Colour Of Frog Lungs
The color of frog's lungs are a purplish brown. Why can't humans breathe through their lungs like frogs? The mechanism of taking air into the lungs is however sligthly different than in humans. Frogs do not have ribs nor a diaphragm, which in humans helps serve in expand the chest and thereby decreasing the pressure in the lungs allowing outside air to flow in.

Frogs respire on land and in the water by two different methods. In water, skin acts as aquatic respiratory organ (cutaneous respiration). Dissolved oxygen in the water is exchanged through the skin by diffusion.

Premium Vector | Anatomy of frog lungs illustration
On land, the buccal cavity, skin and lungs act as the respiratory organs. The respiration by lungs is called pulmonary respiration. In pulmonary respiration, frogs breathe in the atmospheric air into the lungs like human beings, but the mechanism of breathing in and breathing out is different.

The respiratory system is comprised of the respiratory tract and the lungs. Respiratory tract External nares Internal nares Buccopharyngeal cavity Glottis Tracheo bronchial chamber. Learn how frog lungs work, their essential functions, and unique structure within the amphibian respiratory system.

Frog Respiratory System
Respiration in tadpole of frog occurs by means of gills as in fishes. In adult frog, due to its amphibian life, respiration occurs through skin (cutaneous respiration), lining of the bucco-pharyngeal cavity (buccal respiration) and the lungs (pulmonary respiration). Respiratory System of Frog Respiration is a process in which food are oxidized with oxygen in order to release energy.

The released energy is utilized to perform various life activities. The metabolic waste like CO2 is eliminated from the body. C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O +energy Due to amphibious mode of life, frog shows different modes of respiration.

What Is Anatomi
The exchange of "Respiratory. Detailed description of the frog respiratory system: anatomical components, functional adaptations for aquatic and terrestrial respiration. The morphology of the lung of the East African tree frog Chiromantis petersi with observations on the skin and the buccal cavity as secondary gas exchange organs A.
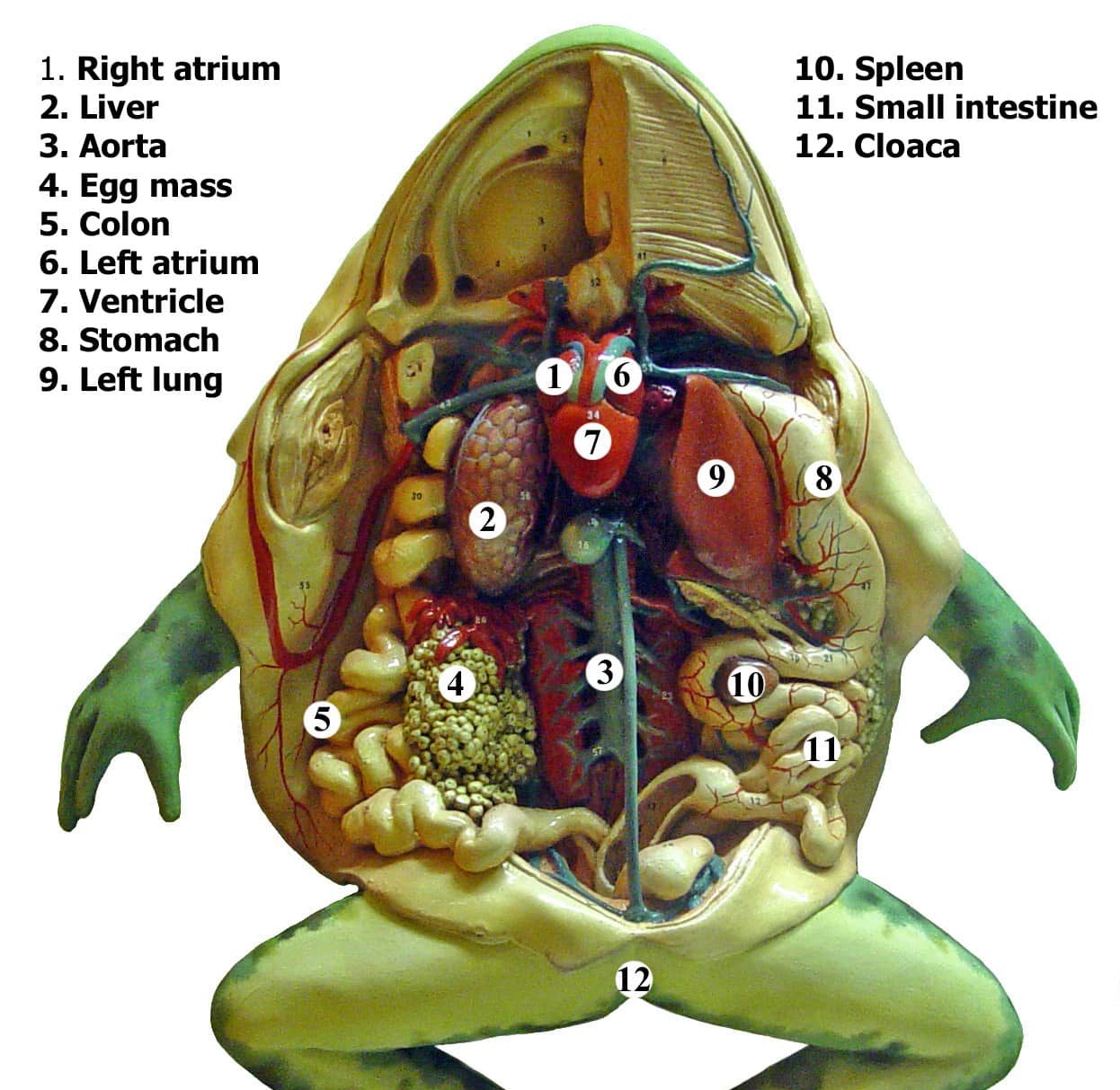
The color of frog lungs can vary depending on factors such as the species of the frog, their health, and their environment. In general, frog lungs are usually a light pink to reddish color due to the presence of blood vessels that supply oxygen to the tissues.