Is Flower Color Qualitative Or Quantitative
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Is the flower color in this plant a quantitative or qualitative trait?, How do you call the determination of flower color in this species?, The population had 100 plants in a year and when they flowered, the following count was made: 64 red, 32, pink and 4 white flowering plants. What is the % allele frequency of 'R' in the. Human perception of plant leaf and flower colour can influence species management.

Colour and colour contrast may influence the detectability of invasive or rare species during surveys. Quantitative, repeatable measures of plant colour are required. Here's a disclaimer: To not use these very long terms quantitative color scale and qualitative color scale in this blog post, I'll often use the less correct but easier-to-read words shades and gradients for quantitative color scale and hues for qualitative color scales.

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Sampling for DUS Test of Flower Colors of ...
So when should you use shades for your data? And when should you use hues? Understanding Types of Data Observing the colors of a plant's flowers, where one notices purple and white flowers, is an example of qualitative data. Qualitative data refers to information that describes attributes or characteristics and cannot be measured numerically. Common examples include color, type, and quality, among others.
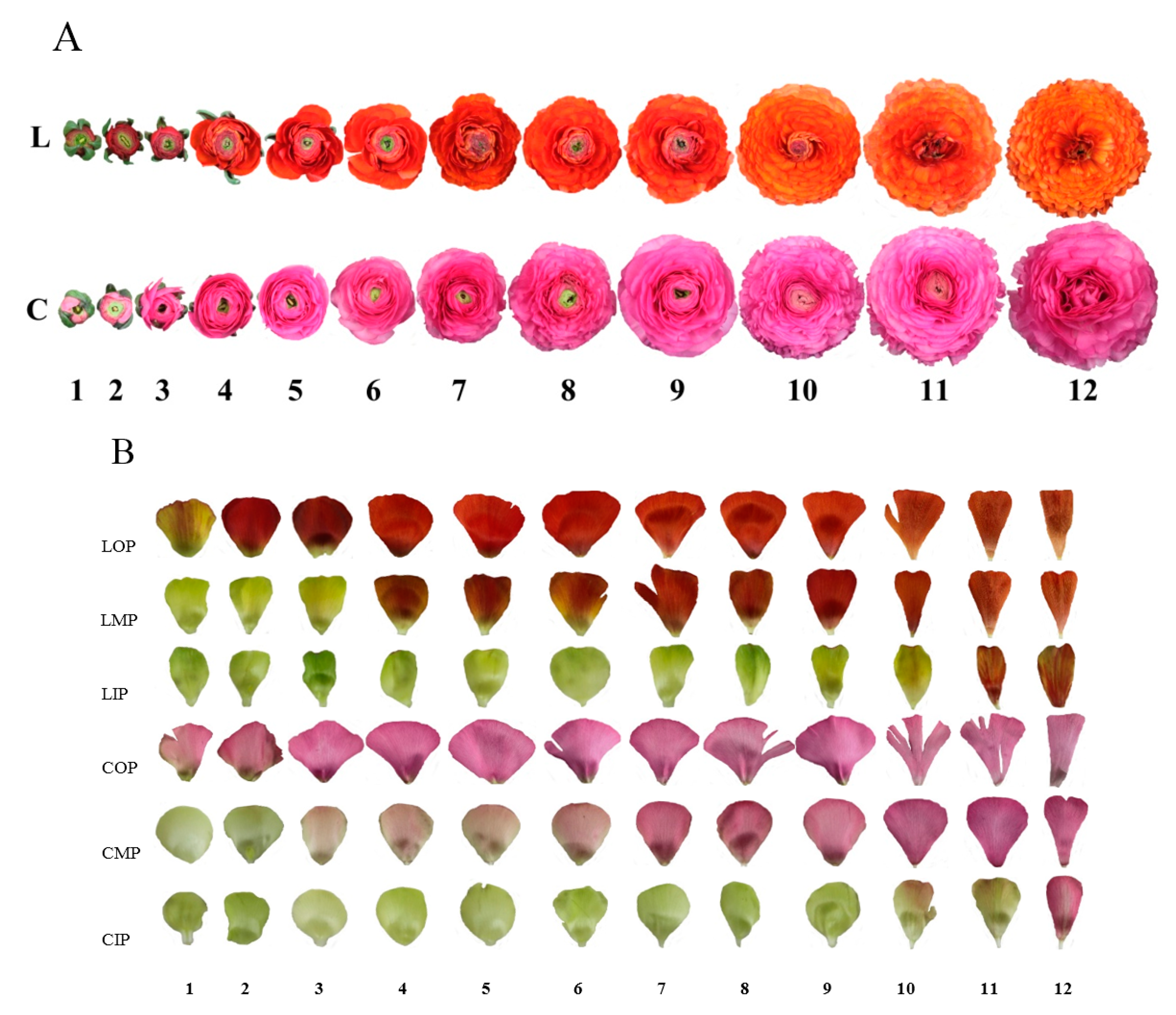
In contrast, quantitative data involves numerical information. For example, researchers may study the genetics of flower color in a plant species with different colored flowers. On the other hand, quantitative traits are valuable in studies of complex traits such as disease susceptibility or behavior.
How to Use a Flower Color Wheel to Achieve Spectacular Results - Rio Roses
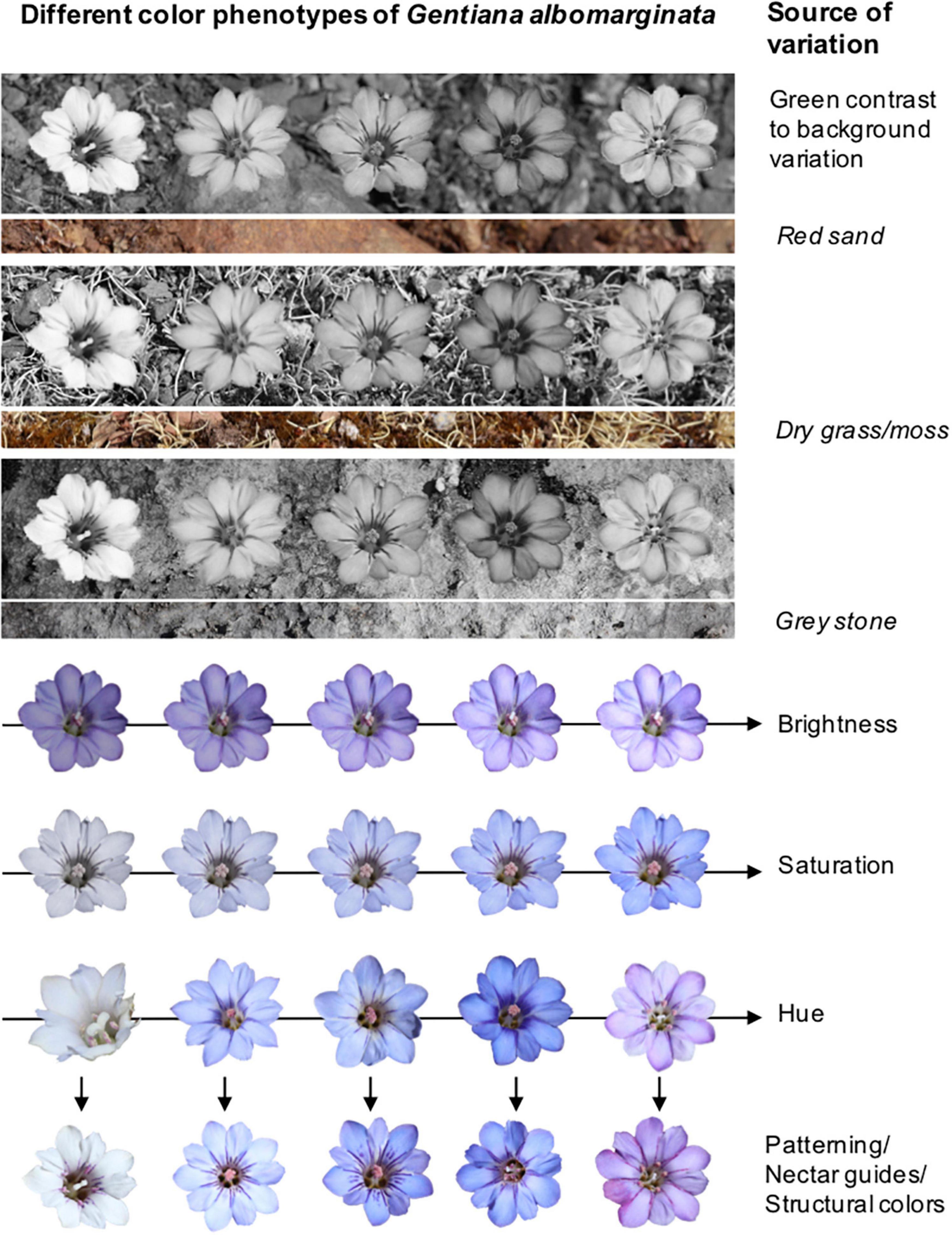
The continuous variation allows for the analysis of subtle genetic and environmental influences on the trait. Flowers perceived red and yellow by humans were dominant and of comparable proportions. Insect pollinators perceive most of the flowers as blue.

Qualitative Variable (A): Colors of flowers are non-numerical and describe a quality or characteristic. They cannot be measured numerically, making this a qualitative variable. The colors of flowers are categories without inherent order.
12 Flower Color Variation: A Model for the Experimental Study of ...
Nominal scales categorize data without any order or ranking. Qualitative variables are non-numerical. Color is a qualitative characteristic.

Answer: b. Qualitative variable, c. nominal Question 7: A population includes all members of a defined group.

A sample is a subset of the population. Answer: A population encompasses all. What is a qualitative color scheme? Qualitative Color Schemes Qualitative schemes use differences in hue to represent nominal differences, or differences in kind.
..jpg)
The lightness of the hues used for qualitative categories should be similar but not equal. Data about land use or land cover, for example, are well represented by a qualitative color. Option a: The color of the flower - This is qualitative data as it describes an attribute.

Option b: The height of the plant in centimeters.
![15: Flower color variations [CD00]. | Download Scientific Diagram 15: Flower color variations [CD00]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279262231/figure/fig21/AS:669385307979782@1536605302380/Flower-color-variations-CD00.jpg)