Sun Color Fade
Conclusion In conclusion, color fading is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of pigment or dye used, the intensity of the sunlight, and the duration of exposure. While red is often considered the most prone to fading, other colors, such as orange and yellow, can also fade quickly in sunlight. Fading from the sun is a common issue faced by many individuals, homeowners, and businesses alike.

As beautiful as sunlight can be, it can also wreak havoc on our belongings, leading to unsightly discoloration and damage. Understanding the causes of this fading can help us make informed decisions about protecting our valuables. In this article, we will explore the science behind sun fading.
How The Sun Causes Colors To Fade
Learn why sunlight fades colors and damages materials. Understand the science of sun bleaching and get practical tips to protect your belongings. What Causes Color to Fade in Sunlight? The primary culprit is UV (ultraviolet) radiation.

Sunlight contains UVA and UVB rays, which break down the chemical bonds in dyes and pigments. This process is called photodegradation. How Fading Happens: UV rays penetrate fabric or surface coatings Energy from the sun excites dye molecules The bonds weaken or break, changing the way the fabric absorbs.

Why Does Sun Fade Colors at Michael Mahoney blog
The result is that the red-emitting chromophores degrade at a faster rate, triggering fading. So simply put, the colour doesn't 'go' anywhere when materials fade - it's just not emitted so well by the chromophores. Why do tattoos fade? How does colour-change lipstick work? Why do clothes get darker when wet? It's an undeniable fact that exposure to sunlight causes colors to fade, giving the material a dull appearance.

While it's easy to think that the sun burns away the colors causing them to lose their sheen, that's hardly the case. Sunlight causes colors to fade by initiating photodegradation, a process that causes irreversible changes to molecules and compounds that give a material its. Consider Color Placement: Strategically placing items away from direct sunlight can also help reduce fading.

Fading Sun Free Photo Download | FreeImages
For instance, positioning artwork in shaded areas can prolong its vibrancy. Conclusion In the quest for color longevity, understanding which hues fade the slowest in sunlight is crucial for artists, designers, and manufacturers alike. Bright sun.

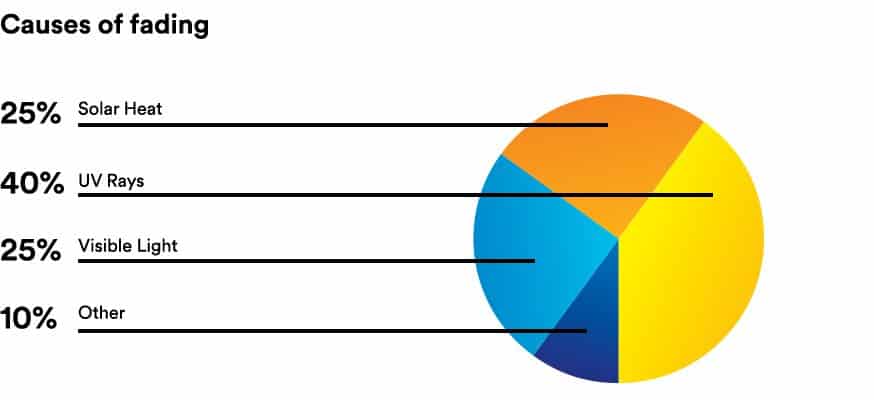
Palo Alto Battlefield National Historical Park, 2017. National Park Service, NPGallery. Ultraviolet rays are one of the causes of fading because they can break down chemical bonds and fade the color in an object.
Other major contributors to fading include visible light and solar heat. It usually takes a few hours to several months for sunlight to fade fabric, depending on factors like the fabric type, color, and intensity of sunlight. You'll notice more fading with prolonged exposure.

Understanding the Concept of Sun Bleaching Consider sun bleach as nature's detergent. Just like store-bought bleaches, the sun's rays work powerfully to remove or fade color from materials. These effects are especially evident in textiles, paper products, and outdoor furniture, where pigments absorb all but certain wavelengths of light.