Define Double Bar Graph
Double Bar Graph is a graph used to relate two similar types of quantities. The representation of the double bar graph contains two bars to compare the required quantities. In this article we will explore the double bar graph, double bar graph definition, and double bar graph representation.

We will also discuss how to draw double bar graphs and solve some examples related to double bar graphs. A double bar graph, or a side-by-side bar graph, is a visual representation showing two sets of interrelated data using bars of different colors or shades. Most often, the x-axis shows the categories being compared for the two groups, while the y.

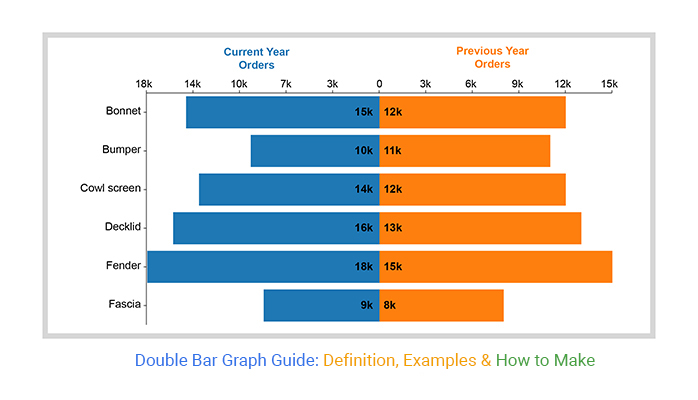
Double Bar Graph Guide: Definition, Examples & How to Make
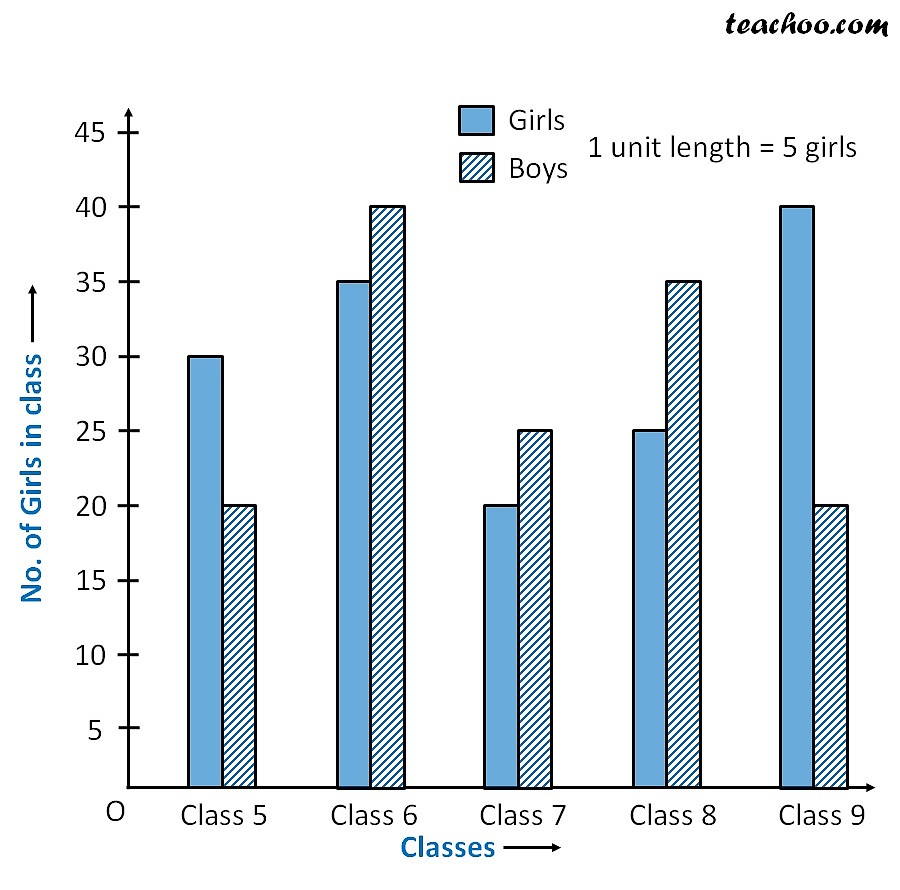
Double Bar Graph Definition Definition: A Double Bar Graph is a data visualization that is used for presenting two sets of data concurrently within a single graph using bars of different colors and heights. This type of chart is similar to a bar chart but features pairs of bars for each item in your data set. A double bar graph is the most common means of representing grouped data in the form of graphs.
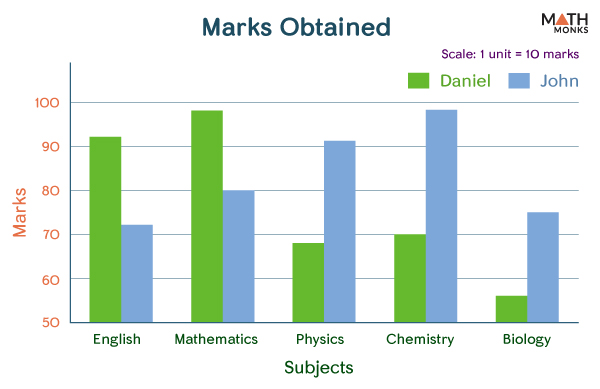
It is used to represent and compare data among items based on two categories. The data analysis and interpretation section of competitive examinations usually has a question on bar graphs. Explore double bar graphs.
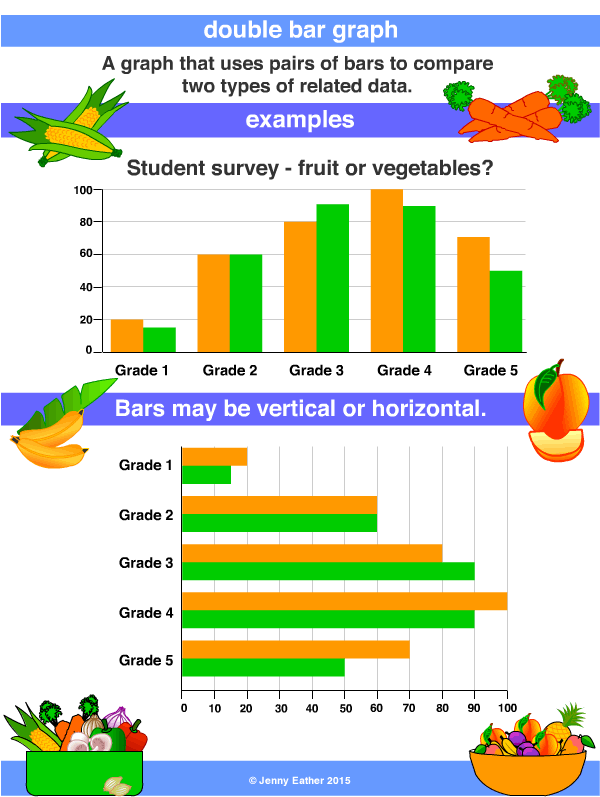
Examples Of Double Bar Graph at Andrew Gillan blog
Learn the definition of a double bar graph and understand how it is constructed and what it includes. See examples of. Learn how to make a double bar graph in Excel using a preset clustered chart or by manually adding a second series to an existing chart.

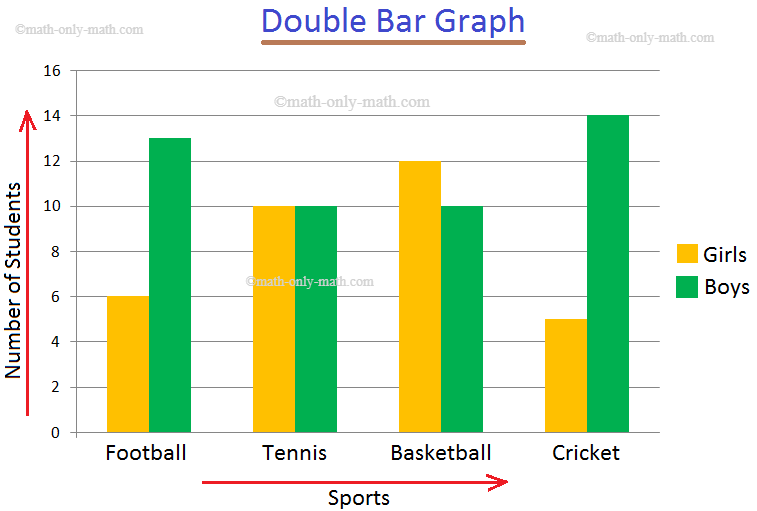
This lesson shows how to understand data on double bar graphs and how to construct double bar graphs to represent data. We would employ a double bar graph, for instance, to compare the number of hours that students worked in one month to another. The double bar graph worksheets demonstrate how to read a double bar graph to find data and address issues.

Double Bar Graph: Definition, Examples & Easy Steps to Read
A bar graph, on the other hand, displays categories on the horizontal (x) axis and frequencies on the vertical (y) axis. This means that bar graphs are more qualitative, and, therefore, display categorical data. The figure below shows 1 bar graph (on the top) and 1 histogram (on the bottom): Let's look at an example of double bar graphs.
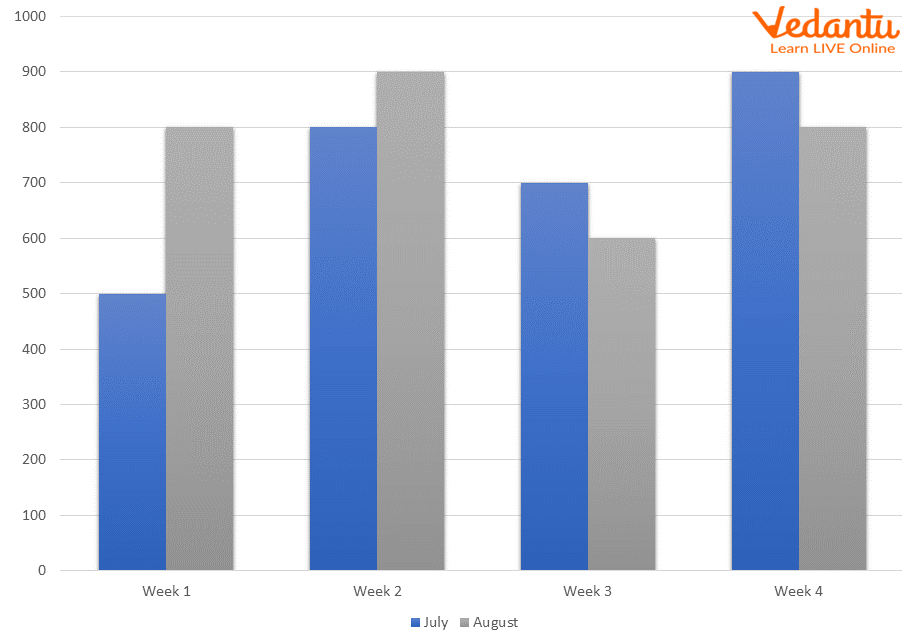
Here, we make a double bar.