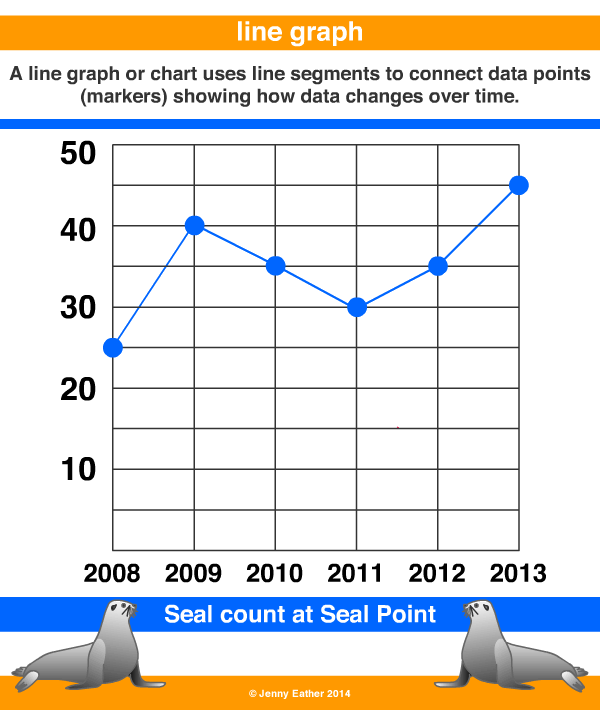
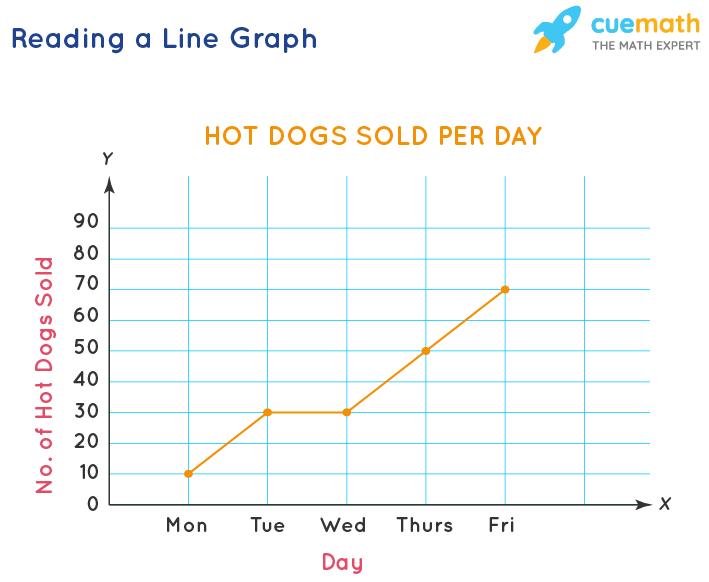
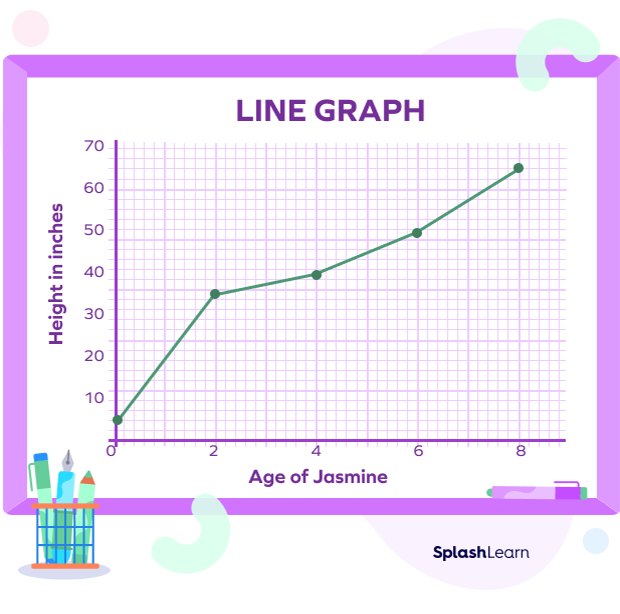
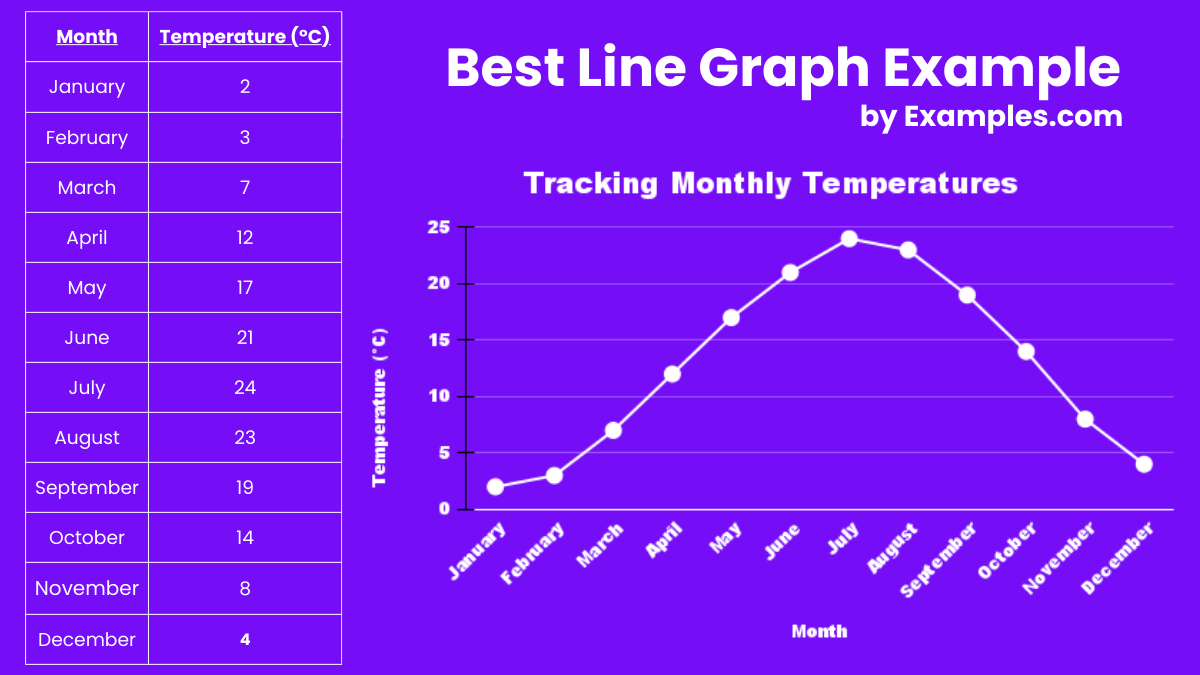
Line Graph Definition And Example
A line graph, also known as a line chart or a line plot, is commonly drawn to show information that changes over time. Learn about its types, contruction, and more! A line graph connects individual data points that reflect numerical values. It is used to visualize the relationship between dependent and independent variables.
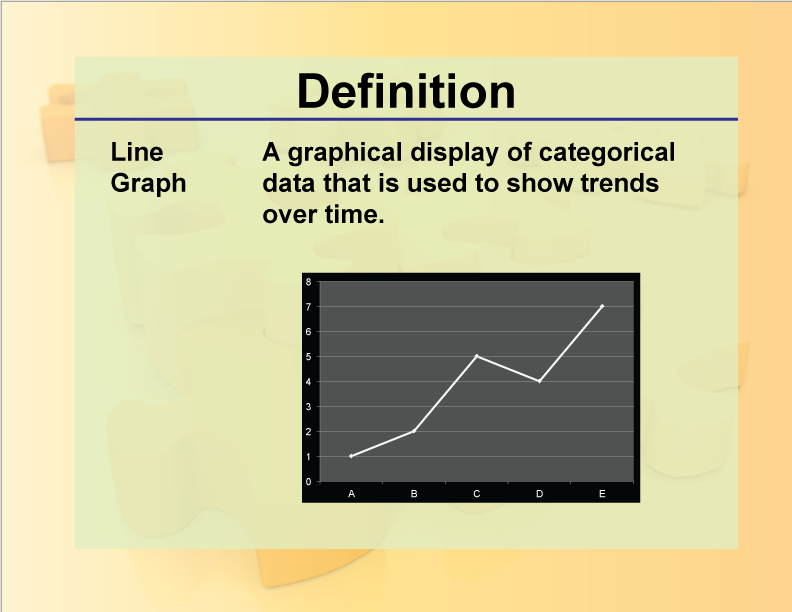
Line graphs are used to represent quantitative data collected over a specific subject and a specific time interval. All the data points are connected by a line. Data points represent the observations that are collected on a survey or research.
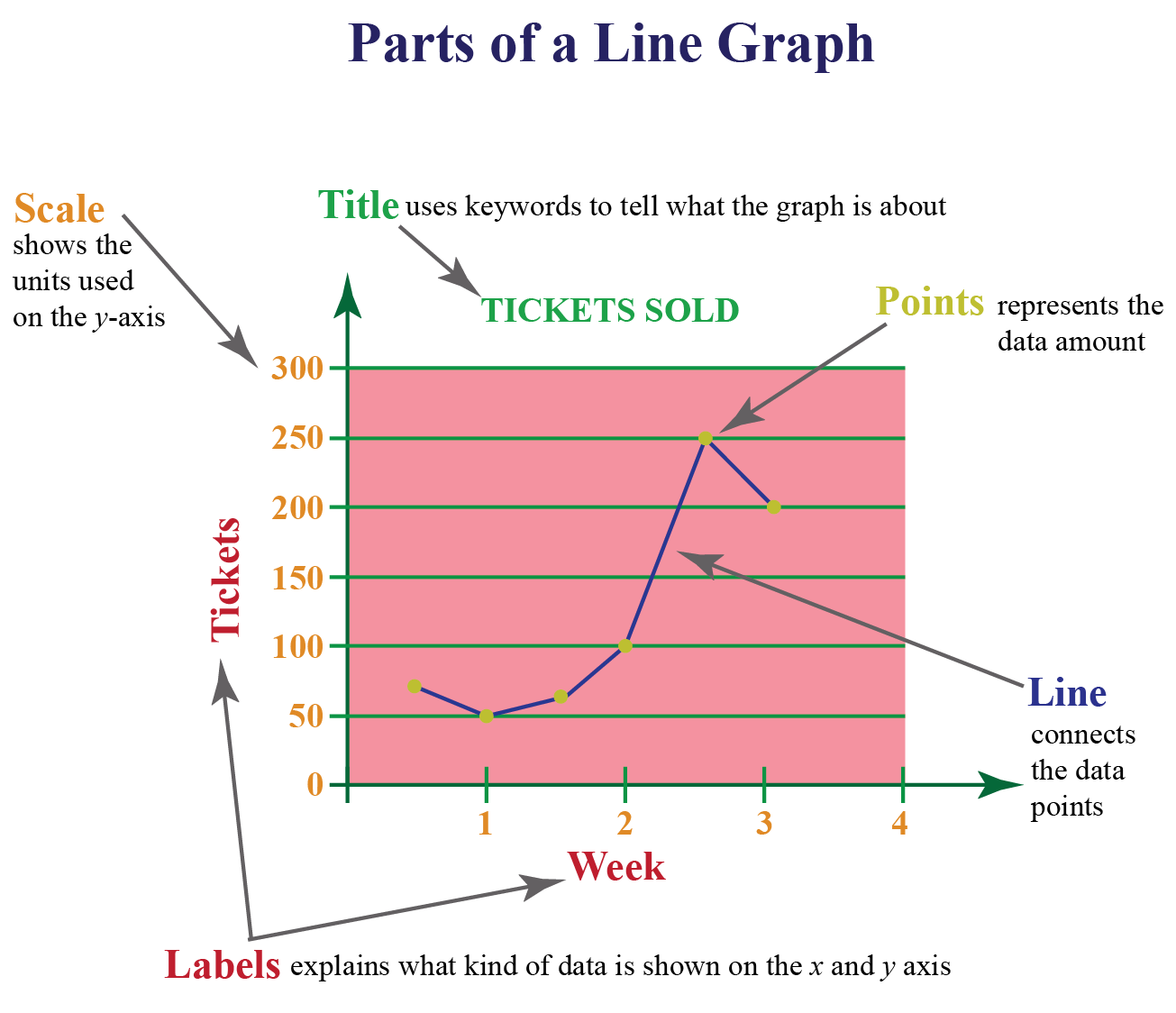
Line Graph - Examples, Reading & Creation, Advantages & Disadvantages
Learn about a line graph, its parts, reading and creating them, advantages and disadvantages along with solved examples. Line graph also known as a line chart or line plot is a tool used for data visualization. It is a type of graph that represents the data in a pictorial form which makes the raw data more easily understandable.
In a line graph data points are connected with a straight-line and data points are represented either with points or wedges. Some other examples of graphs are bar graphs, histograms. Learn about line graphs, their definition, and how to create and interpret them through practical examples.

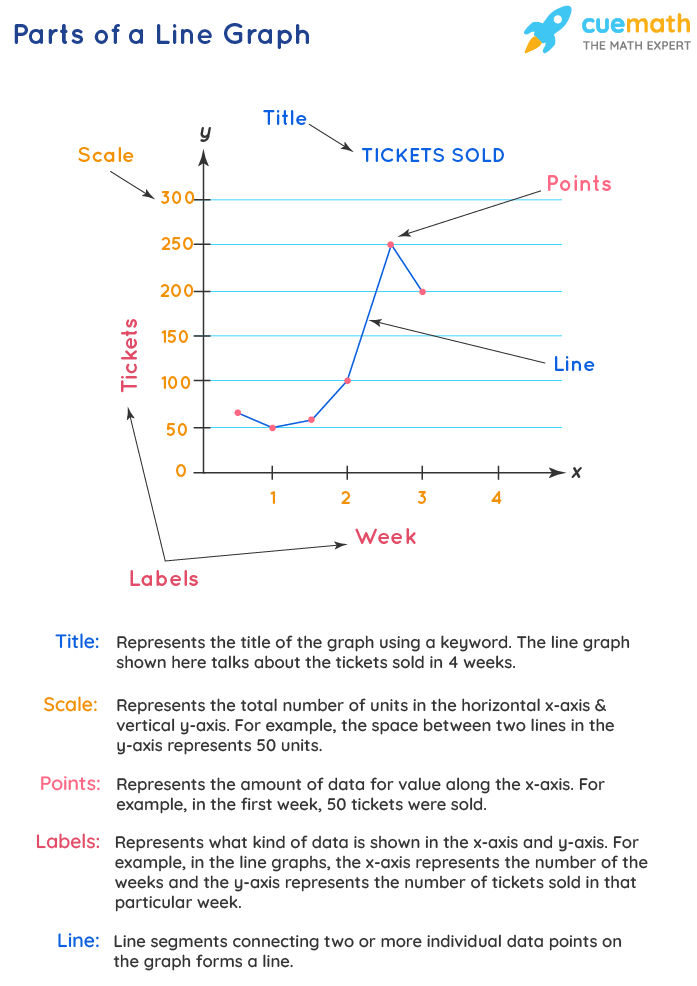
Line Graph - Examples, Reading & Creation, Advantages & Disadvantages
Discover three main types of line graphs and understand how they visually represent data changes over time. Line Graphs - Definition, Examples, Types, Uses A line graph is a unique graph which is commonly used in statistics. This detailed guide is crafted with educators in mind, aiming to bolster their instructional arsenal with lucid and captivating examples.
Perfectly suited for demystifying intricate datasets for students, it simplifies the core principles of line graphs in plain English. Free line graph math topic guide, including step-by-step examples, free practice questions, teaching tips and more! The word "graph" comes from Greek, meaning "writing," as with words like autograph and polygraph. A line graph uses a grid of intersecting perpendicular lines formed by an x -axis and a y -axis, over which you show changes over time, using a line.
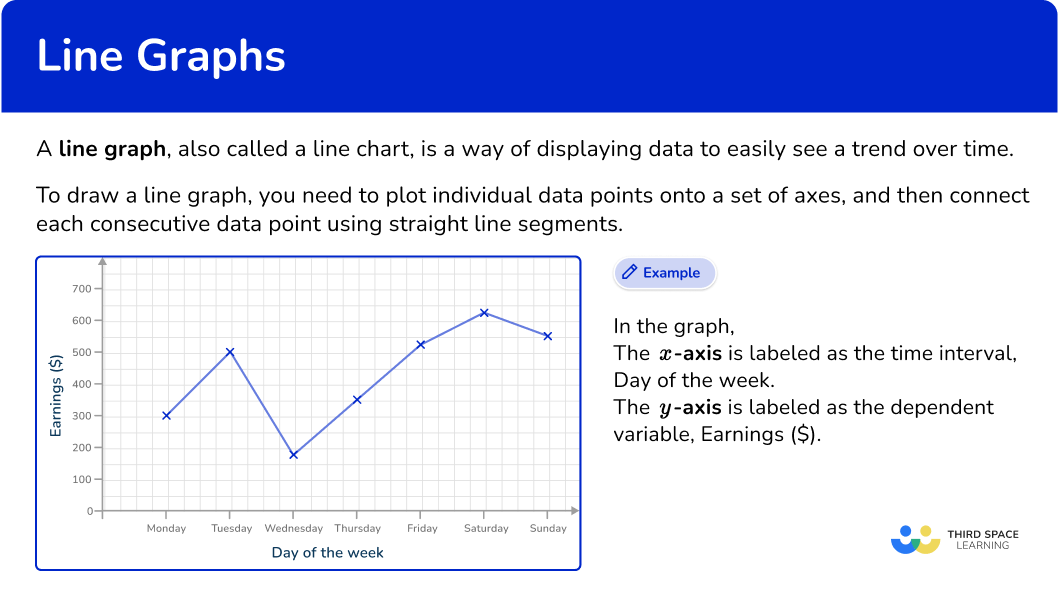
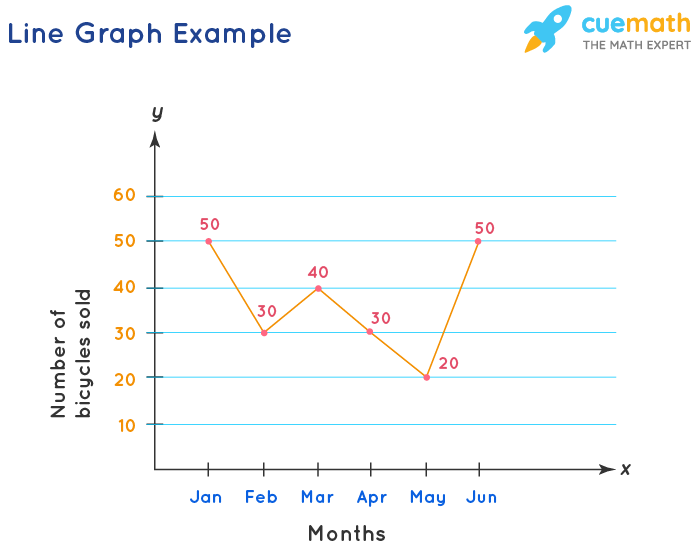
Line Graphs - Definition, Examples, Types, Uses
The most important feature setting a line graph apart from, say, a bar chart is the graphical way it shows the passage of time. The grid can be. Line graphs are good at showing specific data values, meaning that if you have one variable (x) you can easily find the other (y).
You want to show trends. For example, how your investments change over time or how food prices have increased over time. You want to make predictions.
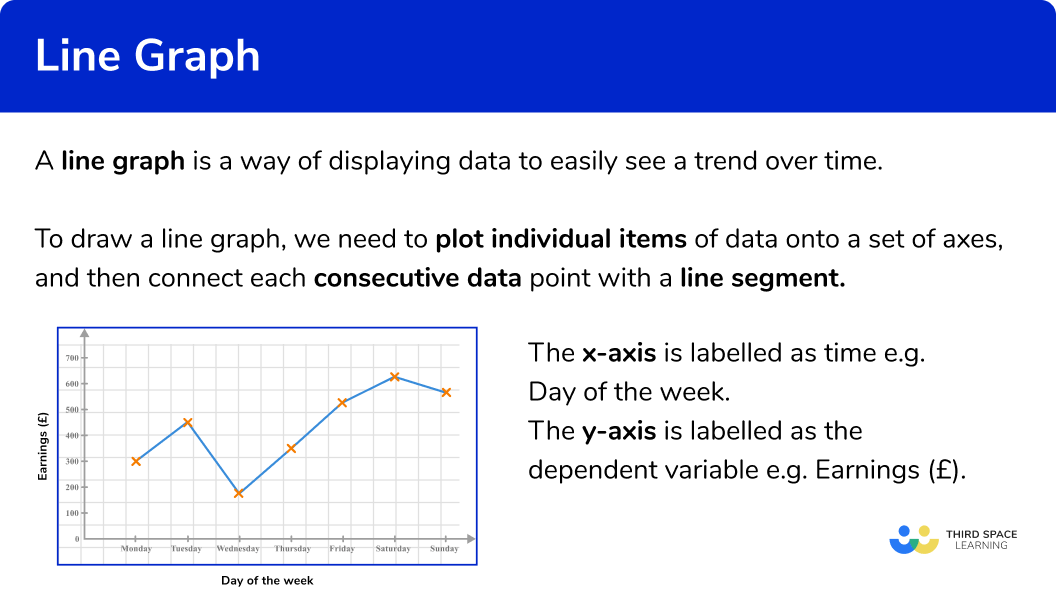
A line graph can be extrapolated beyond the data at hand. A line graph is a plot of data points that are connected with a line. The points are plotted on a coordinate plane and located using the x and y.