How Is Momentum Measured
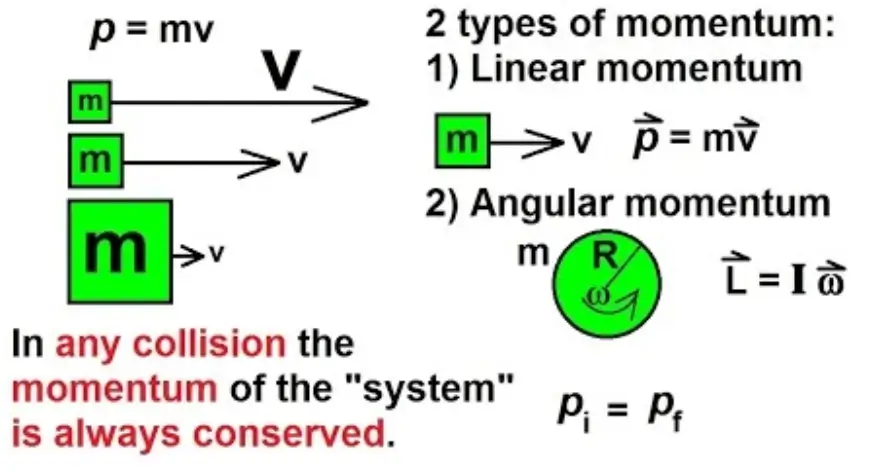
Momentum is a vector quantity: it has both magnitude and direction. Since momentum has a direction, it can be used to predict the resulting direction and speed of motion of objects after they collide. Below, the basic properties of momentum are described in one dimension.
The vector equations are almost identical to the scalar equations (see multiple dimensions). Learn about momentum in physics. Get its definition, units, formula, and worked example problems.

How To Calculate Momentum, With Examples - YouTube
See how it relates to Newton's laws. What is momentum. What are its equations and units.
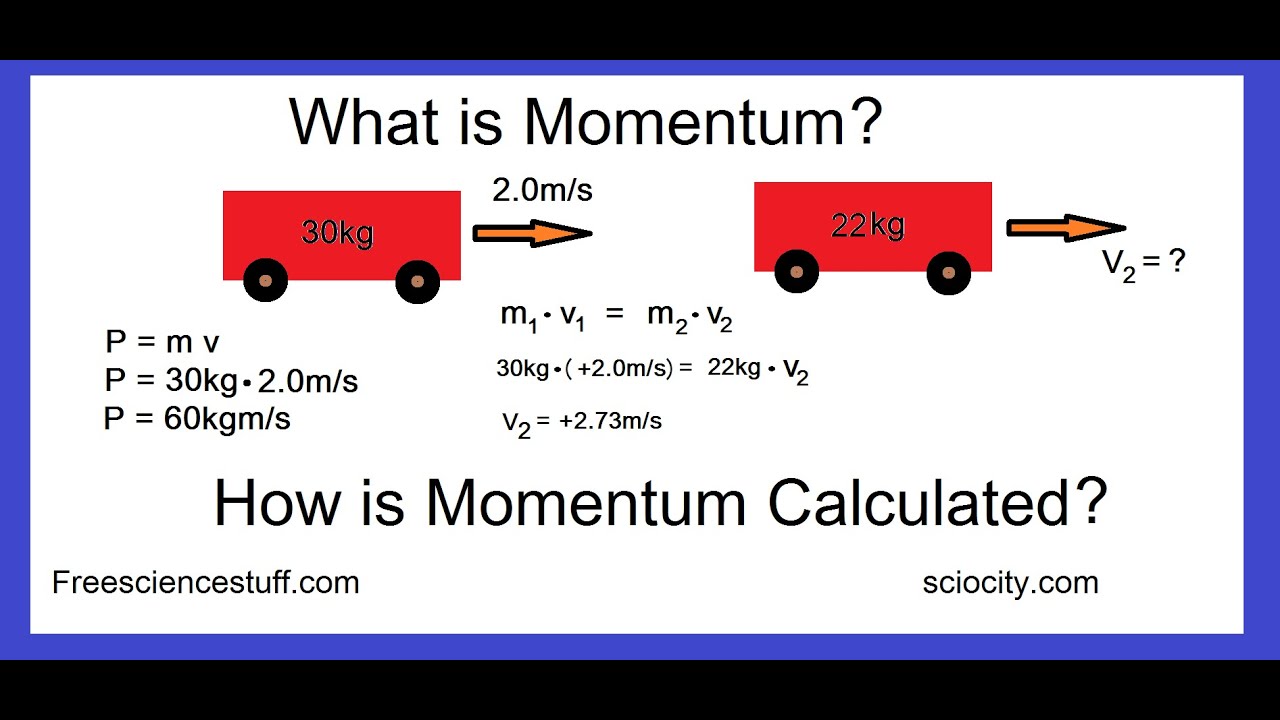
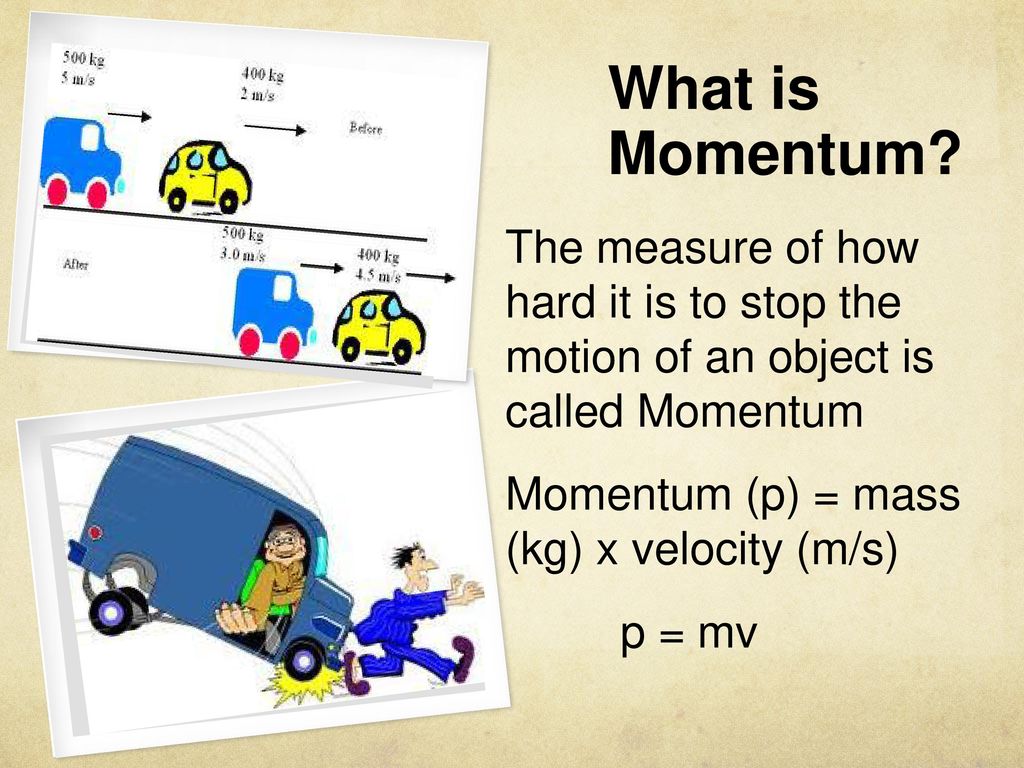
How is it related to force and impulse. Check out a few solved problems. In terms of an equation, the momentum of an object is equal to the mass of the object times the velocity of the object.
Understanding Momentum in Physics: A Comprehensive Guide | Physics Girl
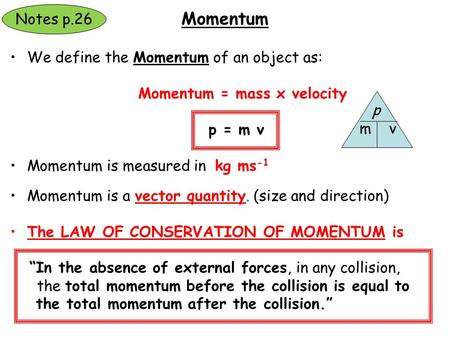
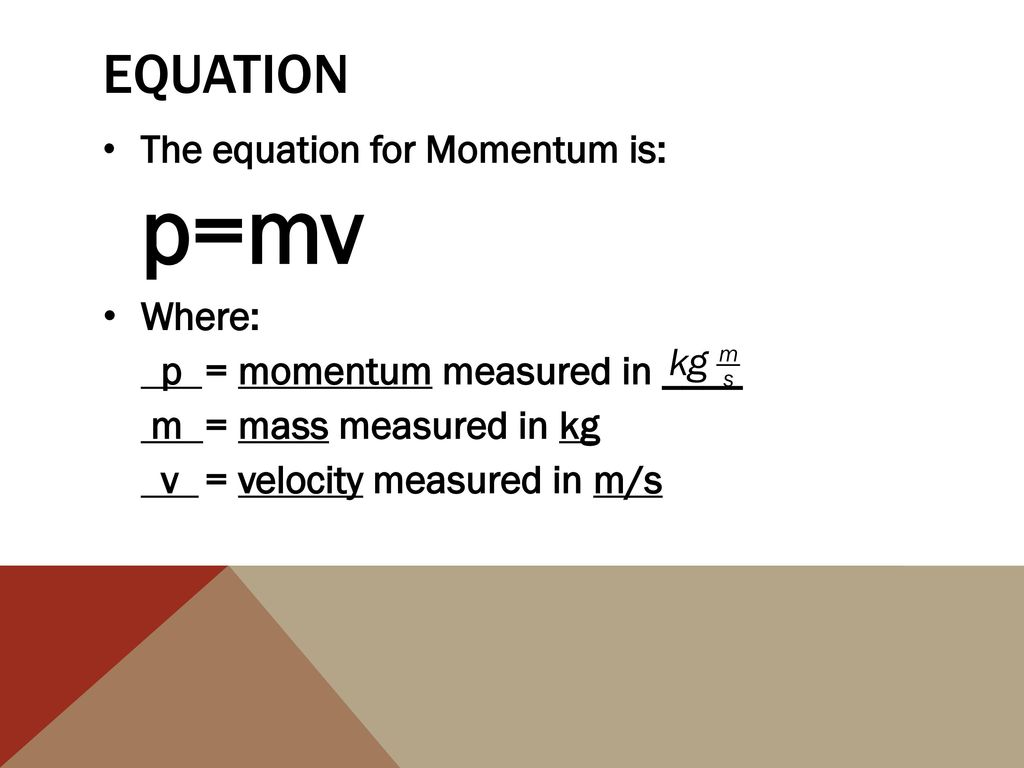
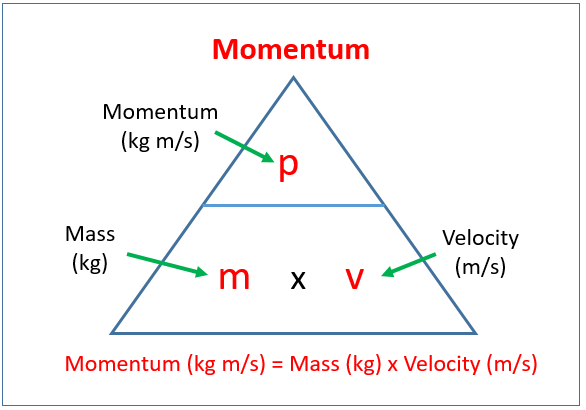
Momentum = mass velocity In physics, the symbol for the quantity momentum is the lower case p. Thus, the above equation can be rewritten as p = m v where m is the mass and v is the velocity. Learn the fundamentals of linear momentum and impulse in engineering.
Explore how mass and velocity determine momentum, and how force applied over time changes momentum through impulse. Includes formulas, examples, and real. Momentum, product of the mass of a particle and its velocity.
Momentum (examples, solutions, videos, notes)
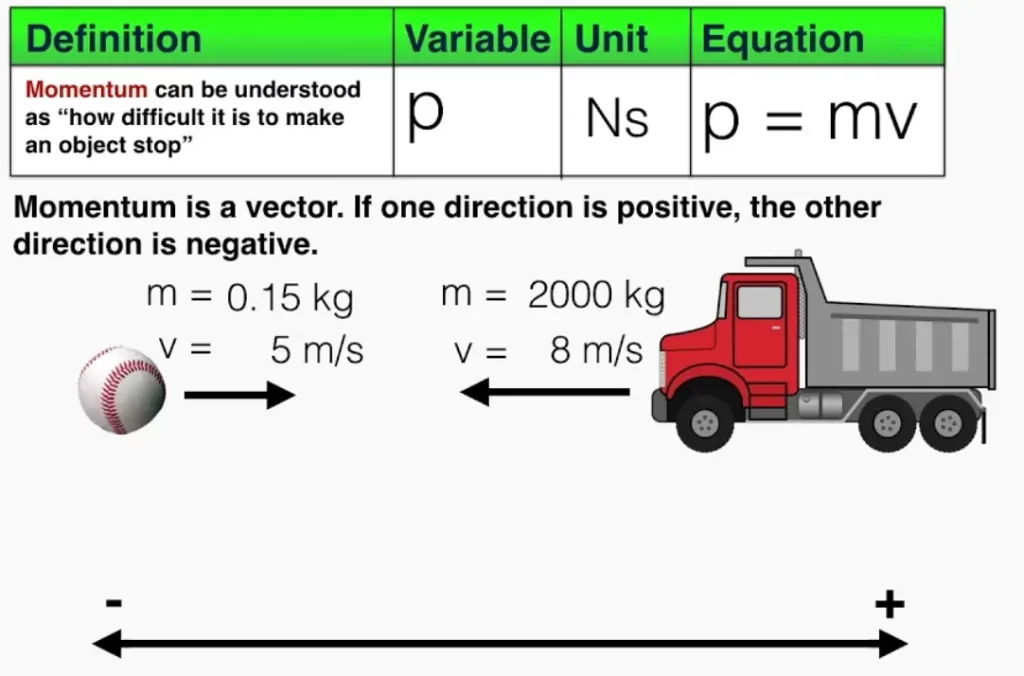
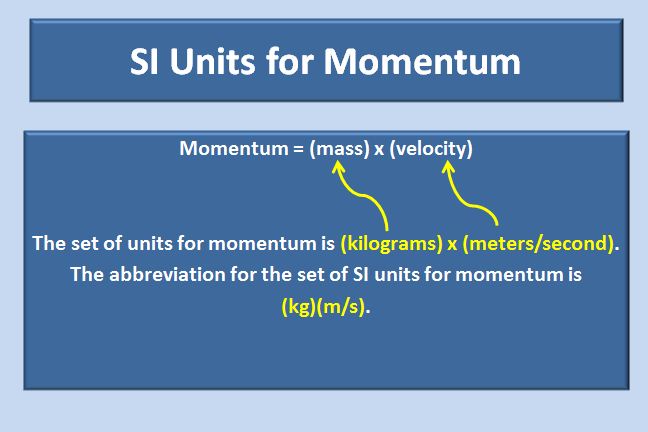
Momentum is a vector quantity; i.e., it has both magnitude and direction. Isaac Newton's second law of motion states that the time rate of change of momentum is equal to the force acting on the particle. The standard unit for momentum in the International System of Units (SI) is the kilogram-meter per second (kg m/s).
This unit is directly derived from the definition of momentum, where mass is measured in kilograms (kg) and velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s). Momentum is a derived quantity, calculated by multiplying the mass, m (a scalar quantity), times velocity, v (a vector quantity). This means that the momentum has a direction and that direction is always the same direction as the velocity of an object's motion.

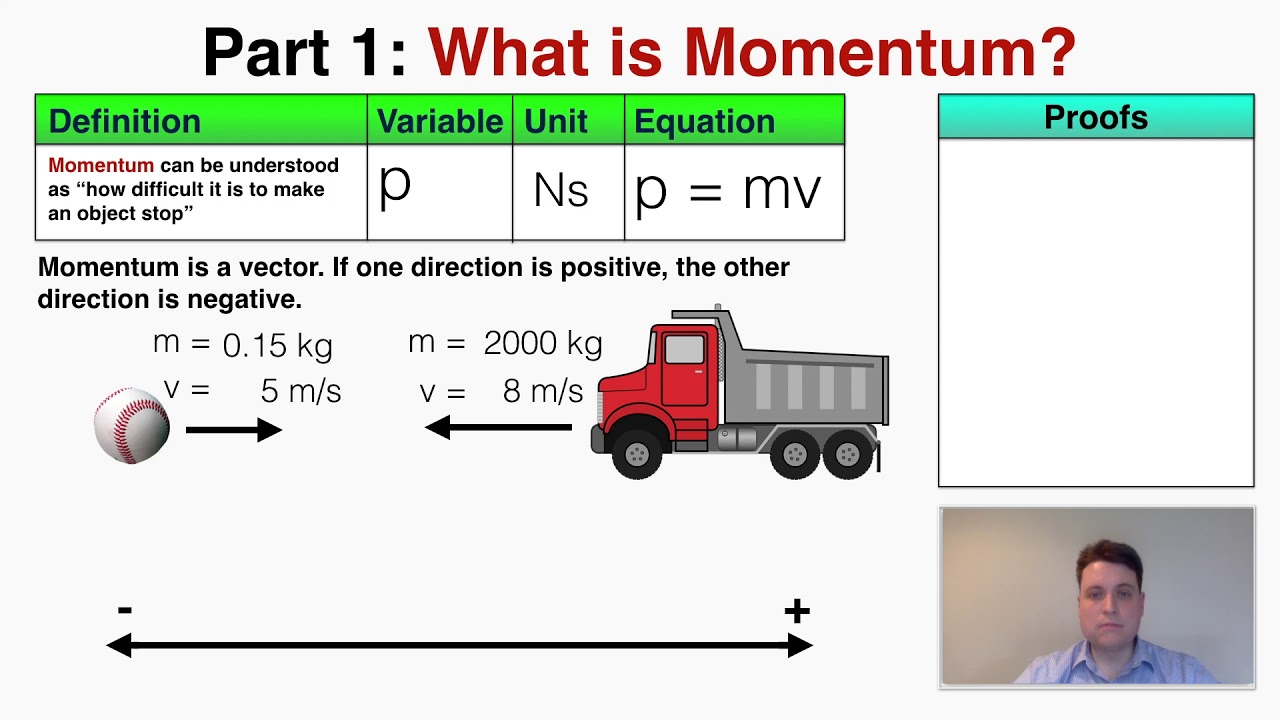
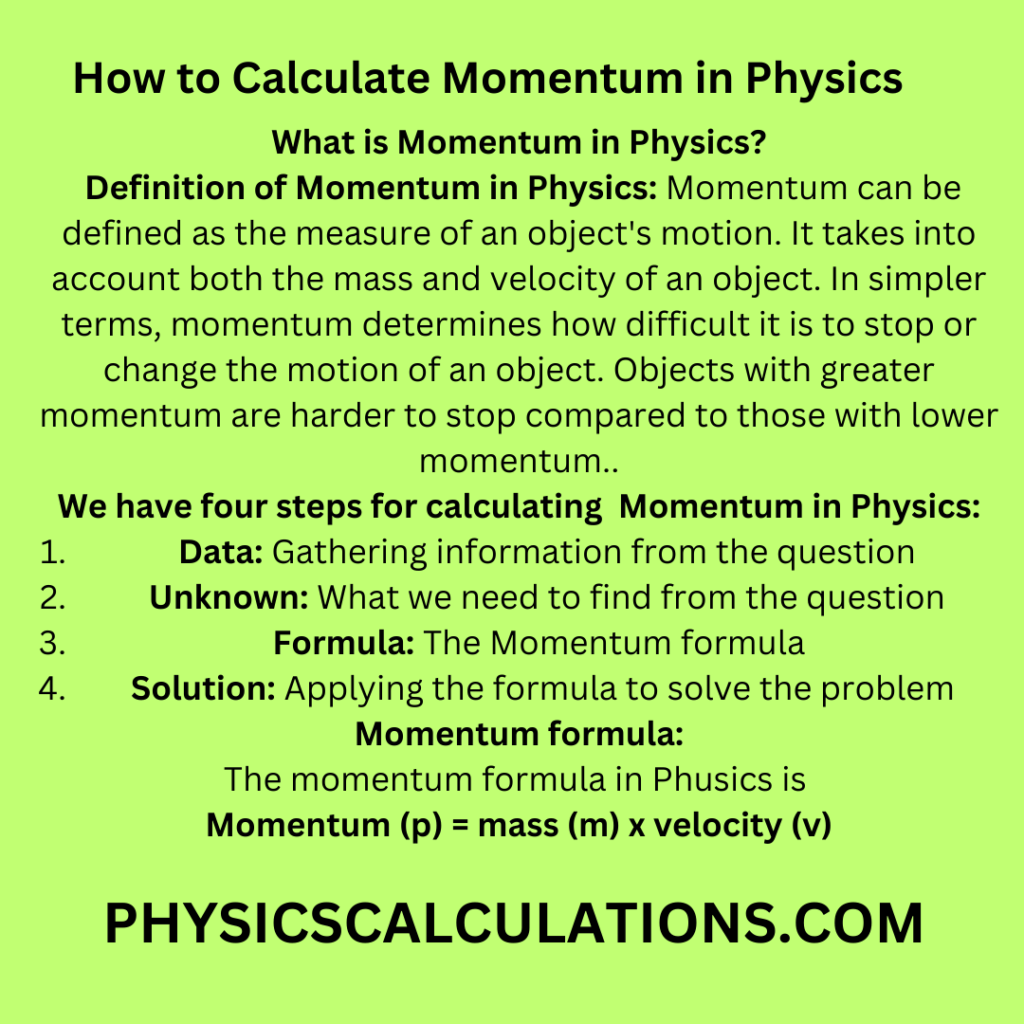
The variable used to represent momentum is p. The equation to calculate momentum is shown below. This post will explain what momentum is in Physics, the equation for momentum, and how to calculate it in real.
Momentum is a Vector Momentum is a vector: it has size AND direction. Sometimes we don't mention the direction, but other times it is important! One Dimension A question may have only one dimension, and all we need is positive or negative momentum: Two or More Dimensions Questions can be in two (or more) dimensions like this one.