Snowflake Number Types
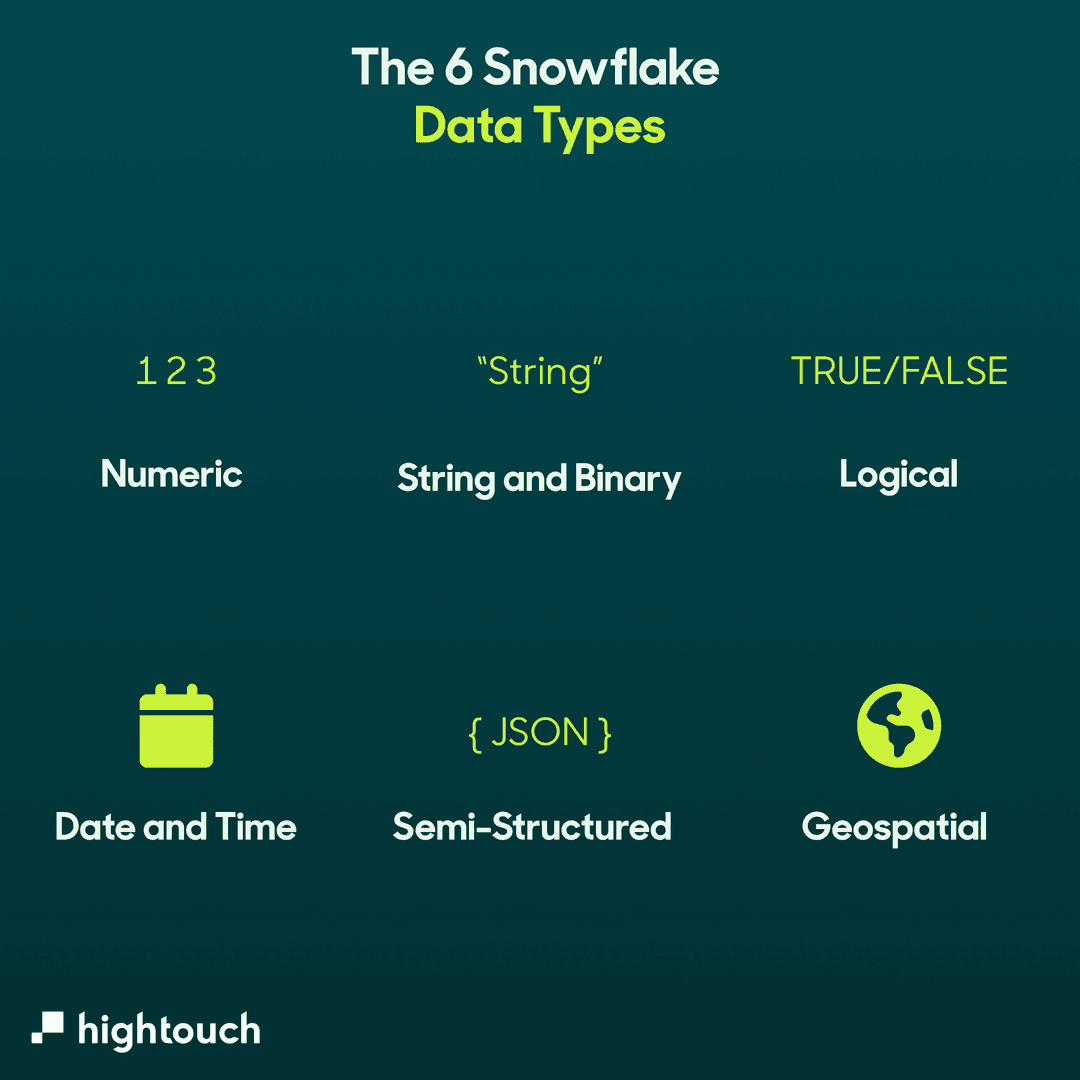
This topic describes the numeric data types supported in Snowflake, along with the supported formats for numeric constants/literals. Learn all 6 key Snowflake data types-from Numeric to Geospatial-and explore their unique characteristics, applications. This article provides an overview of the various data types supported by Snowflake, including numeric, string and binary, logical, date and time, semi-structured, and geospatial data types, as well as the mappings between SQL data types and handler languages used in stored procedures and UDFs.

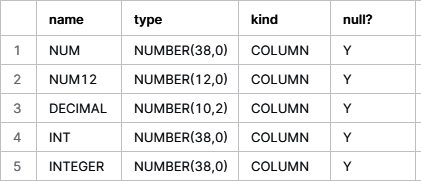
For the conversion of integer data types (INT, SMALLINT, BIGINT, TINYINT), each is converted to the alias in Snowflake with the same name. Each of those aliases is actually converted to NUMBER (38,0), a data type that is considerably larger than the integer datatype. Below is a comparison of the range of values that can be present in each data.

Guide to Snowflakes - SnowCrystals.com
Reference SQL data types reference Summary Summary of data types ¶ Snowflake supports most SQL data types. The following table provides a summary of the supported data types. Dive into the world of Snowflake data types.

Learn about numeric, string, logical, semi-structured, and geospatial data types. Discover how to check data types in Snowflake and the best practices for data modeling. This comprehensive guide is a must.

Numbers 0-20 on snowflakes (SB540) - SparkleBox Snowflake Images ...
Discover Snowflake data types with examples and best practices in this comprehensive guide. Snowflake provides a comprehensive set of data types, including numeric, string, binary, date and time, and Boolean data types, to accommodate various data formats and use cases. Master Snowflake data types with this comprehensive guide, covering key concepts, best practices, and optimization tips.

Understanding Data Types in Snowflake Snowflake supports a wide range of data types to handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Choosing the right data type is crucial for optimizing storage and performance. 1.
The different types of snowflakes and why they matter | wtol.com
Numeric Data Types Snowflake offers several numeric types for storing integer and decimal values: INTEGER: Stores whole numbers. Example: 123 NUMBER (NUMERIC.