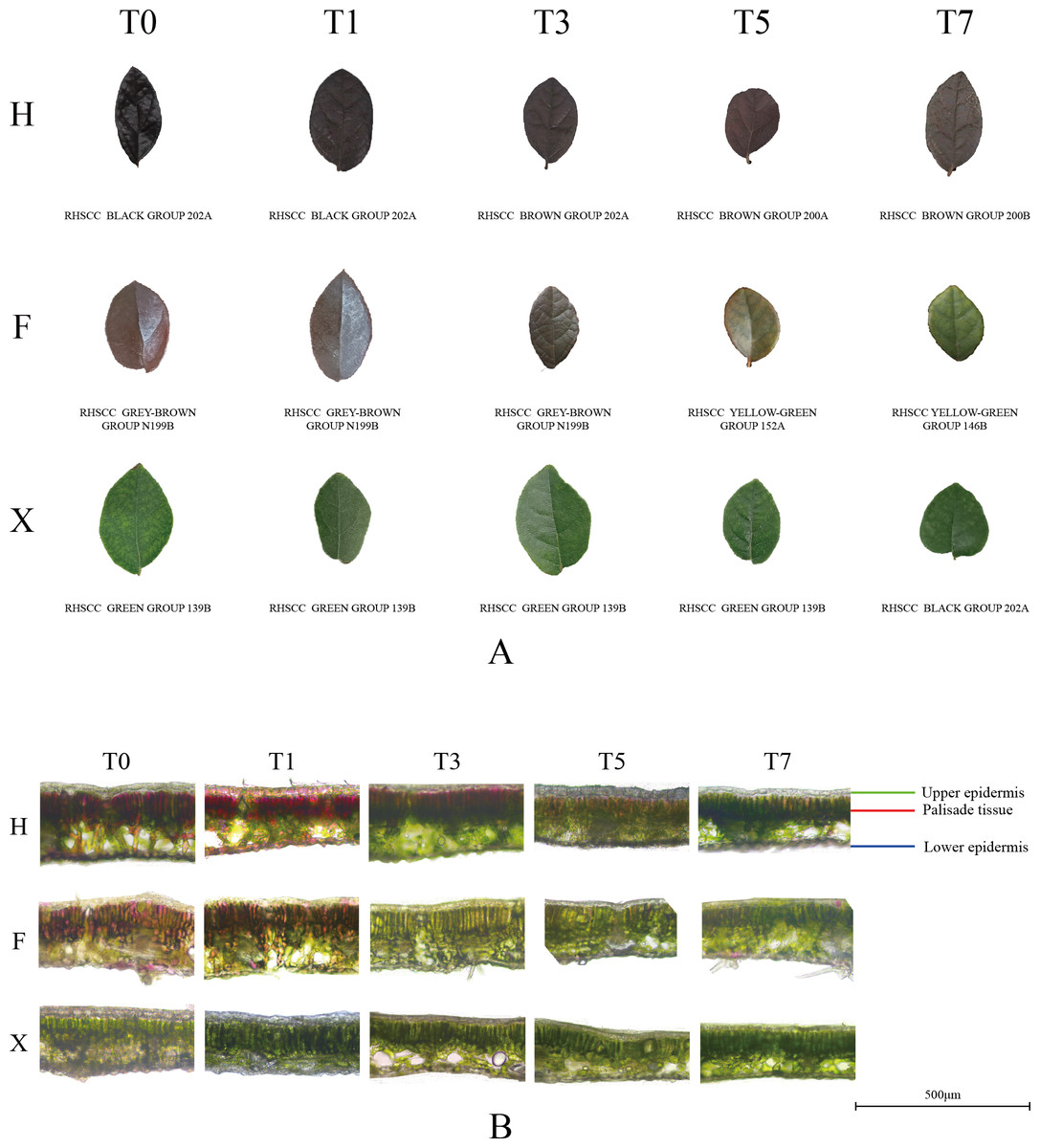
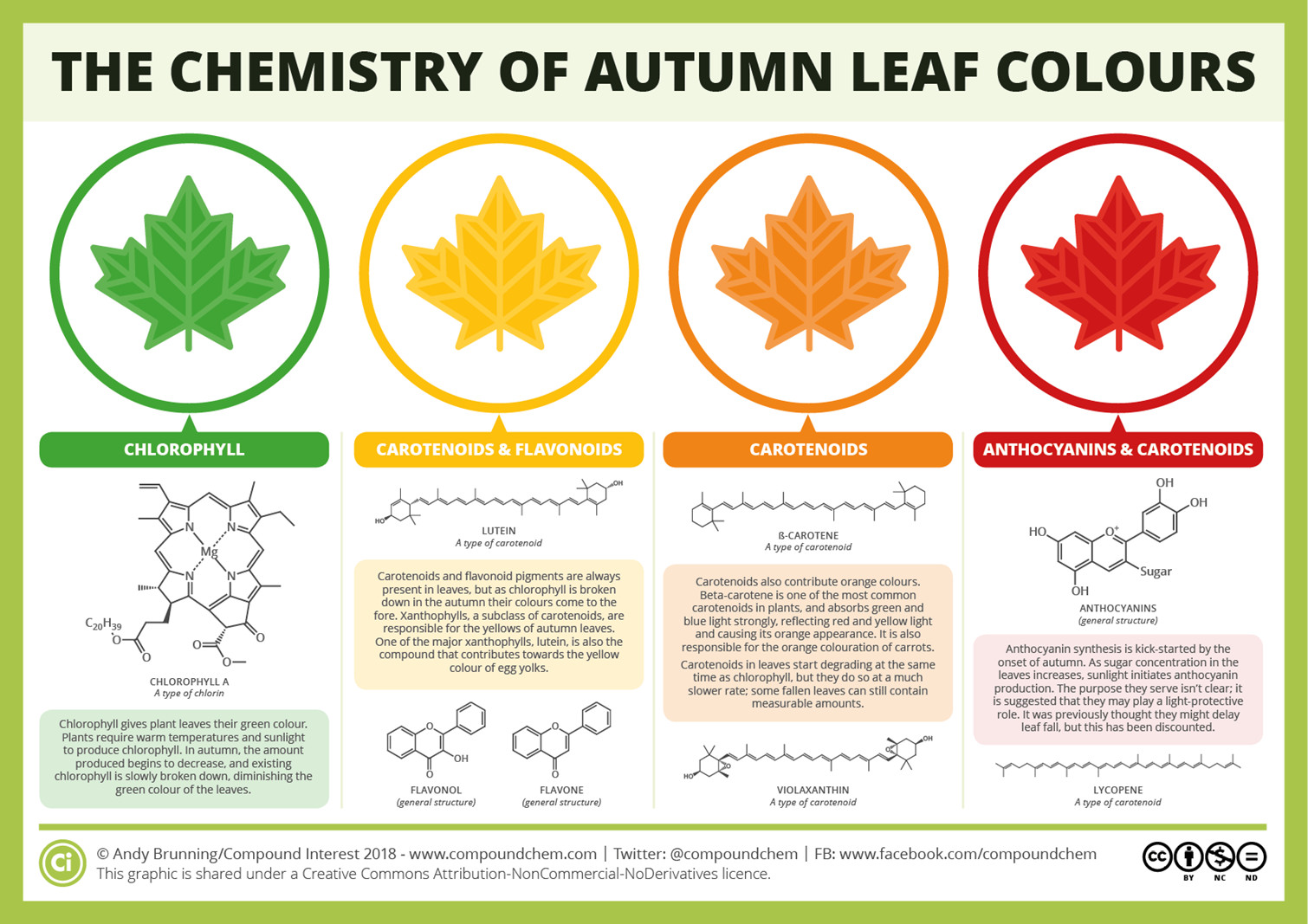
Leaf Color Scale
Plant colors such as 'green leaf' and 'red apple' are often described based on human sense, even in scientific papers. On the other hand, colors are measured based on colorimetric principles in some papers, especially in the studies of horticultural. Absbract Changes in foliar color are a valuable indicator of plant nutrition and health.
Leaf color is measured with visual scales and inexpensive plant color guides that are easy to use, but not quantitatively rigorous, or by employing sophisticated instrumentation including chlorophyll meters, reflectometers, and spectrophotometers that are costly and may require special training. Digital. Understanding what different colors mean enables timely interventions that support plant health and productivity.

LEAF COLOR CHART Tool for real time N
Whether managing crops at scale or nurturing houseplants individually, mastering these techniques enhances our ability to read nature's subtle signals conveyed through the ever. About Leaf Colour Chart (LCC) Leaf Color Chart (LCC) is a Real - Time N management technology of International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) & Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) to determine the exact requirements of nitrogen fertilizer of standing crops, by checking the greenness of Plant Leaf. The color of the plant leaves is a major concern in many areas of agriculture.

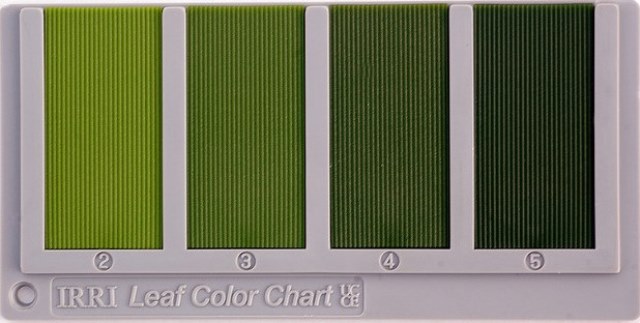
Pigmentation and its pattern provide the possibility to distinguish genotypes and a basis for annual crop management practices. For example, the nutrient and water status of plants is reflected in the chlorophyll content of leaves that are strongly linked to the lamina coloration. Pests and diseases (virus or.

leaf-color-chart | TheModern Farm
Use AI to identify leaf colors. Great for Agricultural Health Monitoring, Environmental Studies, Plant Care Management and much more. Built with Nyckel, an API for building classification models at scale.
The LCC can be used without the need for any specific knowledge or skills, as it involves simply comparing the colour of the leaf and determining its scale based on the standard chart. Introduction The leaf colour chart (LCC) was the first time introduced in the agricultural sector of the world by scientists of Japan. They made it for estimation of chlorophyll formation and its availability in plants, after the continuous studies, many researchers proved that it is pivotal for the measurement of nitrogen deficiency and its correction.

Leaf Colour Chart: A Visual Reference of Charts | Chart Master
The leaf colour chart has six (06. Plant color was an important landscape of the urban green space, and quantitative analysis of its characteristics could provide a basis for plant color configuration. The leaf color attributes of 80 colored-leaf plants were studied and the Scenic Beauty Estimates (SBE) was used to evaluate their beauty.
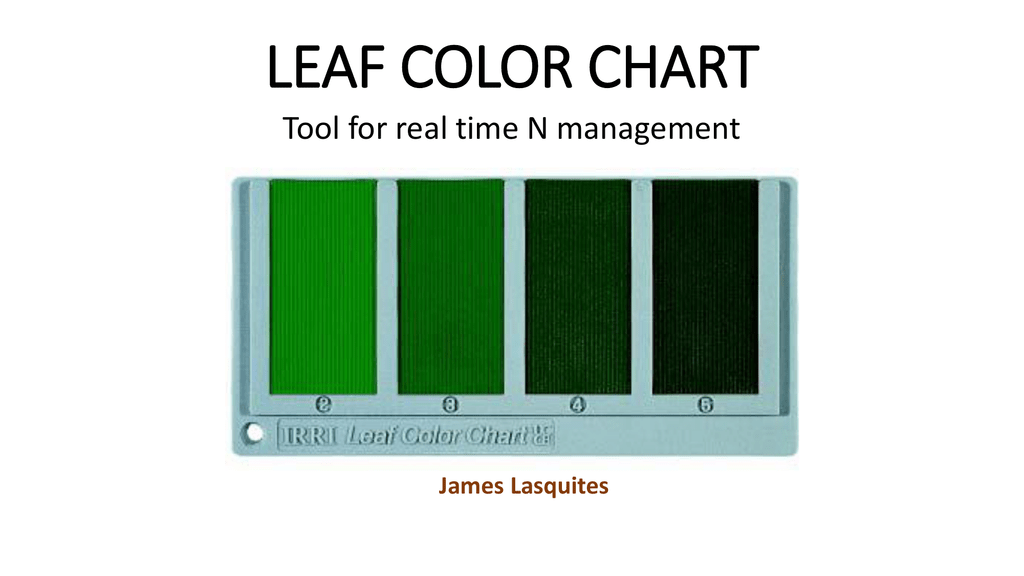
The data of leaves color were obtained by MATLAB software and scanner under the hue. By visual comparison, the panel most closely matching a leaf's color indicates whether the N in the plant is deficient, sufficient, or in excess (Fig. 1).

Leaf color charts were developed from a Japanese prototype, the "standard rice leaf color scale" (Furuya, 1987).