What Colours Do Tigers See
So, because of this missing cone cell, tigers cannot detect a specific light spectrum that results in having two types of color receptors. How do tigers see colors? Tigers don't depend too much on color; instead, they use their eyesight for hunting prey. Because of that, they have more rods in comparison with cones.

Are tigers colorblind or can they see in color like humans? One of the most majestic creatures on earth, tigers are known for their beautiful striped coats and fierce hunting abilities. But what about their vision? Are tigers colorblind? Many people wonder if these impressive animals see the world in the same way humans do, or if they perceive colors differently. To answer this question, we.

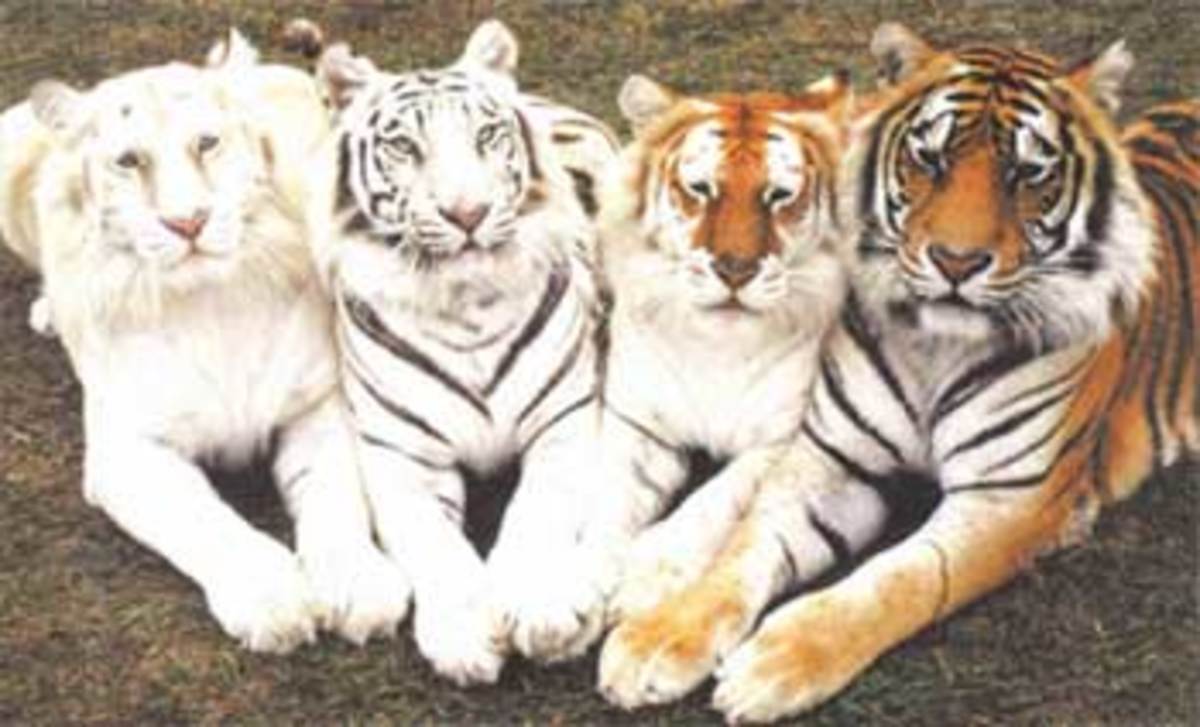
Bengal Tiger: Four Color Variation of Bengal Tigers.
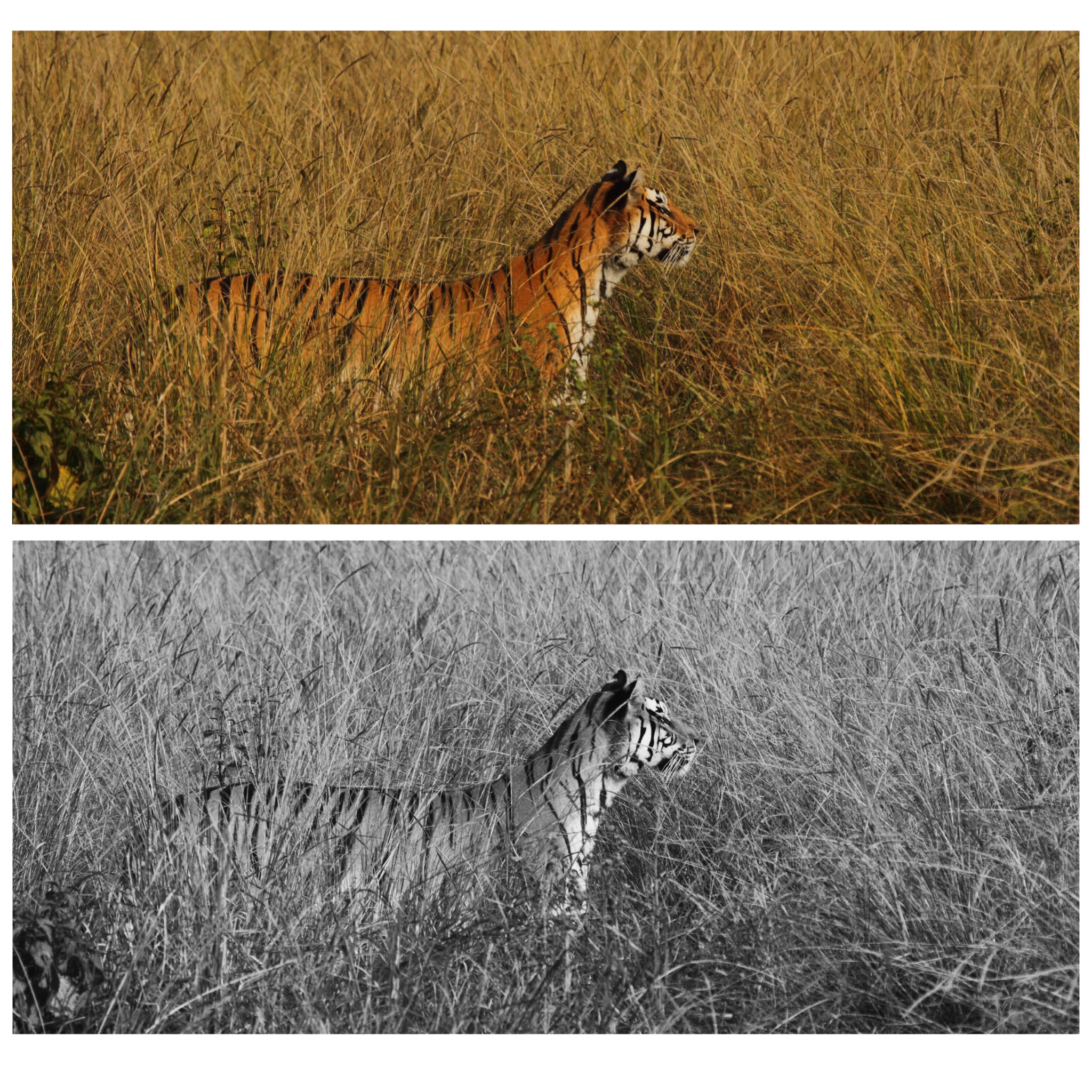
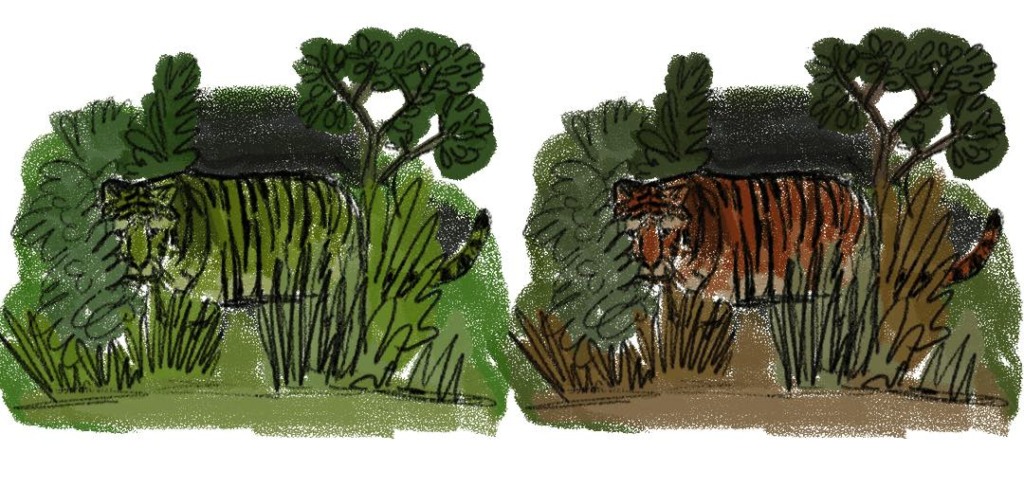
The study simulating what colours preys of the tiger see when looking at the predator found that animals like deers are essentially red. What color do prey see tigers? Tigers appear orange to humans because most of us are trichromatic (or sensitive to all three primary colors). But boars, deer, and other tiger prey are dichromatic and only pick up green and blue light.

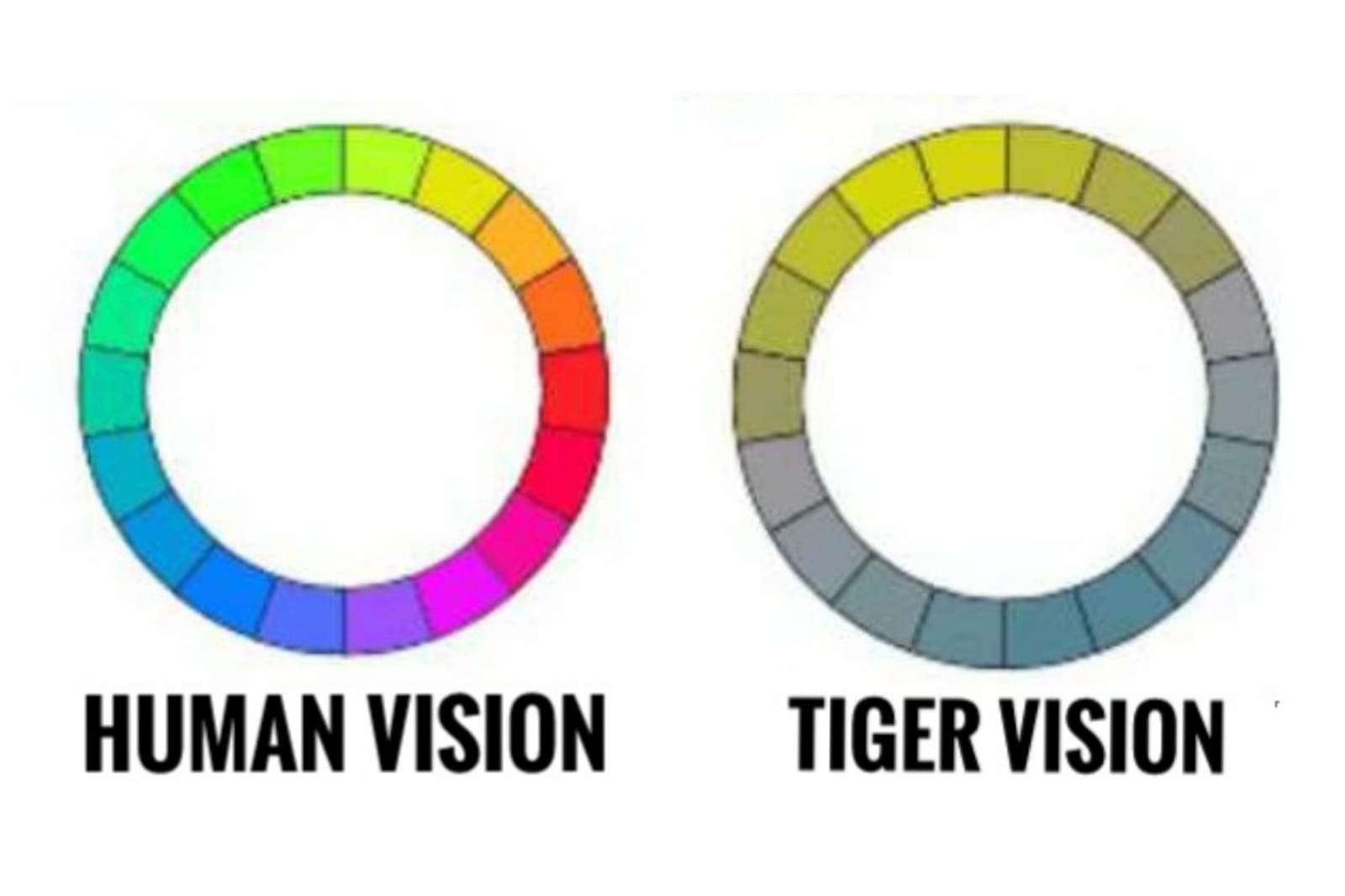
But how can this be? Many Mammals Only See Two Colors Most mammals - and tigers themselves - perceive fewer colors than humans. We have three color receptors, also known as cones, in our retina. These enable us to perceive the colors blue, green, and red.

Tiger Imgur | Wall Control
Most mammals only have two types of cones. This is also known as dichromatic vision. Do tigers lack color vision? No, tigers do not lack color vision.

Tigers have a dichromatic vision, which allows them to see mixtures of two colors. Tigers can perceive different shades of color because they have two cones in each eye, a condition known as dichromatic vision. Tiger eyes have large lenses and pupils that increase the amount of light let into the eye.
Tigers' Bright Orange Color Is Actually Excellent Camouflage and Now We ...
This characteristic helps the tiger with night vision and when there are low light levels available. Research suggests that cats in general are capable of seeing the colors green, blue and possibly red, just in less saturation or strength than we see them. This mechanism enables tigers to see in much dimmer light than humans, requiring approximately six times less light to see than humans do.

The retina of a tiger's eye contains a concentration of rod cells, which are sensitive to low light and movement. The Science of Tiger Vision To understand what colors tigers can see, we need to look at the structure of their eyes and the way they process visual information. The human eye has three types of cones that are sensitive to different parts of the visual spectrum, allowing us to see a wide range of colors.

Tiger's Limited Color Vision It is a common misconception that tigers lack the ability to see colors at all. In reality, they are capable of seeing shades of blue and green, but with significantly less clarity than humans.






