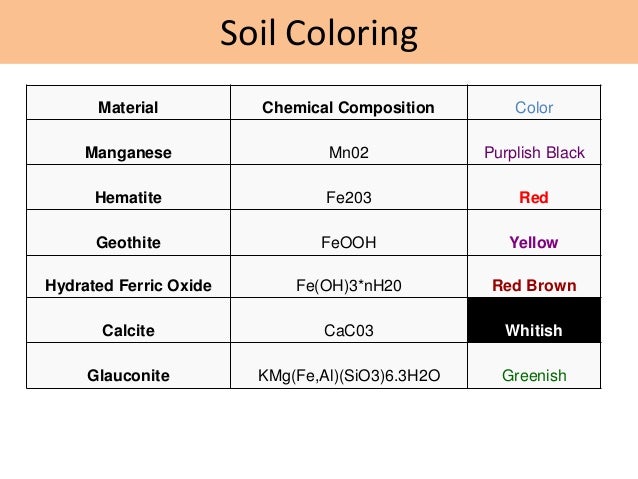
Soil Color Name
Soil color is often the most visually apparent property of soil. While color itself does not influence the behavior or practical use of soils, [1] it does indicate important information about soil organic matter content, [2] mineralogy, [3] moisture, [4] and leaching. In this article, we'll be exploring the different colors of soil and what they reveal about its composition, history, and potential uses.
From the bright red of iron-rich soil to the deep black of peat, each color tells a unique story about the land and its inhabitants. Maps that show soil color at various depths for individual States and the Continental United States. Soil Color Color: A key property in soil interpretation Most evident (observable) Influenced by Organic Matter (OM) content and redoximorphic (redox) sensitive metals such as Iron (Fe) and Manganese (Mn).

What Are The Different Types Of Clay Soil at Caitlyn Buvelot blog
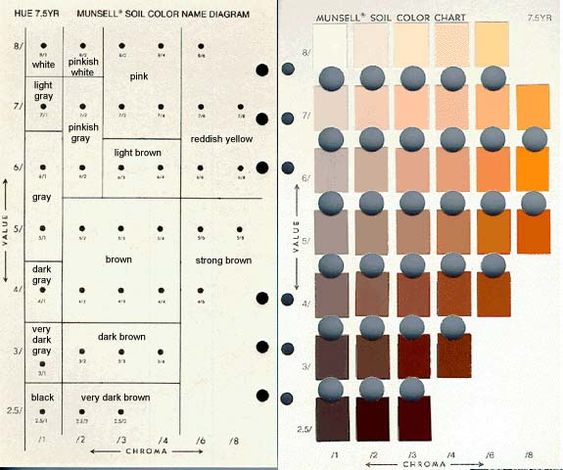
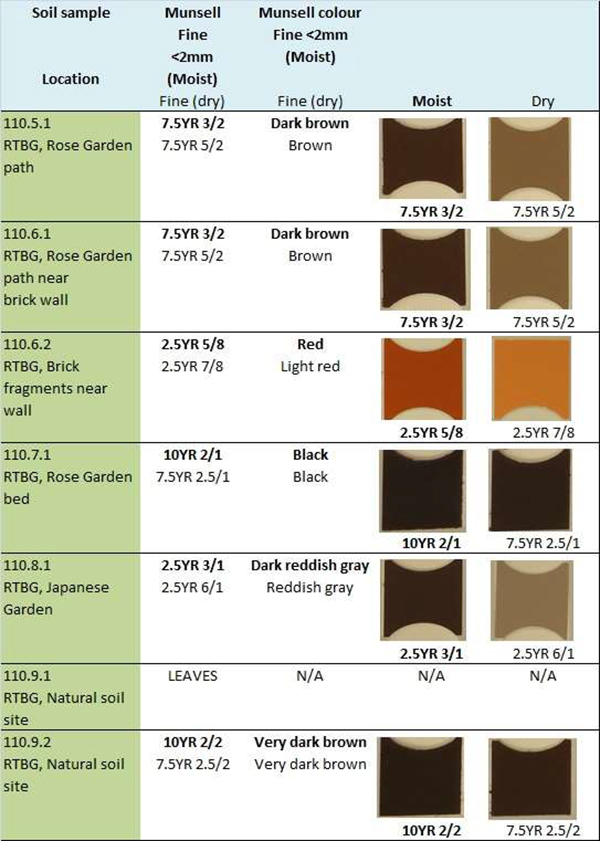
The Munsell Color System describes a soil's color, based on Hue, Value & Chroma. The Munsell Book is a collection of color chips with varying degrees of hue, value & chroma. Take a small soil sample and match it up with the appropriate color chip to determine that soil's Munsell "code.".

This textbook introduces readers to introductory soil science topics including the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soils; soil formation, classification, and global distribution; soil health, soils and humanity, and sustainable land management. Soil color refers to the visual appearance of soil, which is used to identify and differentiate specific soil properties. It is determined by three main components: hue (resemblance to red or yellow), value (relative darkness and lightness), and chroma (weak or strong color appearance).

PPT - Soil Science PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1923890
With a soil color book with Munsell notations, a science student or teacher can visually connect soil colors with natural environments of the area, and students can learn to read and record the color, scientifically. Soil color by Munsell notation is one of many standard methods used to describe soils for soil survey. Blackish Black soil color is the result of a mixture of different factors, including mineral content, moisture content, and organic matter.

Organic matter consists of carbon. Soil colour is a fundamental property of soil that provides valuable information about its composition, fertility, and overall health. It is a critical aspect of soil science, and understanding soil colour can help farmers, gardeners, and environmentalists make informed decisions about soil management and conservation.