Leaves Colored In
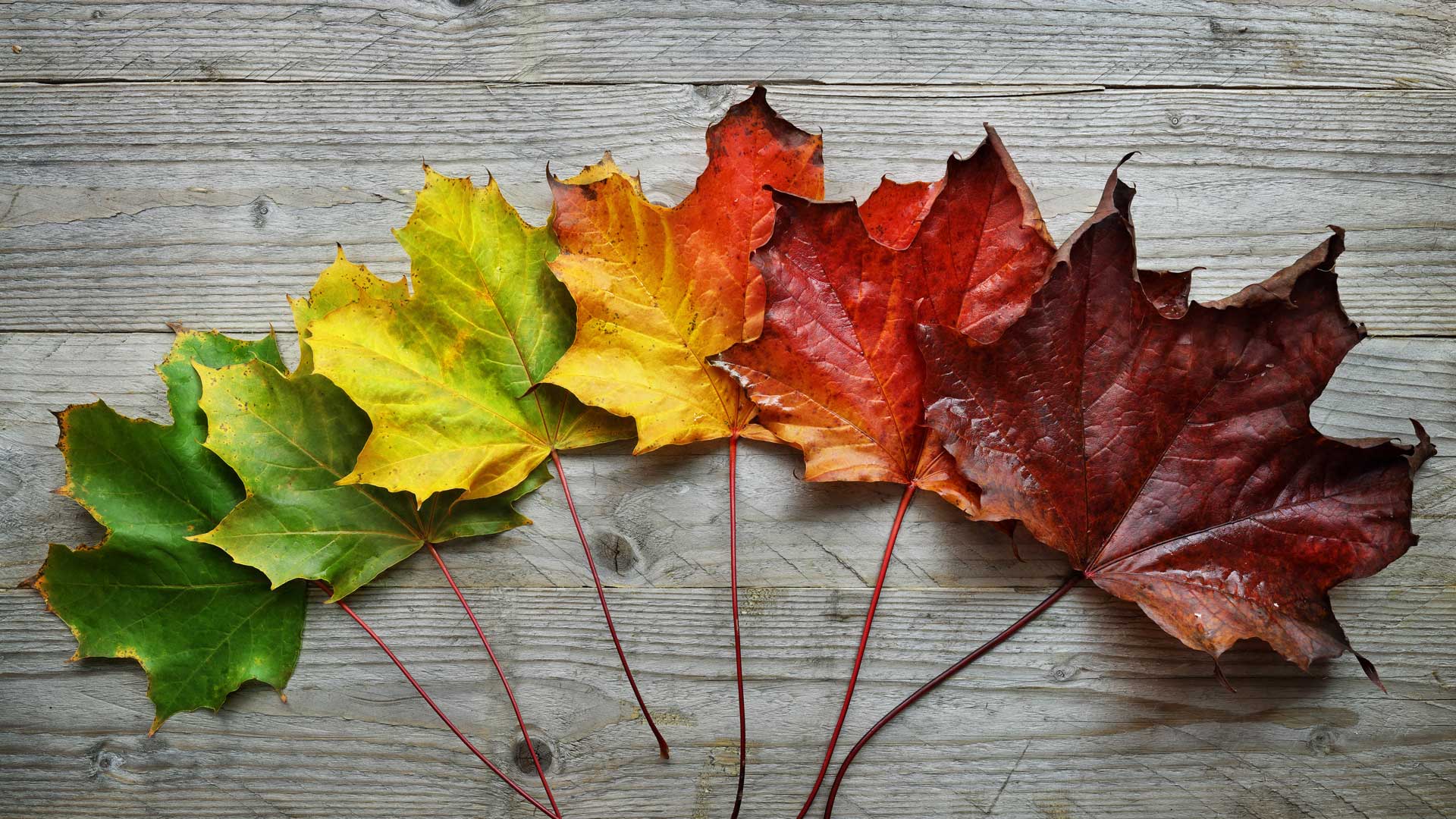
When do leaves reach peak color? The peak dates for fall foliage in the U.S. vary from region to region. In other plants, pigments called anthocyanins accumulate in the leaves at this time, giving them shades of red and purple.

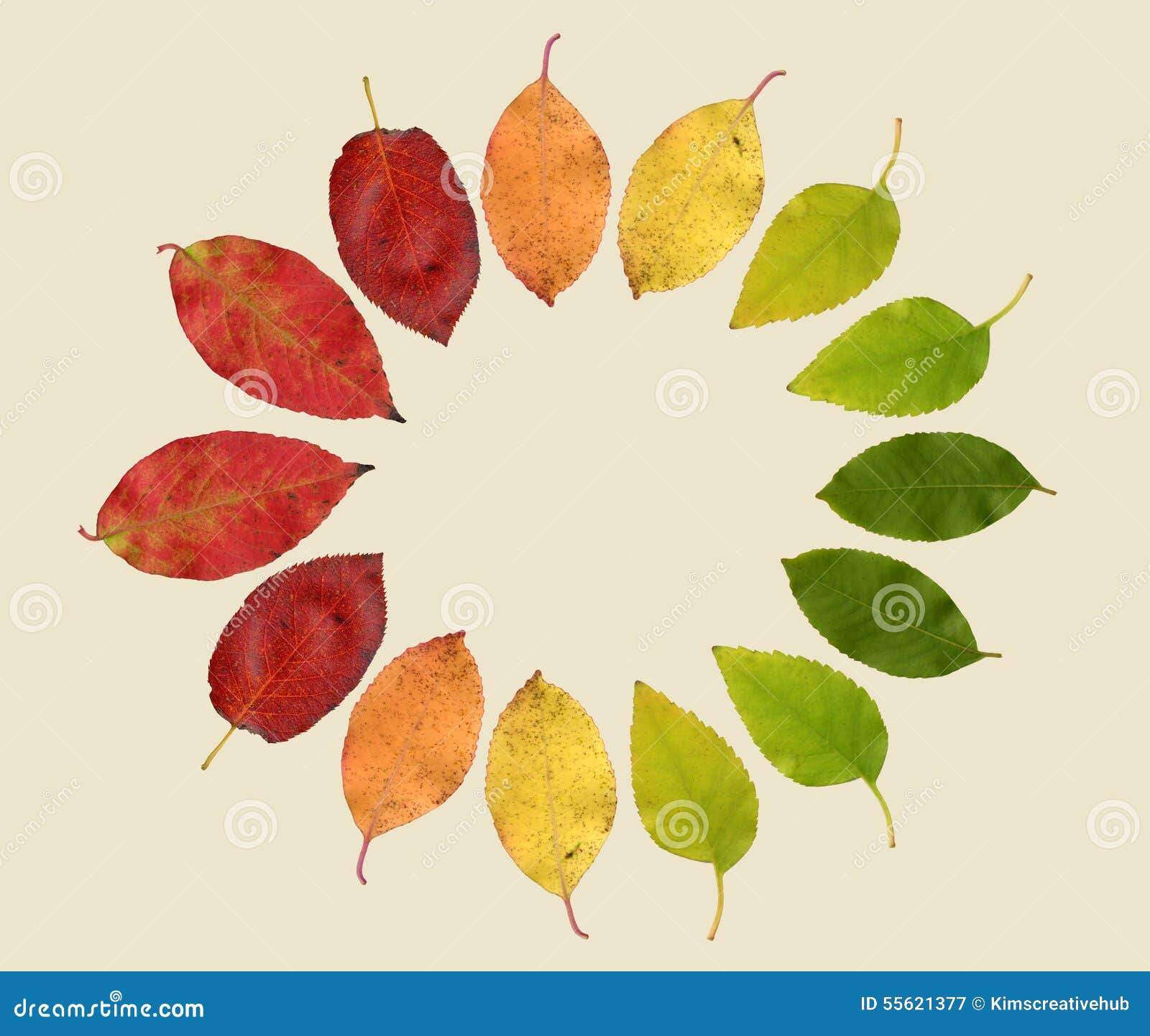
Some of the most beautiful fall foliage features both types of pigments, often with one color giving way to the next as the season progresses. Autumnal leaves in vibrant hues are a beautiful part of the season, but those leaves are also a vital part of keeping trees alive. Trees that have leaves that change color in fall are deciduous.

Why do leaves change color? Fall foliage, explained - City of Spokane ...
(Evergreen trees with needles, which stay green to continue the photosynthesis process through the winter, are coniferous.) Deciduous trees usually have large, broad leaves. Most of the year, these. In this science activity, let's use paper chromatography to uncover the hidden pigments lurking in tree leaves.

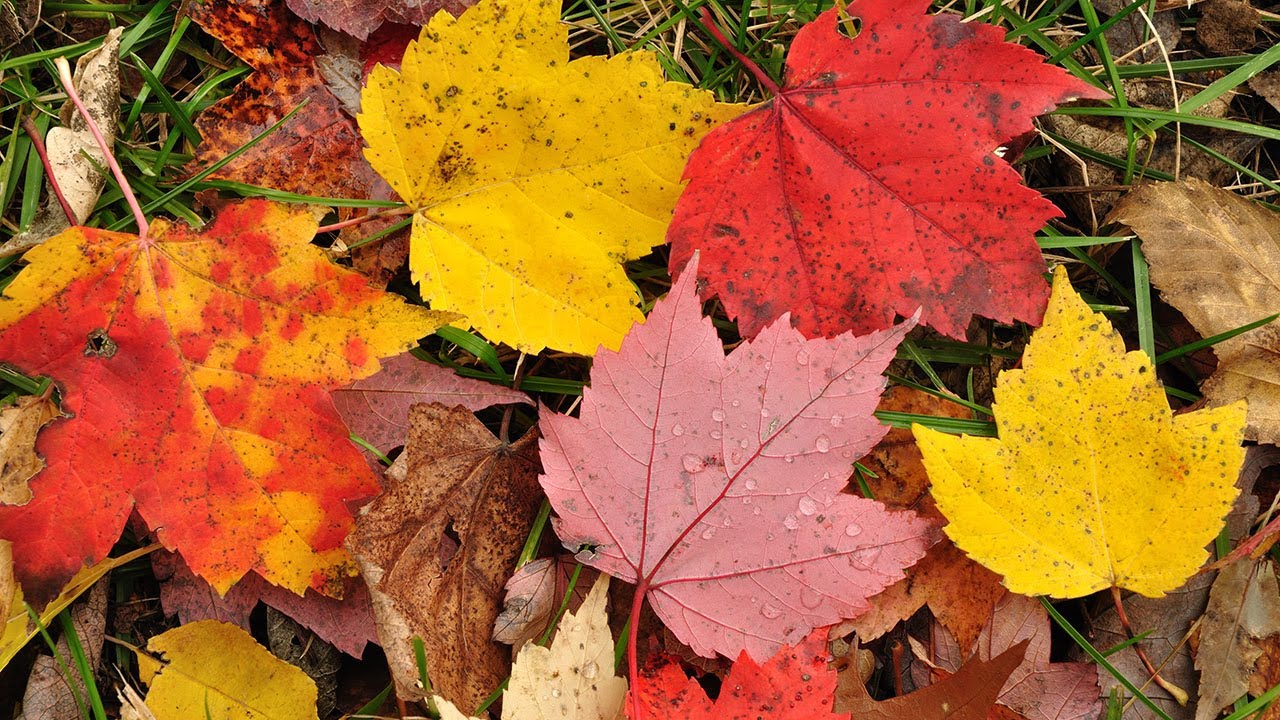
Materials Leaves at different stages of turning fall colors (the more the better - about 20 of each color, from the same tree, is best) Scissors Strong, white, heavyweight, ultra. Brilliant Fall leaves on the Superior National Forest. (Forest Service photo) Certain colors are characteristic of particular species: Oaks: red, brown, or russet Hickories: golden bronze Aspen and yellow-poplar: golden yellow Dogwood: purplish red Beech: light tan Sourwood and black tupelo: crimson The color of maples leaves differ species by species: Red maple: brilliant scarlet Sugar maple.

Why Leaves Change Color in the Fall - Chemistry
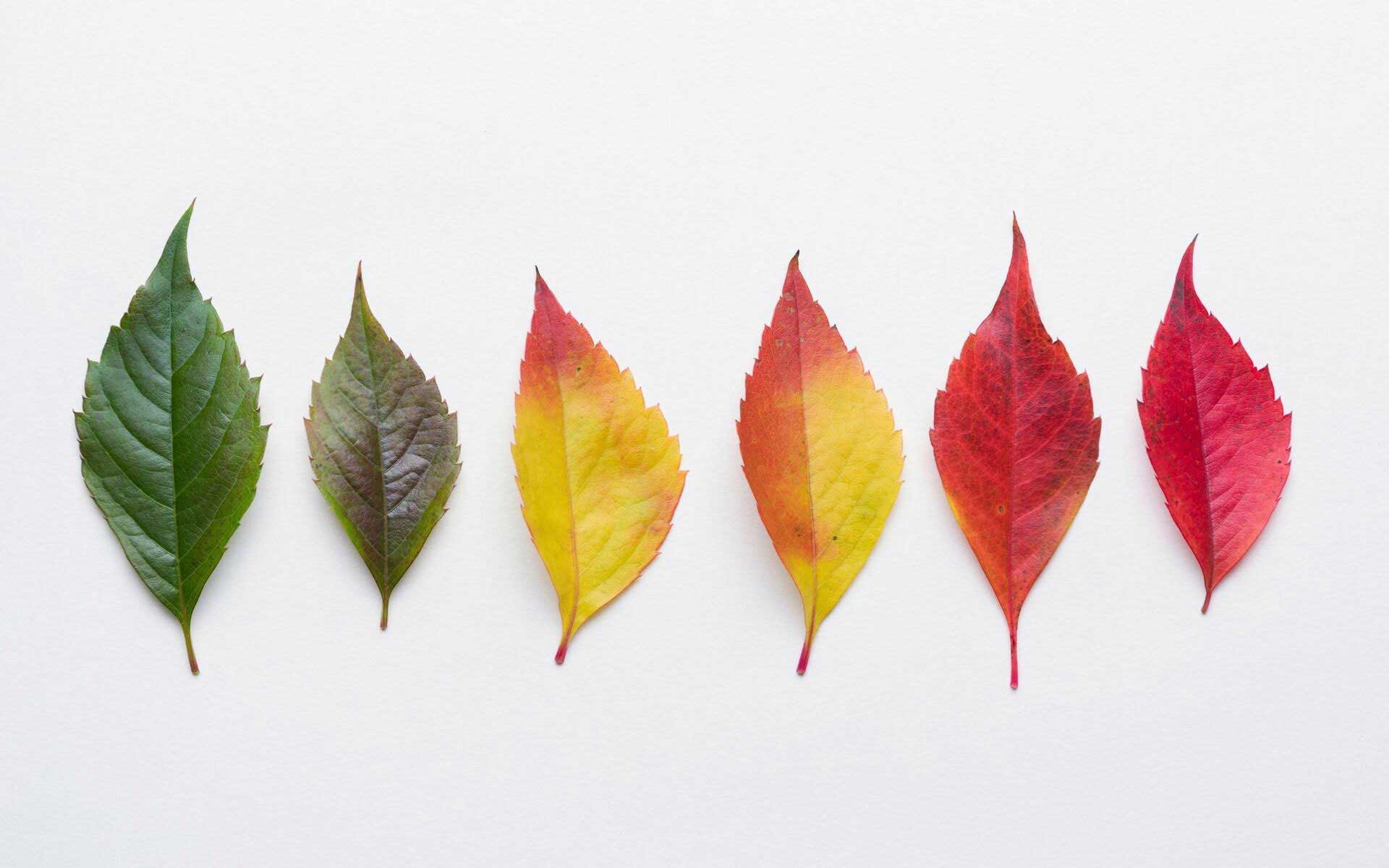
As summer fades into fall, the days start getting shorter and there is less sunlight. This is a signal for the leaf to prepare for winter and to stop making chlorophyll. Once this happens, the green color starts to fade and the reds, oranges, and yellows become visible.

Leaf color changes are among the most visually striking phenomena in the natural world. From the vibrant reds, oranges, and yellows of autumn foliage to the subtle shifts in green hues during various growth stages, these transformations tell a compelling story about plant biology, environmental conditions, and ecological interactions. Understanding why and how leaves change color involves.

Autumn Leaves in Different Colors Stock Image - Image of isolated ...
Ever since the leaves on the trees bloomed in the spring, they have actively been helping the tree grow. Each leaf contains a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is the most common pigment in a leaf.

It absorbs the sun's rays to turn sunlight into food and energy for the tree. Chlorophyll is also what gives a plant its green color. Leaves change color during the autumn because the amounts of pigments change as the leaves prepare to fall from the trees.

All leaves gradually lose chlorophyll during the growing season, and this loss accelerates before leaf fall. Under optimal conditions this process of chlorophyll loss is very orderly and allows the plants to resorb much of the nitrogen in the structure of the pigment. Learn why leaves change color in the fall and see the chemistry of the pigment molecules responsible for different leaf colors.