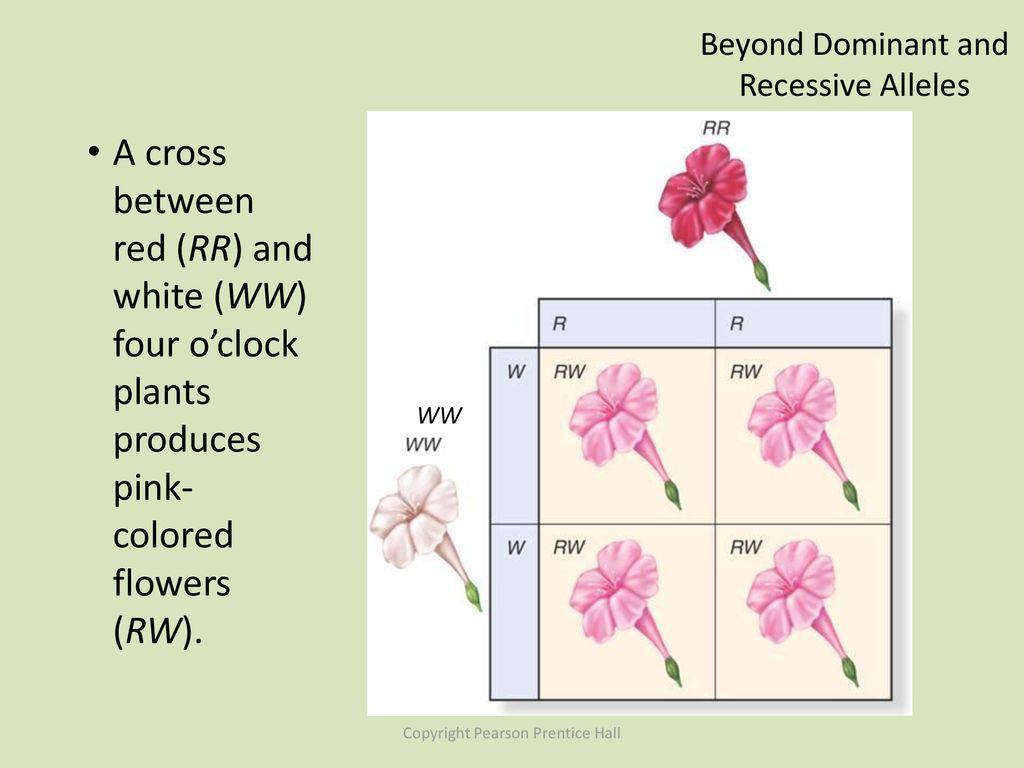
Flower Color Recessive
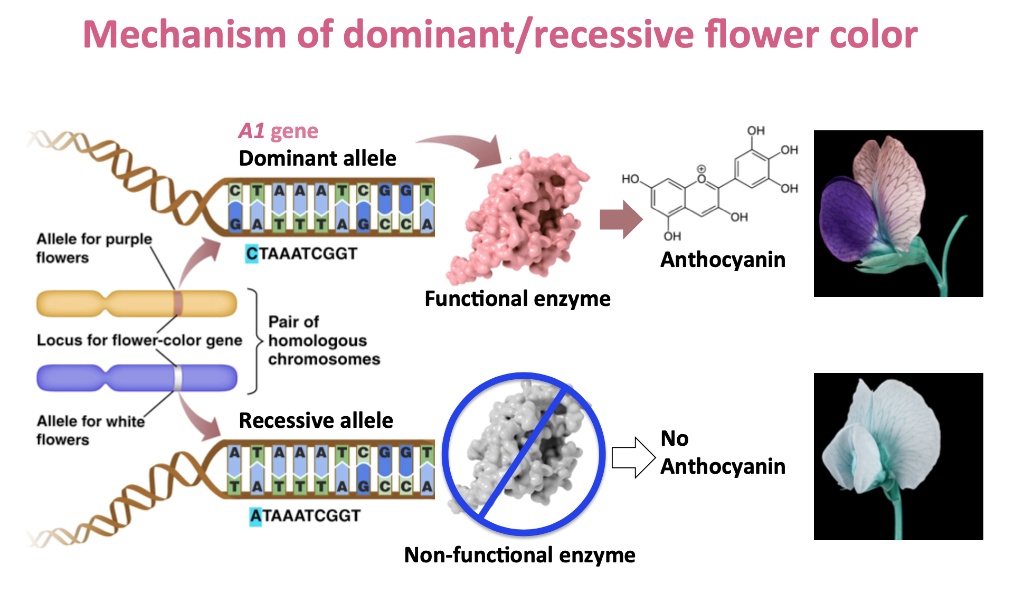
Flower color is the result of pigment molecules accumulating in cells, but it's not as simple as just making pigment. The location, type of pigment, and amount produced, are all very important. These aspects are genetically controlled.

Two main groups of genes control flower color. One group includes genes that code for the protein machinery required to make pigment molecules. The other group.

Dominant Vs Recessive Traits List
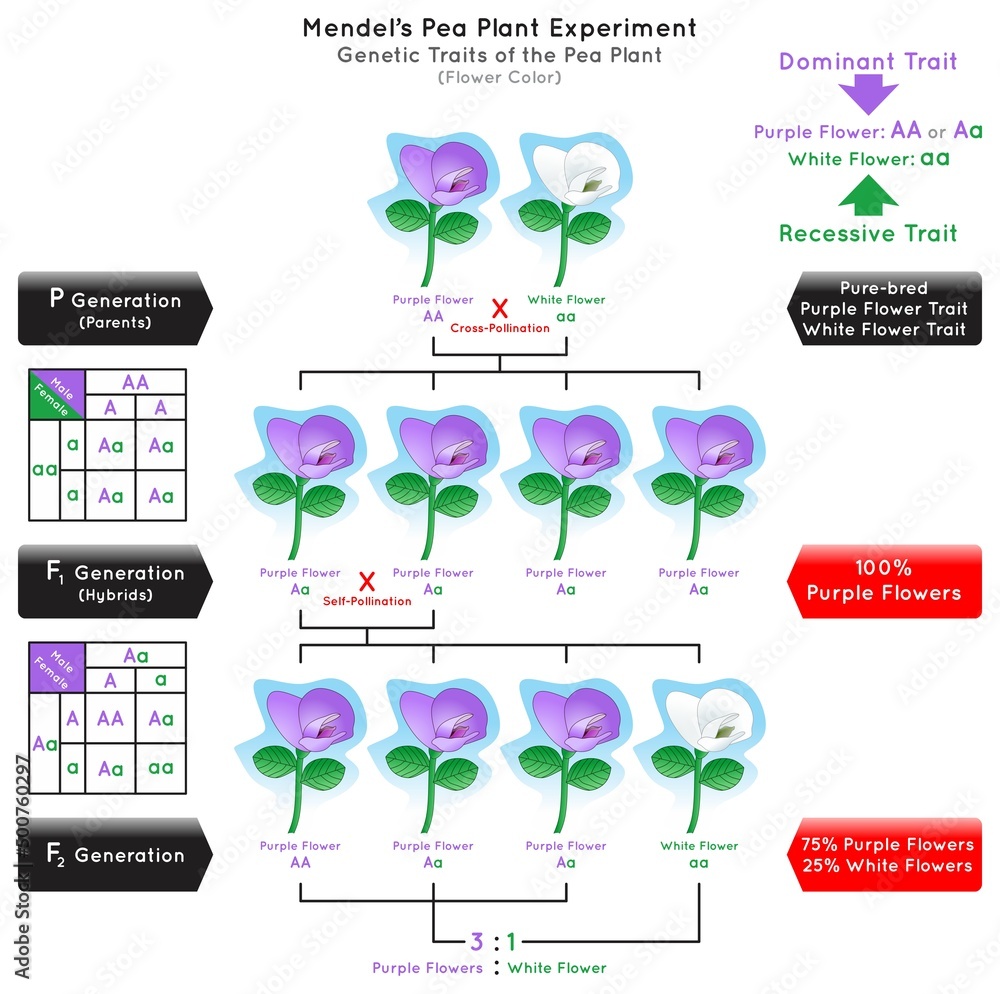
Explore how dominance, co-dominance, and recessive genes determine flower color. A plant biology primer from the experts at Plant Specialists NYC. The diagram shows how flower color is inherited in pea plants.
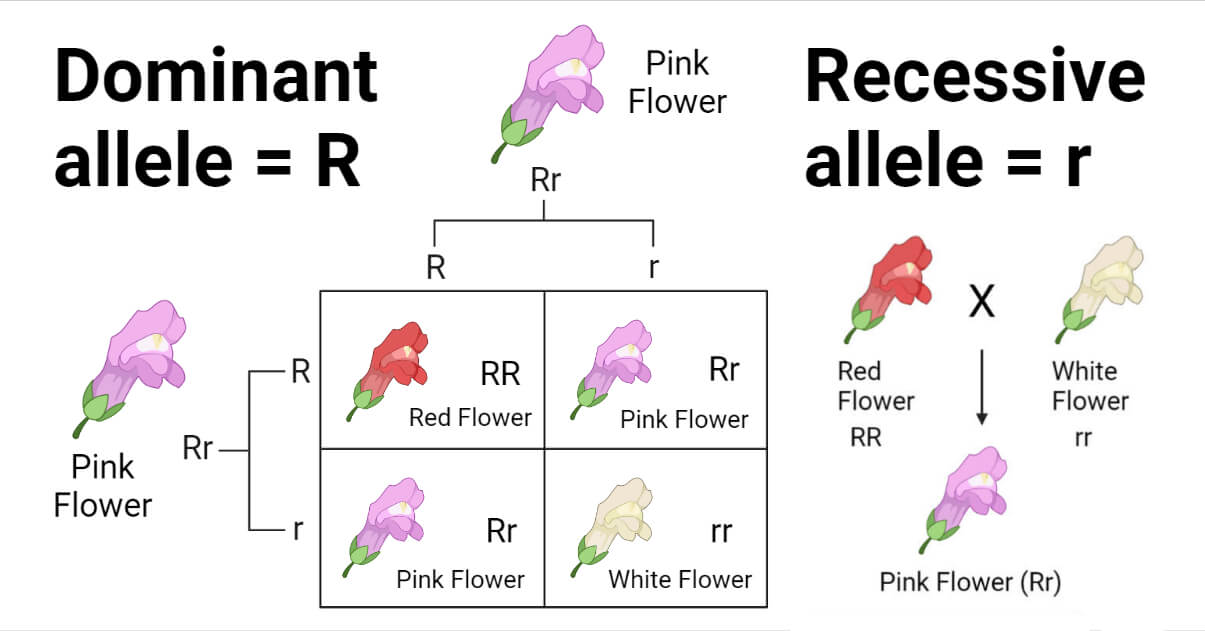
In this example, what is the recessive trait? How do these results suggest that flower color is determined?, Calculate the probability of homozygous recessive offspring with from the cross Aa Bb cc dd Ee Ff × Aa Bb Cc dd Ee Ff., A particular flower can be purple, blue, red, or white. Two different pure. The color of a flower is determined by pigments called anthocyanins that are produced in the petals.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. - ppt download
Some plants have the genetic ability to make purple anthocyanins, while others do not. In this article, we'll explore the genetics behind flower color in plants, focusing on how a plant can produce either purple flowers or flowers of another. Flower colours captivate our senses, offering vibrant displays that are far from random.

The shades we see in blossoms-pinks, yellows, reds, and blues-are the result of complex genetics and molecular chemistry. Flower colour is primarily determined by pigment molecules in cells, and it's the genetic blueprint of each plant that dictates where, how much, and what type of pigment is produced. So, for example, in the pea plants above, the possible genotypes for the flower-color gene were red-red, red-white, and white-white.

Punnett Squares: Part ppt download
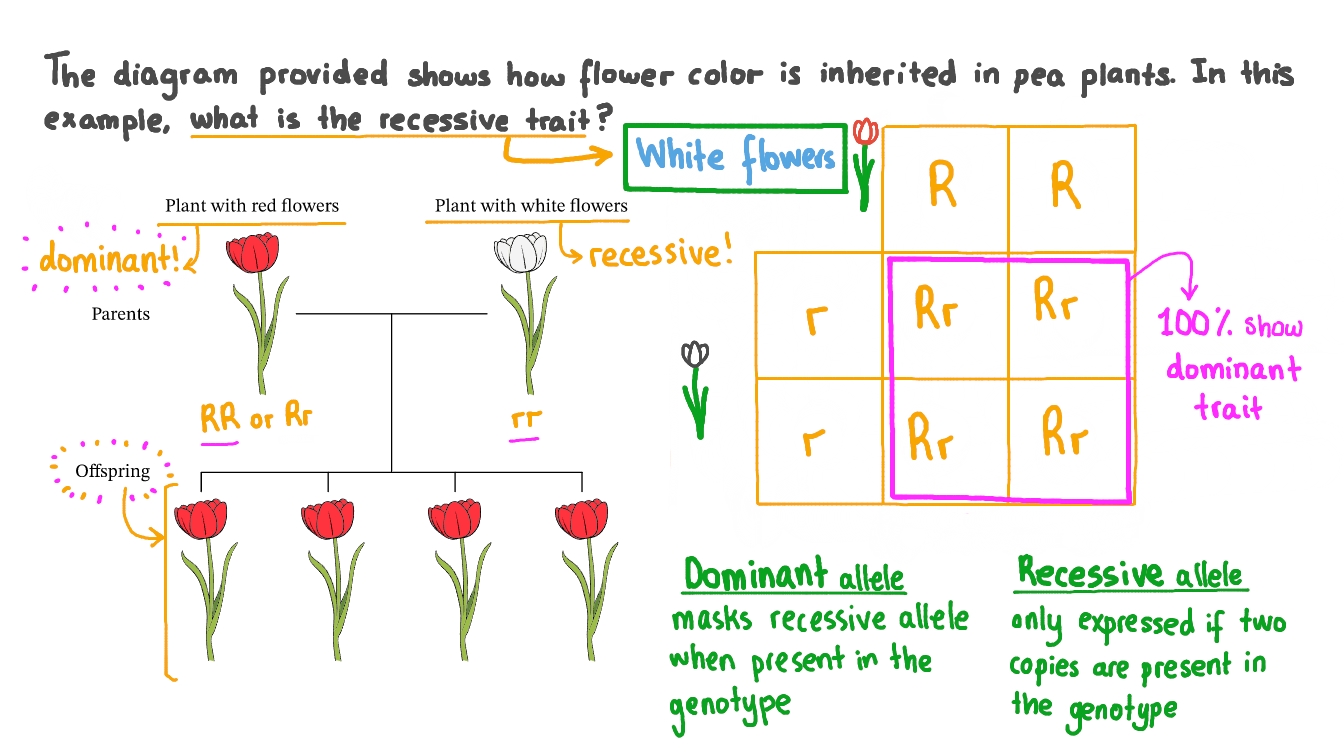
The is the physical manifestation of an organism's allellic combination (genotype). For the pea plants, if the red allele is dominant and the white allele is recessive, only two phenotypes are possible. Flower color refers to the different pigments present in rose petals that determine their color, such as carotenoids, anthocyanidins, and flavonols.

The inheritance of petal color in roses can be controlled by multiple genes, with yellow flower color being controlled by major dominant genes and pink flower color by codominant genes. White-colored flowers are a recessive trait for this same characteristic (flower color). The fact that the recessive trait reappeared in the F 2 generation meant that the traits remained separate (not blended) in the plants of the F 1 generation.

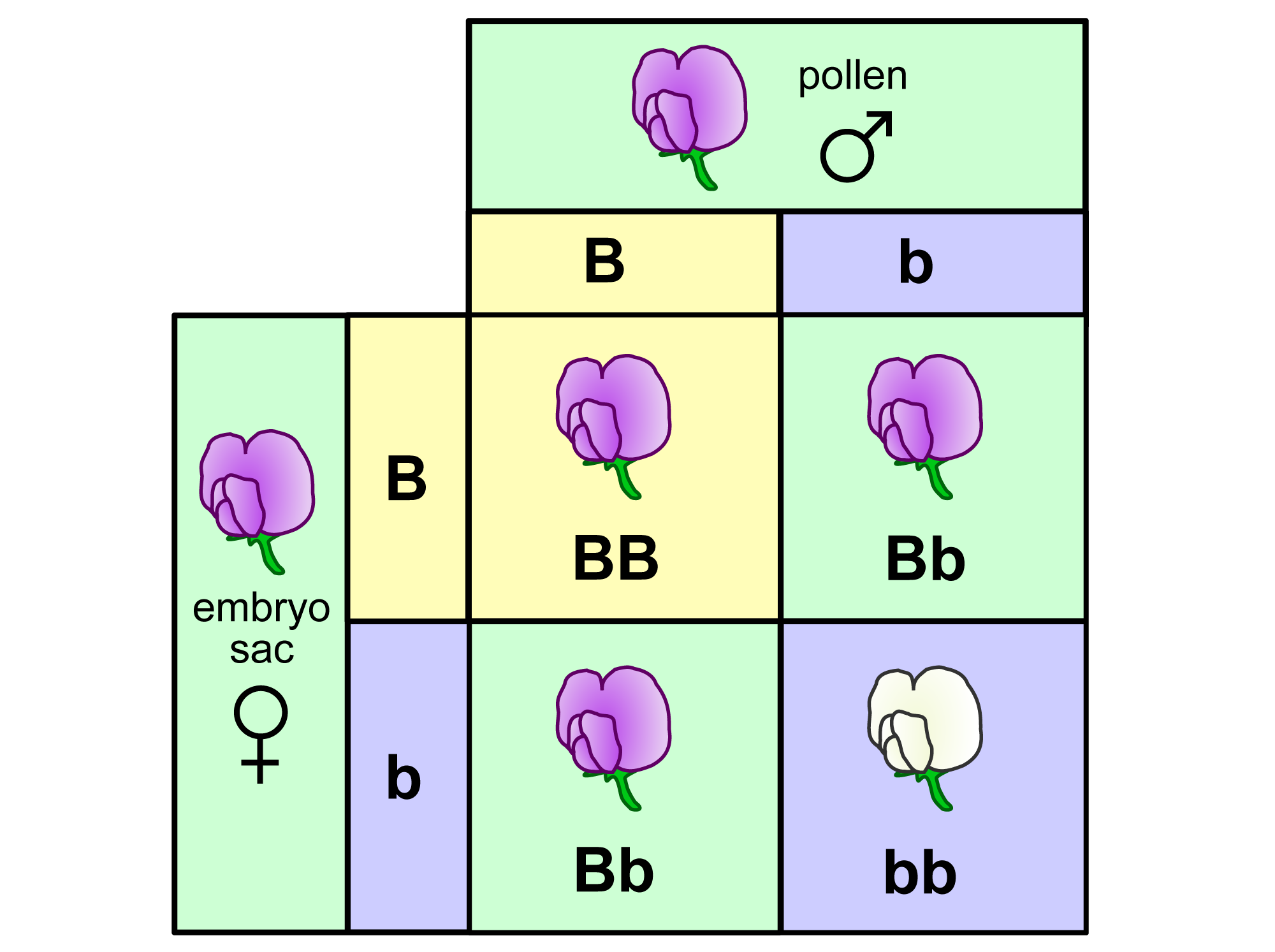
0 Task description: The BLUE flower color stems from a recessive allele, which we denote with b. Assume now that the parental generation both are heterozygous for that recessive allele (Bb). One of the offspring flowers shows a "normal" white color.

Calculate the probability that this flower is also a "carrier" of the BLUE flower allele.