How Do Lambs Get Orf
ORF or contagious ecthyma or sore mouth is a contagious viral disease of sheep, goats, and other ruminant animals. The disease causes severe economic loss of sheep farms by spreading rapidly to the herd, production loss, and treatment cost. The disease can be controlled and spread reduction by taking adequate measures and vaccination.

Scabby mouth (contagious ecthyma, orf) is a highly contagious, viral disease of sheep, goats, and occasionally humans. This disease is a potential problem of live sheep exports [and confinement type operations] due to the close confinement of animals and the feeding of sheep with pellets and hay that cause minor abrasions to the mouth and lips. What it is Sore mouth disease is caused by orf virus, a type of poxvirus.

Better orf control | Lambing Advice
It occurs worldwide, anywhere sheep, goats and similar animals live. People can get painful sores called lesions if they have contact with animals infected with orf virus. Certain activities like feeding, petting and getting bitten by infected animals put people more at risk for infection.

Simple prevention steps can. Orf virus infections do not generate enduring immunity so you can be infected multiple times over your lifetime. Where is Orf found on the farm? Orf virus can be found on sheep or goats or contaminated equipment.

How to vaccinate for orf disease in lambs - Farmers Weekly
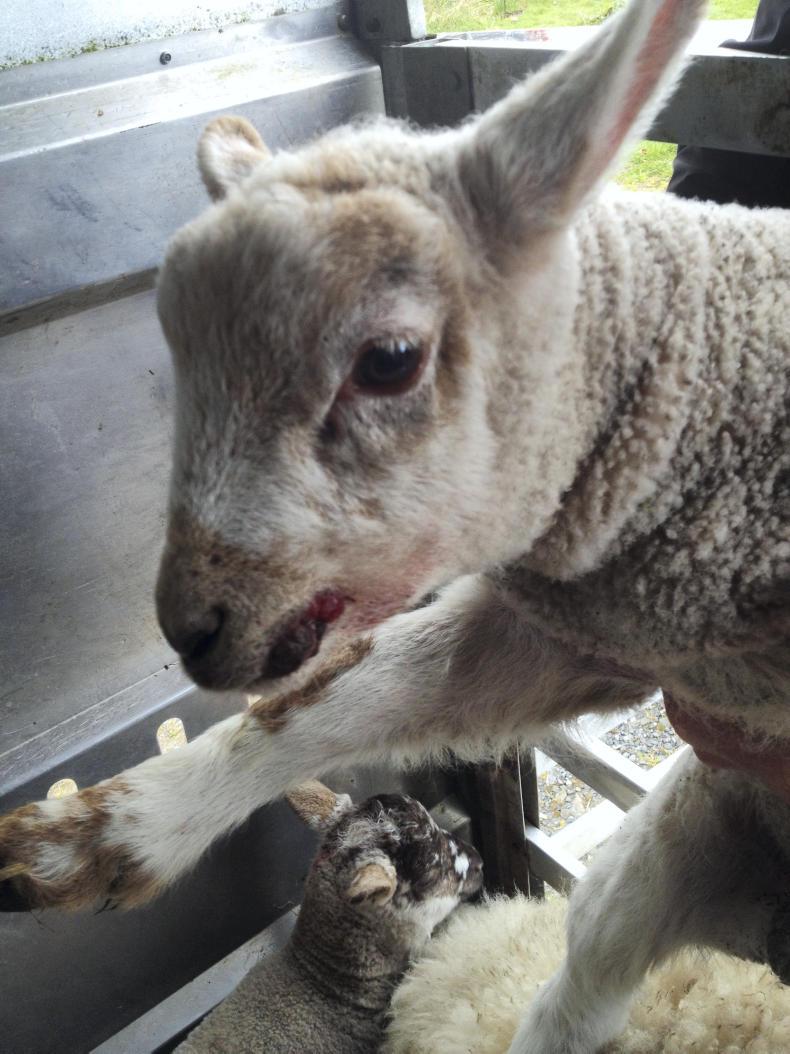
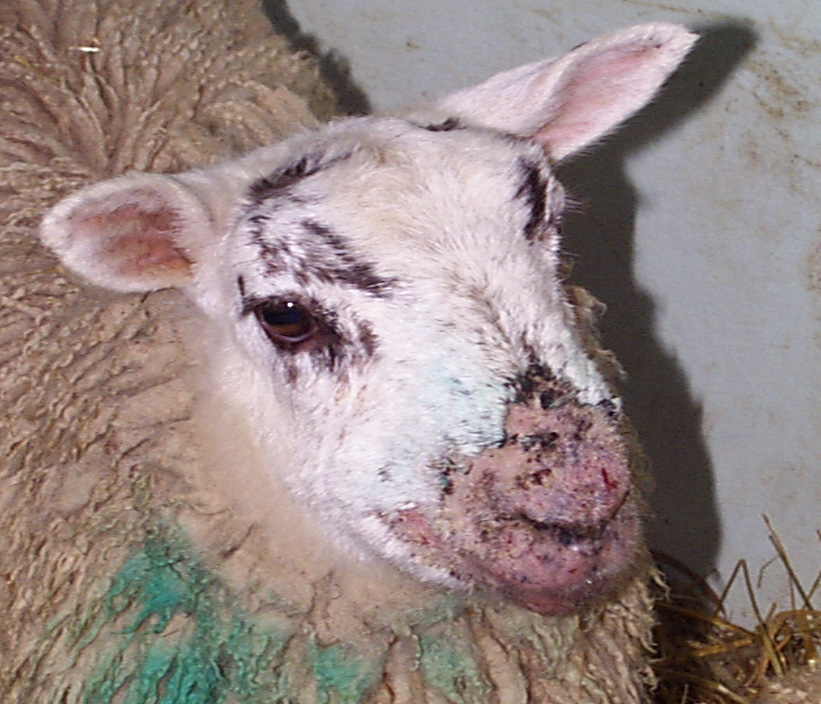
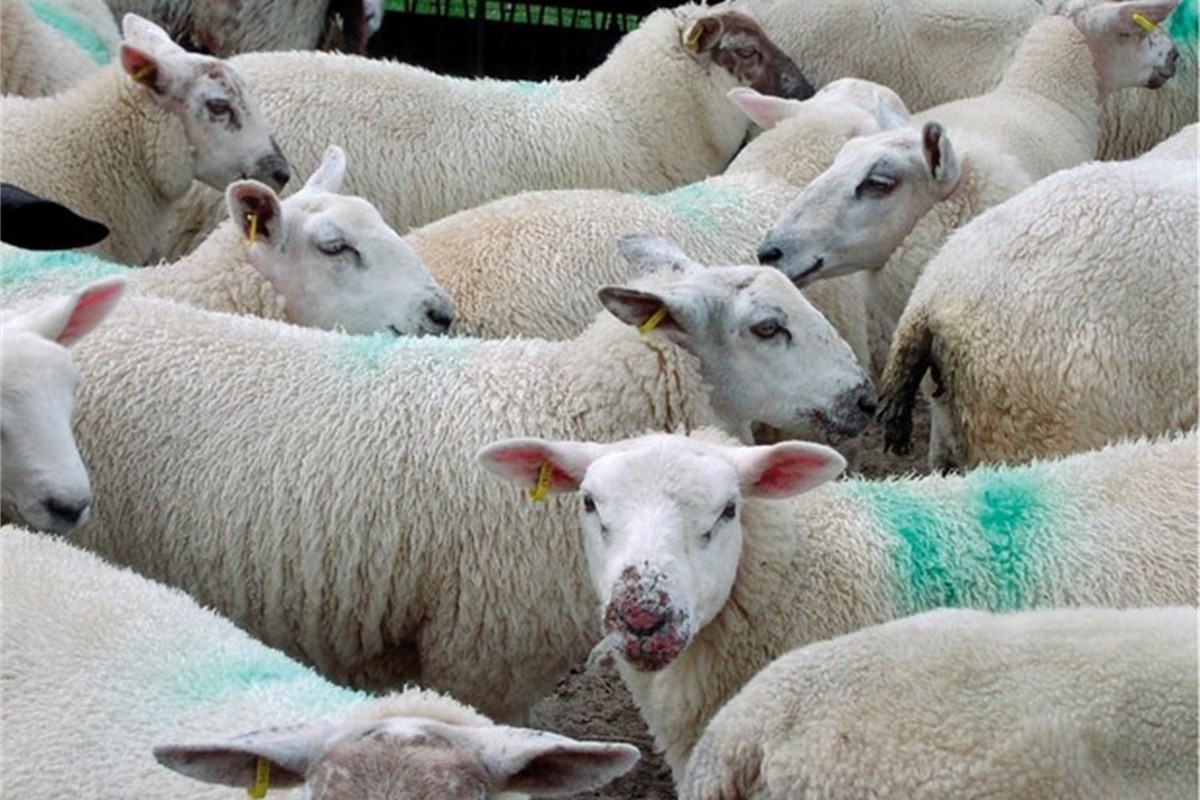
It is most common in young lambs and their ewes and older lambs in the late summer. The animals may have visible lesions in the mouth/muzzle area, but can also spread the virus. How does orf spread? Should the skin of the sheep get grazed or cut by a thistle or rough food, the orf virus can then attack the vulnerable areas which lead to an outbreak of orf.

It can also spread on feeding equipment and is more prevalent in housing with many sheep. Orphaned lambs are particularly susceptible to orf. When to look for it Aside from artificially reared lambs, orf is also common in sheep that have recently been turned on to new pasture.

Orf infection around the mouth and nose of a Friesland Friesian sheep ...
You may notice lesions around the mouth and nose of sheep around 2 weeks after putting them onto fresh grass, especially if they are grazing fields with a lot of thistles, gorse or other prickly plants. Orf in lambs: symptoms, causes, and treatment options explained. Discover how to prevent and manage this contagious sheep skin disease effectively.

Orf Orf is a skin infection you can get from infected sheep or goats. It most often affects the fingers, hands, forearms or face. It usually clears up without treatment in about 6 weeks.

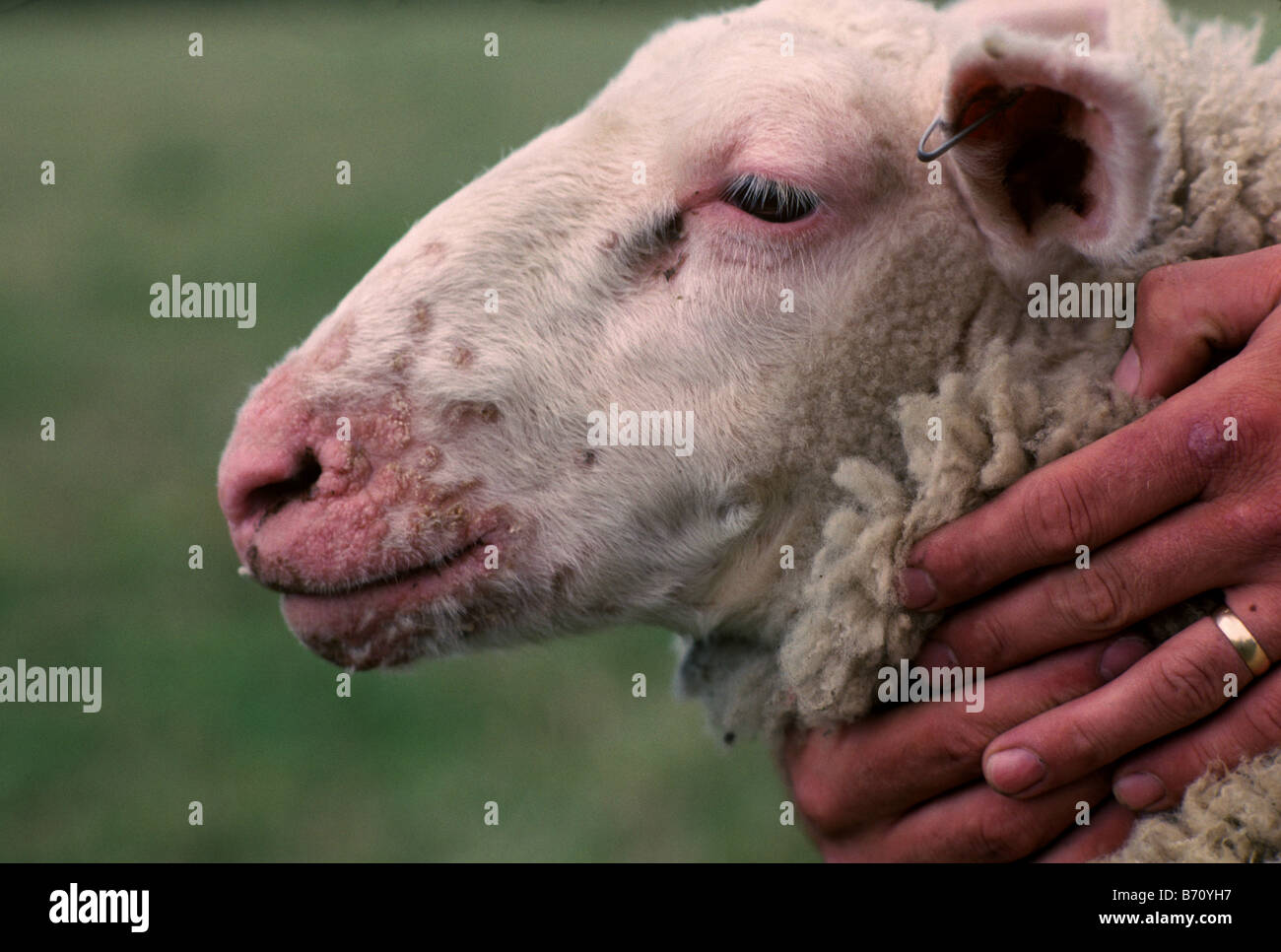
Orf is a contagious virus that usually causes scabs and lesions in the mouth and gums of the infected animal. It mainly affects animals in the first year of their life, however, infected lambs can transmit the virus to the ewes udders whilst suckling. Understanding orf Caused by a parapox virus, orf is highly contagious and can affect sheep of all ages.

Characterised by scabby lesions around the nostrils and mouth. It can spread to other parts of the body, such as teats, feet and tail. Orf is a zoonosis - people handling infected sheep, wool or skins can catch orf.