Graph Colouring State Space Tree
Time Complexity: O (V * mV). There is a total of O (mV) combinations of colors. For each attempted coloring of a vertex you call issafe(), can have up to V-1 neighbors, so issafe() is O(V) Auxiliary Space: O (V + E).

The recursive Stack of the graph coloring function will require O (V) space, Adjacency list and color array will required O (V+E). Are you struggling to understand Graph Coloring in ADA? In this video, we explain the State Space Tree for M Coloring when N = 3, M = 3 in the simplest way possible. State-space search has an advantage over the iterative approach in that it does not require the large number of message exchanges between chares to mediate coloring con icts.

Write a short note on Graph coloring
However, the state-space search does require the use of many more chares than the iterative approach and could incur higher memory overhead. Given the Charm runtime features likes load balancing, prioritized message. The number of anode increases exponentially at every level in state space tree.

With M colors and n vertices, total number of nodes in state space tree would be. Each level of the tree would represent the coloring of one node. Branches would represent different color choices for a node, and leaf nodes would represent complete valid colorings of the graph.
Graph Colouring Problem using C | Find Chromatic number of a graph and ...
Step 8: Find all valid colorings By exploring the state space tree, we can find all possible valid colorings of the graph. State space exploration takes a different approach to dividing work between processors. A state in the state space tree is a partially colored input graph, and child states are produced from parent states by coloring one of the uncolored vertices.

Graph coloring Apply color to all vertices in a graph in such a way that adjacent vertices do not have same color. Like the above graph coloring method we need to find all the possibilities of coloring in each vertices in a graph using state space tree. This problem is also called m coloring problem fDraw the root node, starting from the first vertex A, we can color with 1, 2, 3 (1=red,2.
Coloring using backtracking. A tree is obtained showing different ...
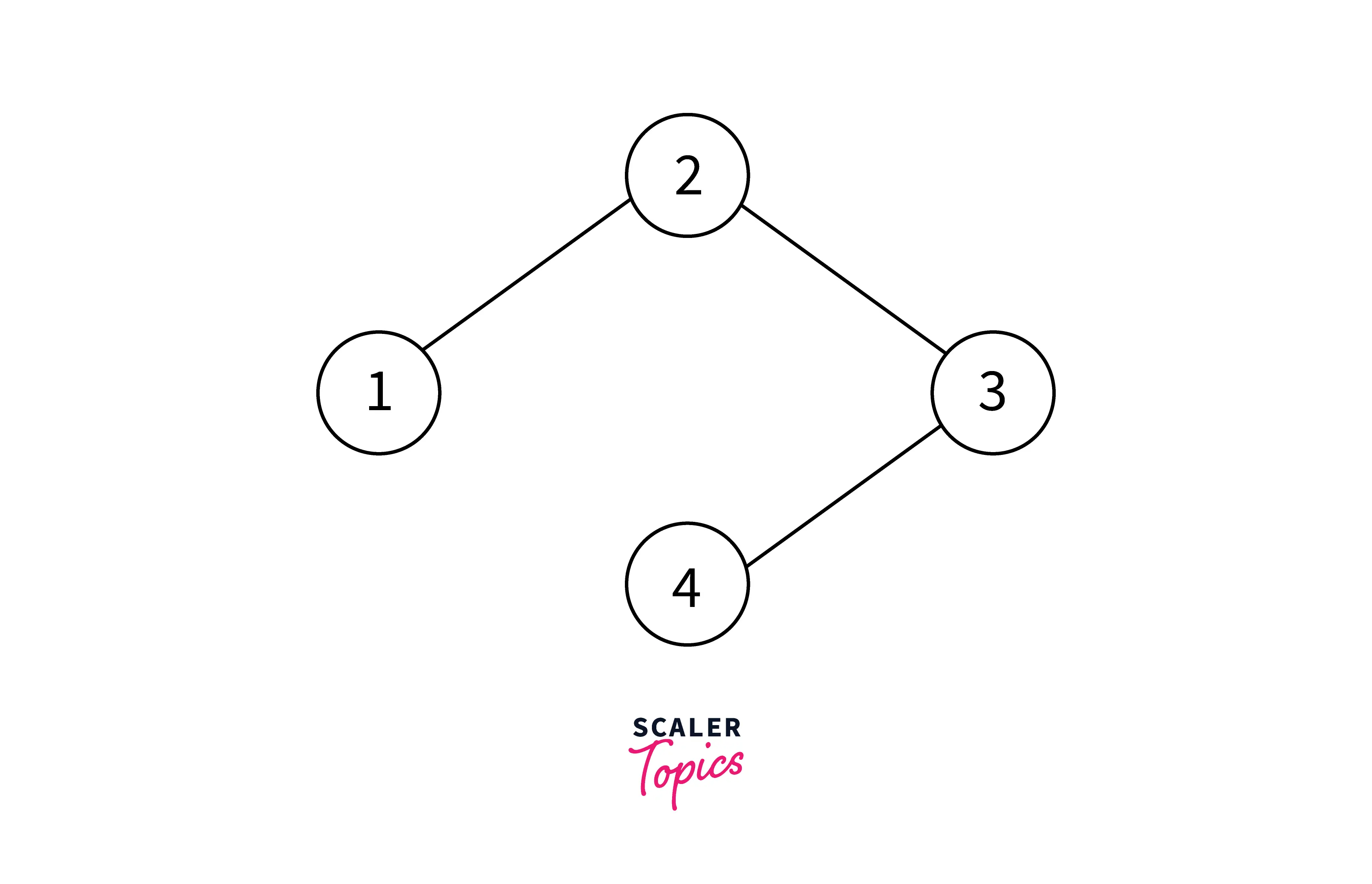
In backtracking, a state-space tree is a tree-like structure that represents all possible states (solutions or non-solutions) of a problem. Backtracking algorithms explore this tree using a depth-first search approach, systematically checking each path until a solution is found or all possibilities have been exhausted. Figure 2: State space search tree - all possible C COLORINGS of G where c=3 Figure 1 shows a simple graph with n = 4 vertices.
The tree which is generated by the algorithm CCOLORING is shown in Figure 2. Every path to a leaf represents a coloring using at most c = 3 colors. There are 12 solutions exist with exactly c = 3 colors.

A tree is obtained showing different possible coloring of a graph from publication: Quantum Algorithms for Colouring of Graphs Colouring of graphs is one of the most important concepts in graph.