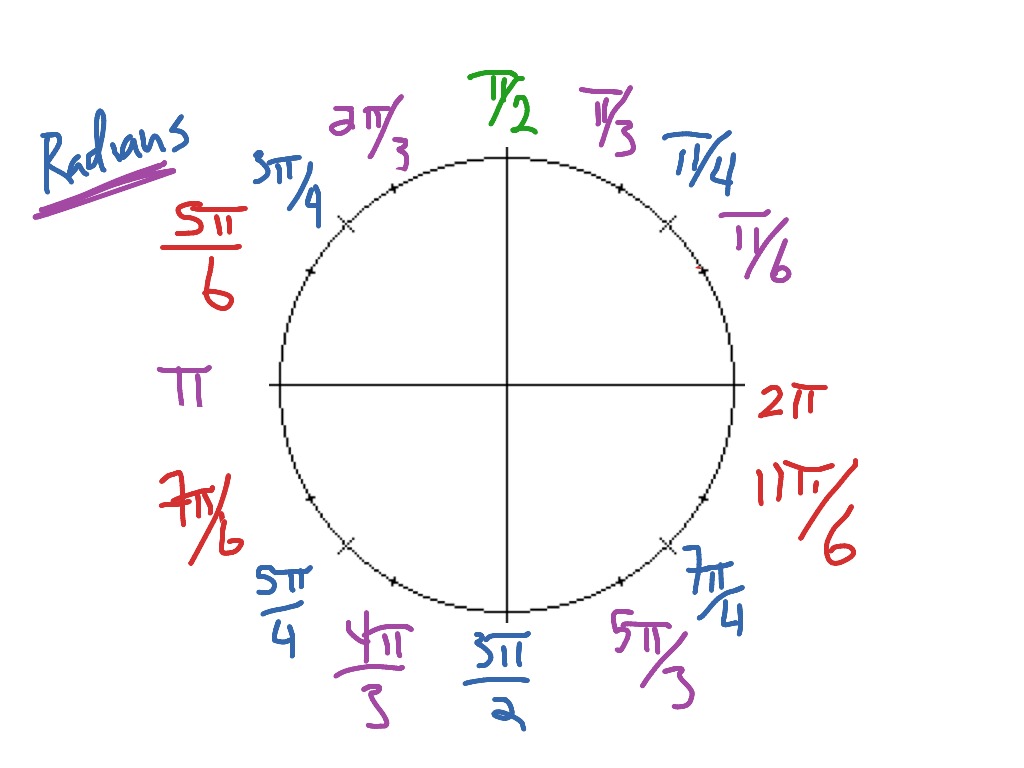
Learn sine, cosine, tangent values, radians vs degrees, and memorize key angles. A radian (rad rad) is the angle (\theta θ) which subtends an arc equal to the length of the radius of a circle and the SI unit of angles. The angle of a circle is 2\pi 2π radians.
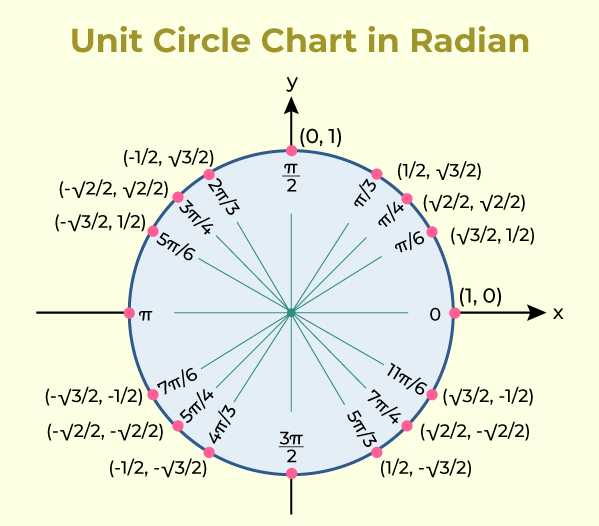
Radians are defined slightly differently, as this diagram shows: For a circle of radius r, if we draw an arc of length r, then the angle at the centre will be 1 radian. The angle of the sector shown is 1 radian. Symbol for radians Radians are sometimes abbreviated to rad, so we would write 2 radians as 2 rad.