Error Bar Graph
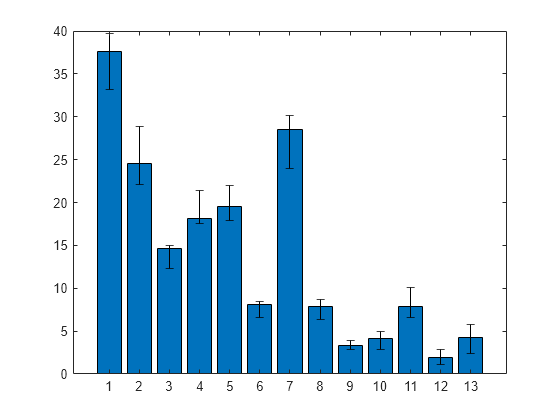
Error bar A bar chart with confidence intervals (shown as red lines) Error bars are graphical representations of the variability of data and used on graphs to indicate the error or uncertainty in a reported measurement. Learn what error bars are and how to interpret them on graphs. Error bars show the variation or spread of data around the mean and can indicate the reliability and significance of the results.
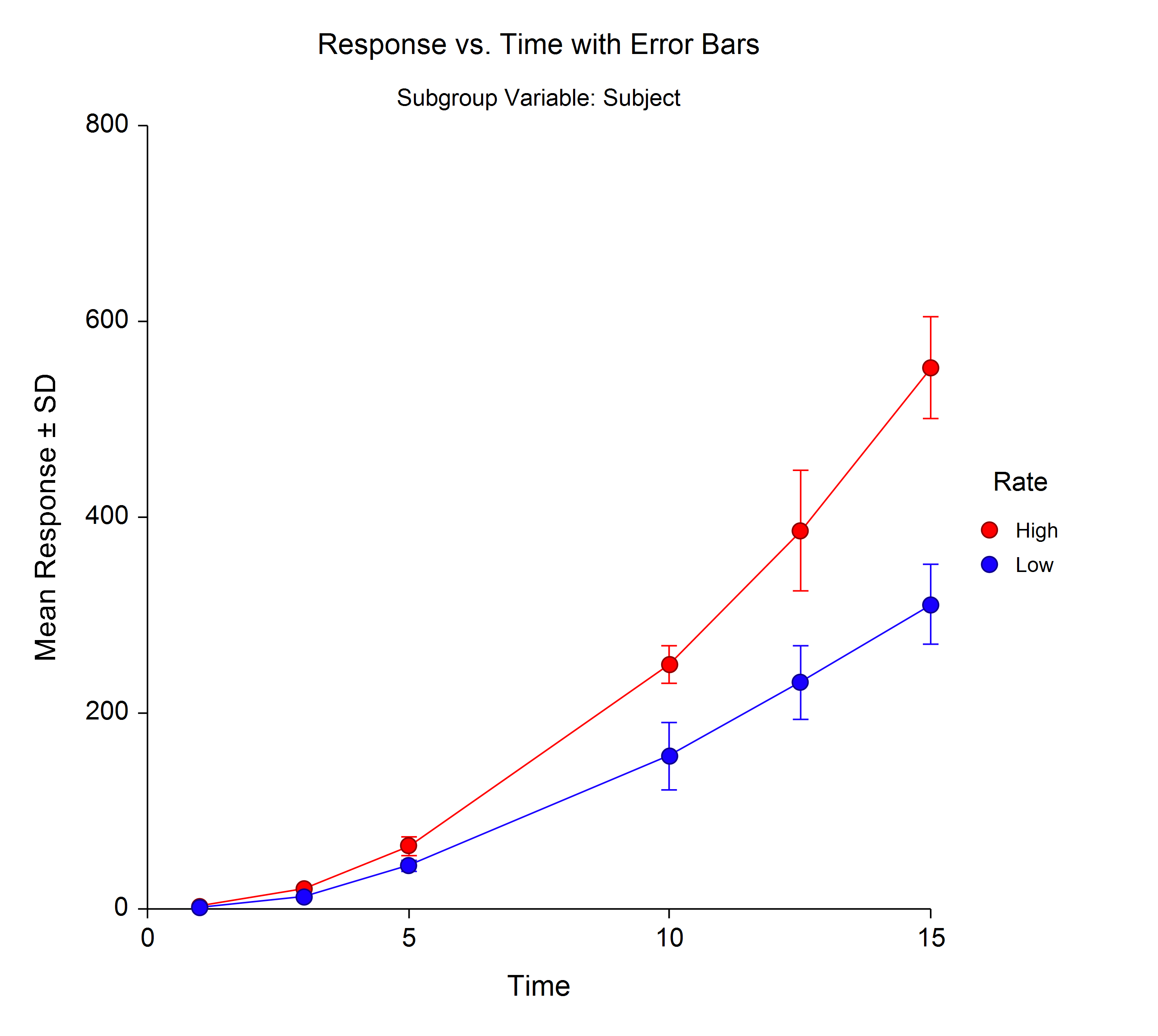
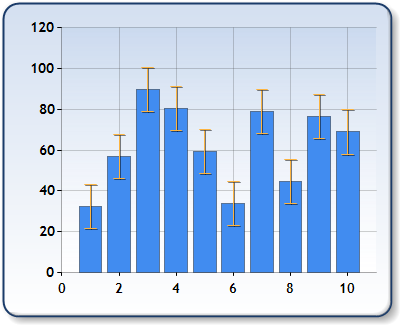
Learn how to use error bars in 2-D charts to show margins of error and standard deviations. Find out how to choose error bar options, set your own values, and review equations for calculating error amounts. Uncover how visual data representations convey variability and precision.

Bar chart with error bars
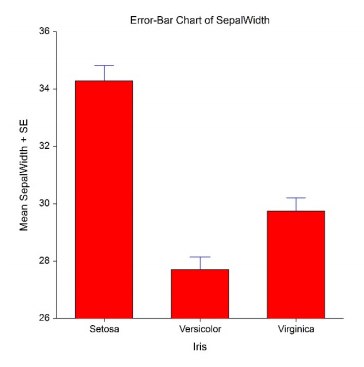
Learn to interpret the uncertainty in scientific graphs for accurate conclusions. The next graph shows the estimates and 95% confidence intervals but there is a problem of detection - it is not easy to read the values off the graph - as the confidence interval bars overlap. This problem has a simple solution (shown in the first graph) but it is not used as often as it should be.
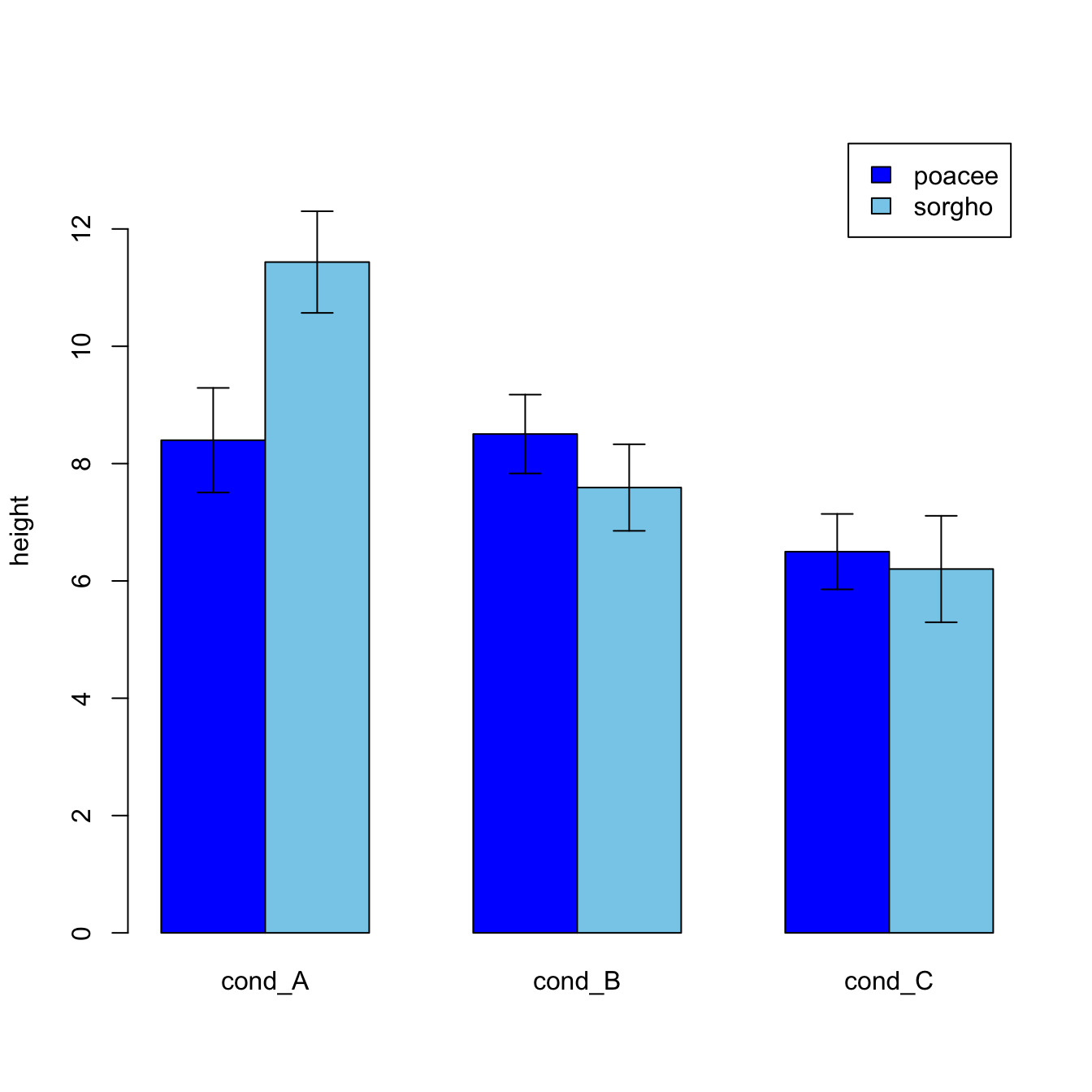
Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more. Statistics Definitions > What is an Error Bar? An error bar is a (usually T-shaped) bar on a graph that shows how much error is built in to the chart. Learn how to calculate error bars accurately using manual methods, statistical software, and Excel functions.
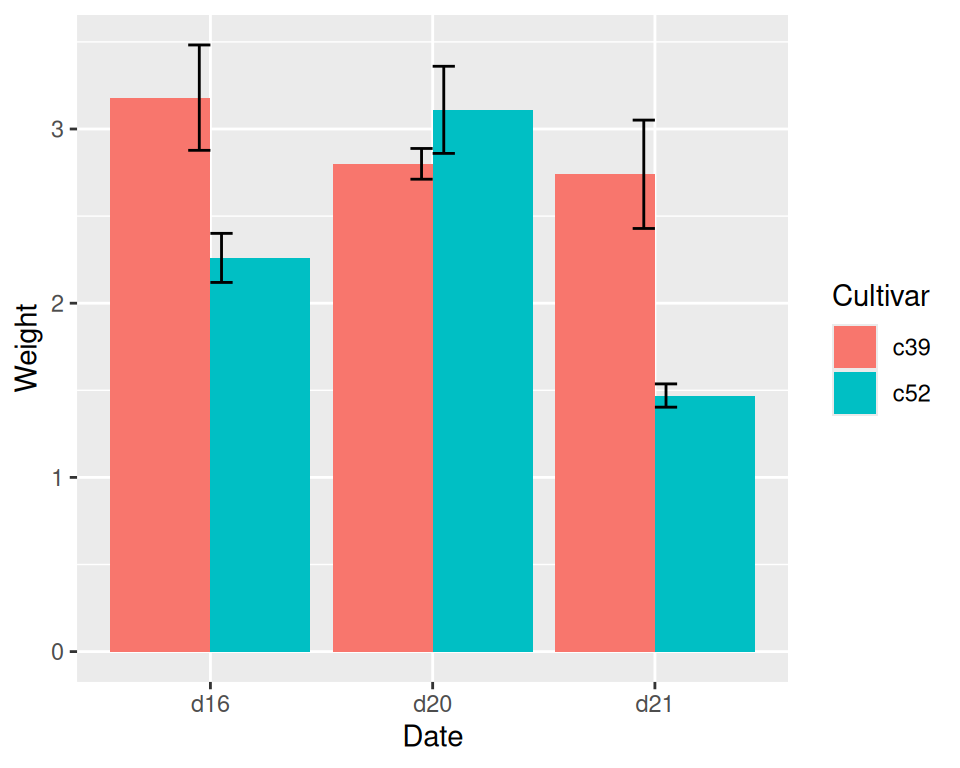
Error Bar Chart | Data visualization, Bar chart, Visualisation
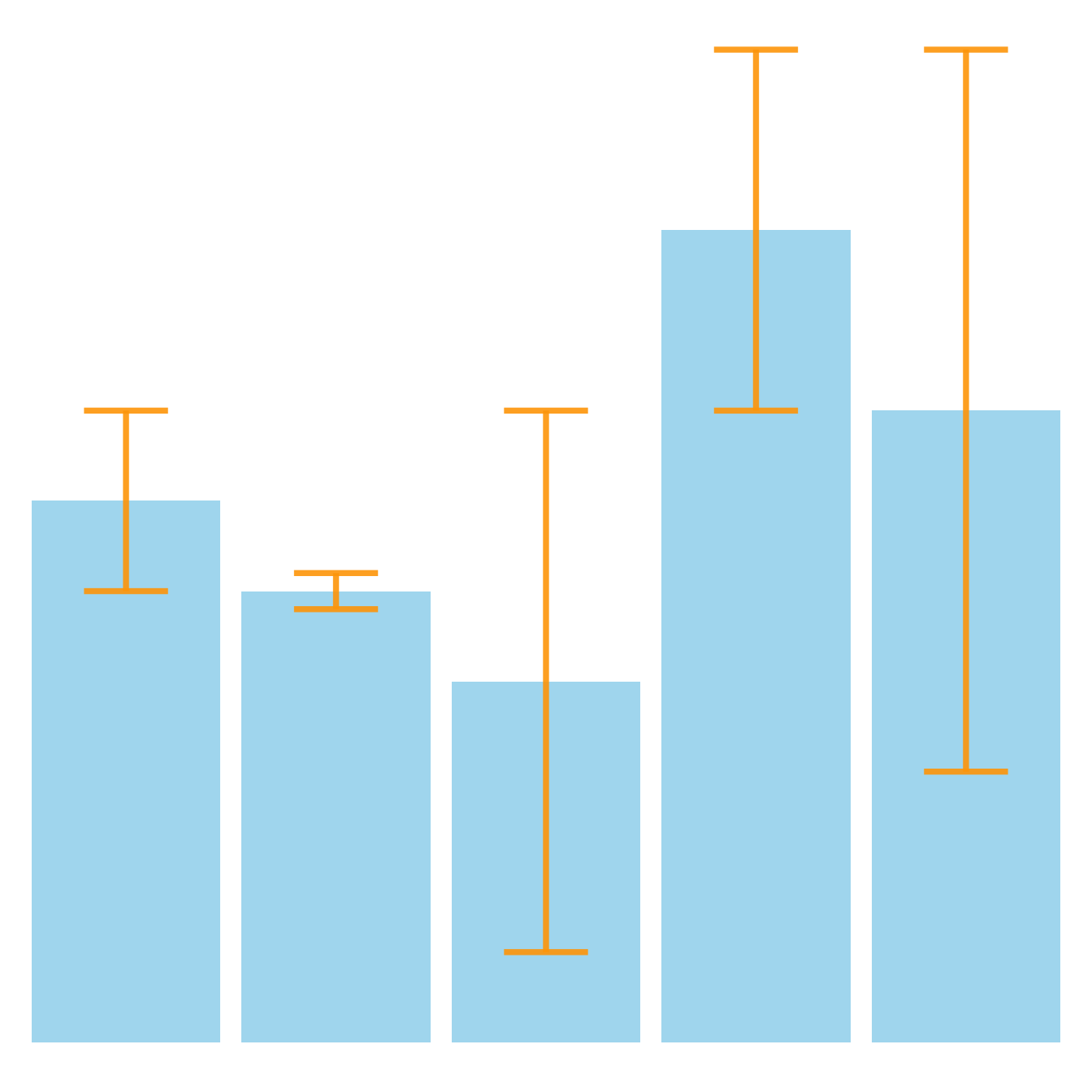
Understand the importance of error bars and how to. An error bar is a line through a point on a graph, parallel to one of the axes, which represents the uncertainty or variation of the corresponding coordinate of the point. Learn how to interpret error bars in graphs, which quantify the uncertainty and precision of data points.

Discover the types of error bars (standard deviation, standard error, confidence intervals) and how they affect statistical significance and data comparison.