Sheep Urine Color
Bloody urine is classified in farm animals as hematuria, hemoglobinuria, and myoglobinuria. In small ruminants, discolored urine is reported due to several etiologies which is sometimes fatal. Of these causes are babesiosis, bacillary.
Urine normally contains very low quantities of protein, and urine dipstick analysis normally shows no or only trace amounts. However, the normal alkaline urine of sheep and goats influences the protein reaction, leading to falsely elevated protein readings 14 of 1+ or 2+. A sheep at this point is anemic, with very pale mucous membranes and lethargic.
Vet 2300 lab procedures slides
The visible membranes rapidly yellow as jaundice (icterus) sets in throughout the body. At post mortem all the tissues of a CCP sheep are pale to dark yellow. The kidneys are very dark, and the urine a bloody color.
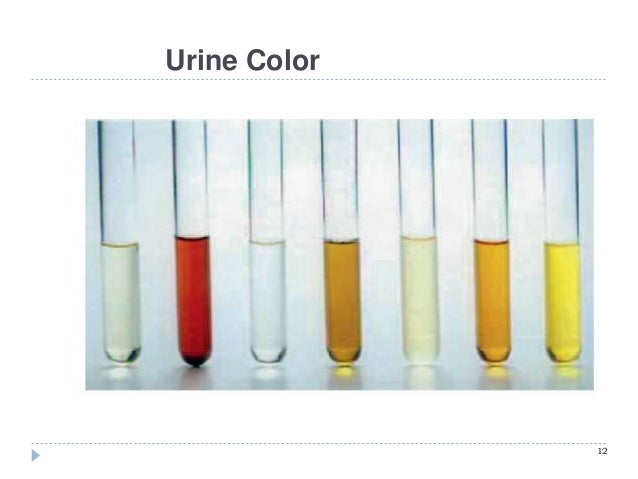
Urine "stones" may start as small crystals that you can detect by examining the end of the urethra. Observe each ram when he is urinating for normal posture, for free flow of the urine, and for urine color (pale to straw colored). Then the "Redwater" or haemolytic anaemia (red urine caused by the rupture of red blood cells) may be the sign of something more serious and it is important to work with your local veterinarian to obtain an accurate diagnosis and treatment.

Dark hemoglobin containing urine from a sheep with copper toxicity ...
Copper poisoning occurs primarily in sheep when they are fed a cattle or hog mineral or feed. A urinalysis is indicated for evaluating animals with urinary abnormalities such as increased urine production, increased urinary frequency, straining to urinate, bloody urine or abnormal color to the urine. This test can also be helpful in cases of unexplained fever, loss of appetite or weight loss.

Abstract This study conducted to evaluated 150 sheep urine sample [91 female (59) male] for the physical characteristi c (color, odor, and specific gravity). Other causes of discolored urine in sheep include bacillary hemoglobinuria caused by C. hemolyticum infection (Randhawa et al., 1995).
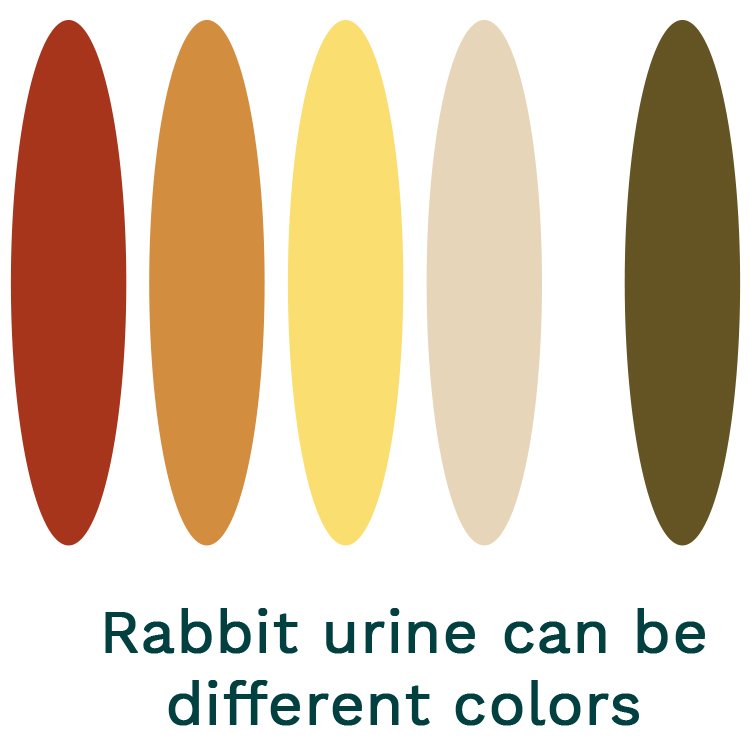
rabbit urine what pee tells you about a rabbits health pet bunny ...
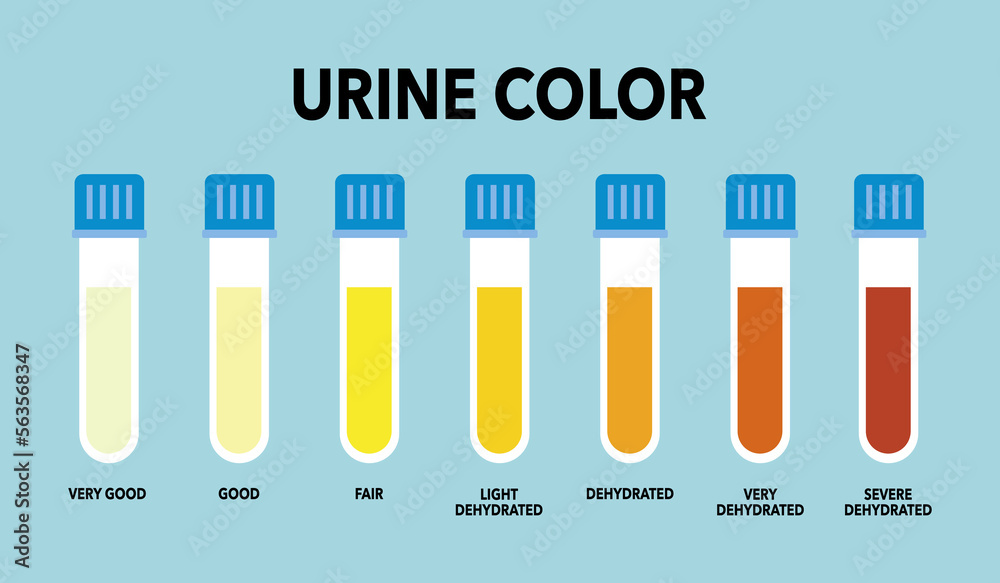
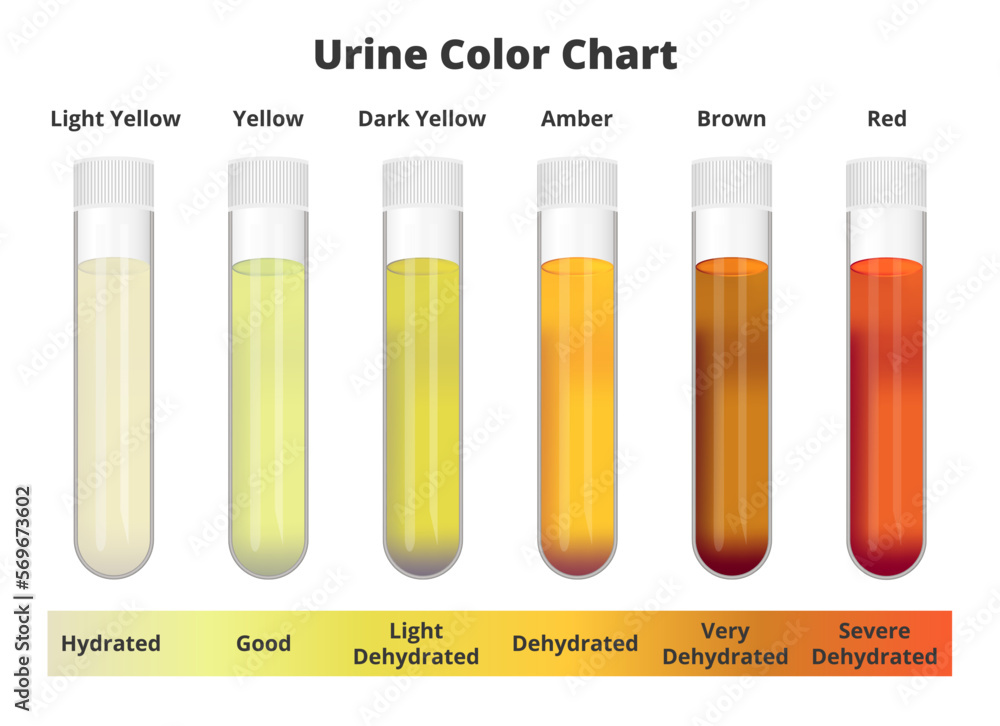
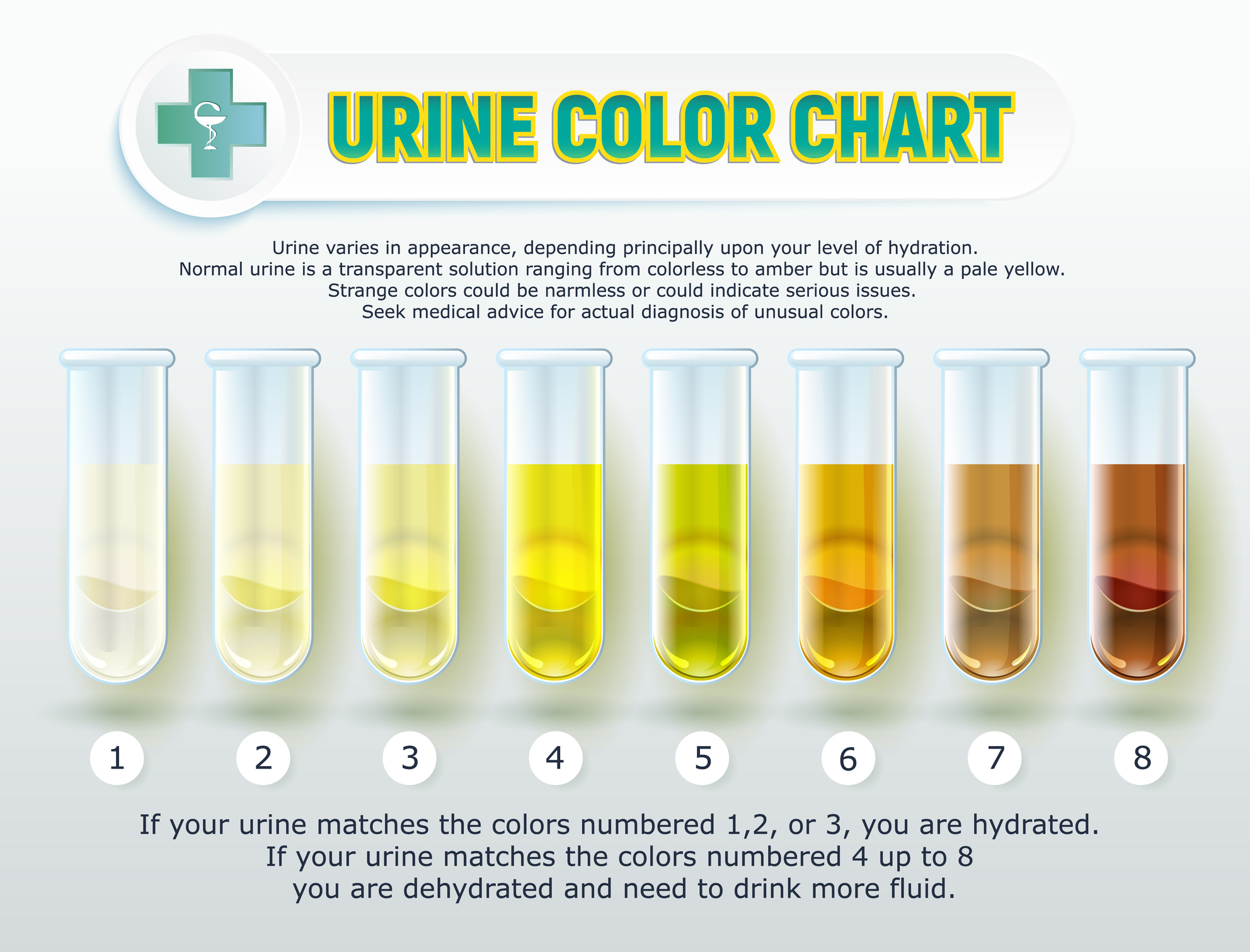
The disease in the later report was manifested clinically by elevated rectal temperature, constipation, hemoglobinuria, ataxia, and finally recumbency. Concentrated color in urine usually means dehydration. If it is super cold, are they drinking enough water? If your water barrels are too cold, they may not be drinking enough water.
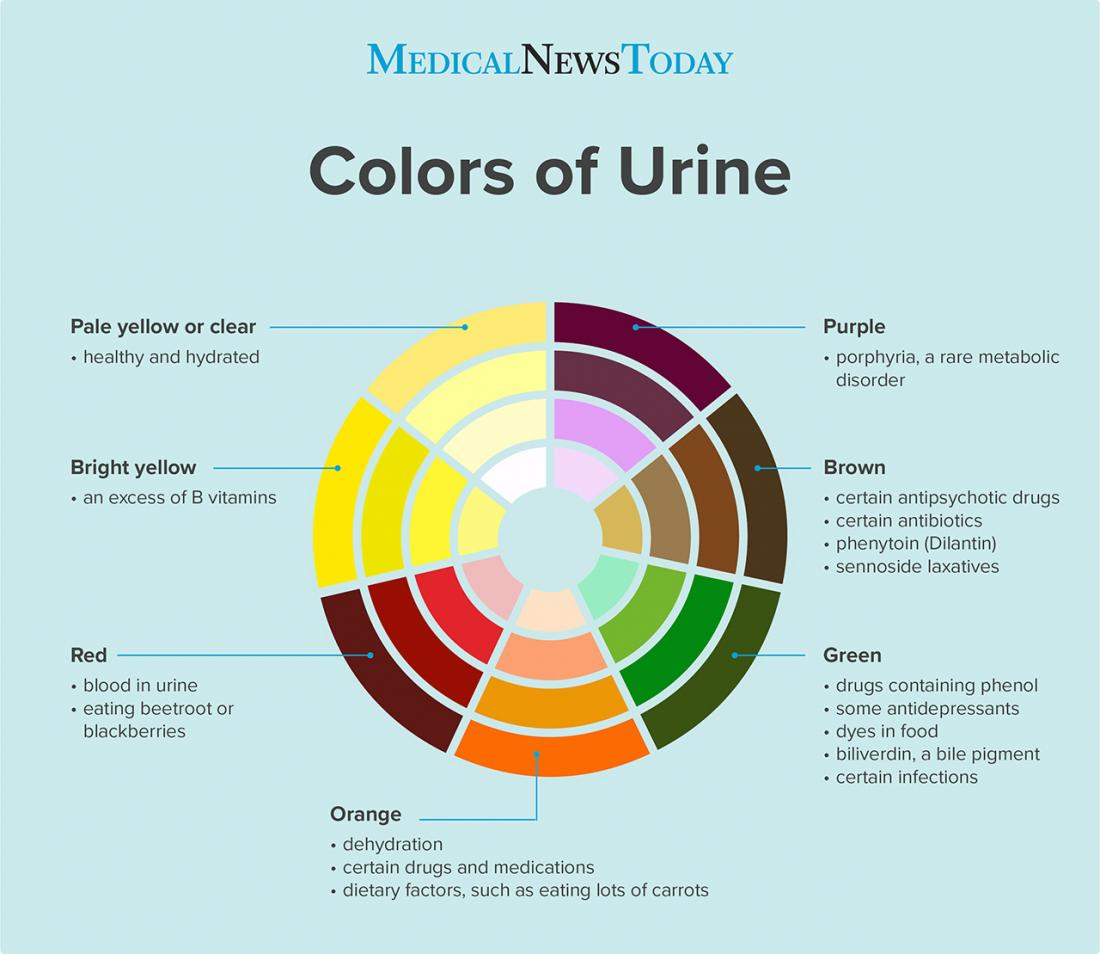
Super cold temps requre ivestock to drink more just like super hot temps. This is because in super cold temps livestock will often refuse to drink much icy water. Problem Definition and Recognition Urine normally appears as varying shades of yellow to amber.

The depth of color is related to urine volume. Dark urine does not necessarily mean concentrated urin.