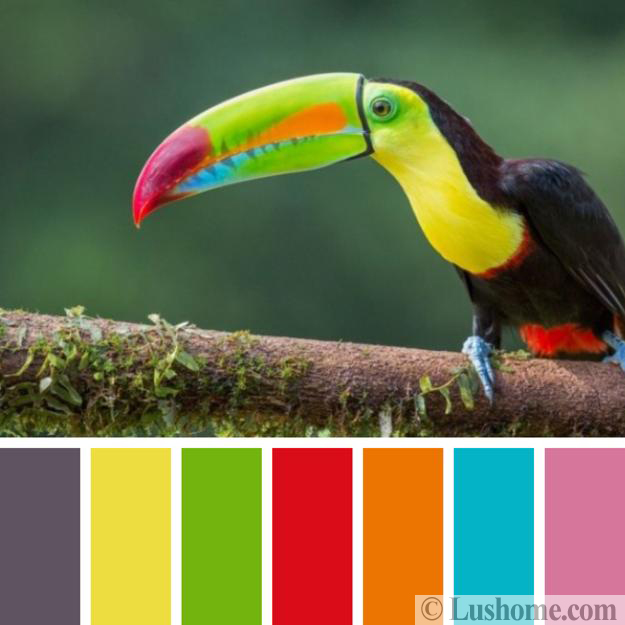
Bird Color Range
Bird colors exhibit a remarkable range, influenced by both biological and environmental factors. These colors play essential roles in communication, camouflage, and mate selection. But why do birds come in different colors and species? This article delves into the fascinating world of avian coloration, exploring the reasons behind the diversity of bird colors and species.

Birds have evolved their colors through a combination of genetic factors and natural selection. Birds have unique vision abilities that allow them to see a wider range of colors than humans, including ultraviolet light. This ability is crucial for their survival as it affects their mate selection and foraging behaviors.
A Small Guide to Bird Colours by Eurwentala on DeviantArt
By studying these color preferences, we can understand how the environment and biological traits influence bird interactions. These insights can also reveal important. Birds have excellent color vision compared to humans.

Their retinas contain four types of cone cells that allow them to see ultraviolet light in addition to the red, green, and blue light that humans can see. This gives birds a richer visual experience and allows them to distinguish colors that humans cannot. Understanding what colors birds see best can provide insights into how they find food.

Unveiling the World of Avian Vision: How Birds See Color?
When selecting bird feeders, red is a good choice for attracting hummingbirds, while orange feeders draw orioles, and yellow feeders appeal to goldfinches. For a broader range of garden birds, green and silver feeders are favored. Avoid artificial red dyes in hummingbird nectar, as they can be harmful.

Bird species colors range from subtle browns in sparrows to vibrant reds in cardinals. Your eye naturally catches these plumage types first, making color your gateway to successful bird identification before considering size or behavior. Birds change into abnormal colors regularly when the pigmentation level is higher or lower than the usual range.
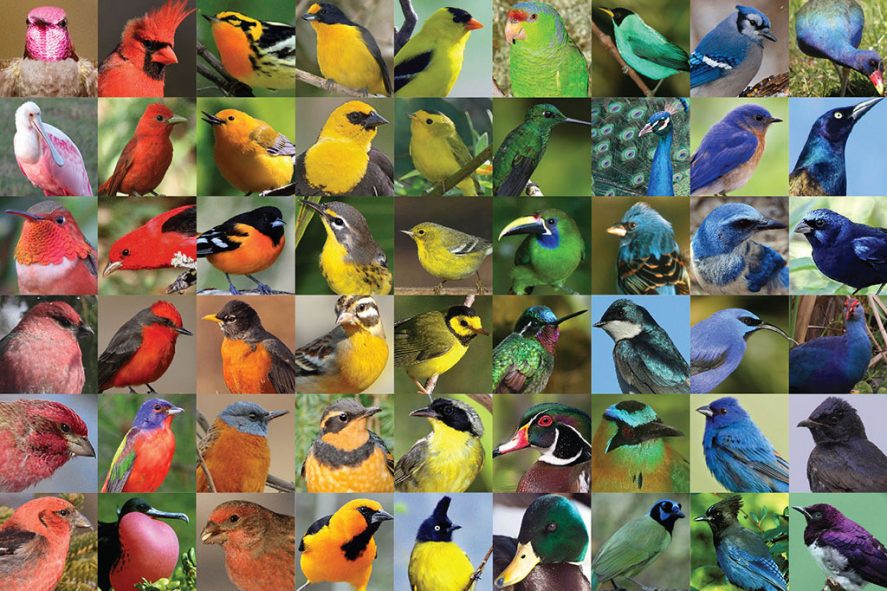

Getting a bird's eye view - Curious
The avian species like American crow, Common grackle, House sparrow, and Canada gooses show aberrant white patches. Overview Birds are one of the most colorful groups of animals on the planet, with over 10,000 different species exhibiting an astonishing range of colors and patterns. From the iridescent blues and greens of peacocks and hummingbirds to the subtle browns and tans of sparrows and finches, the colors of birds play a crucial role in their survival and success.
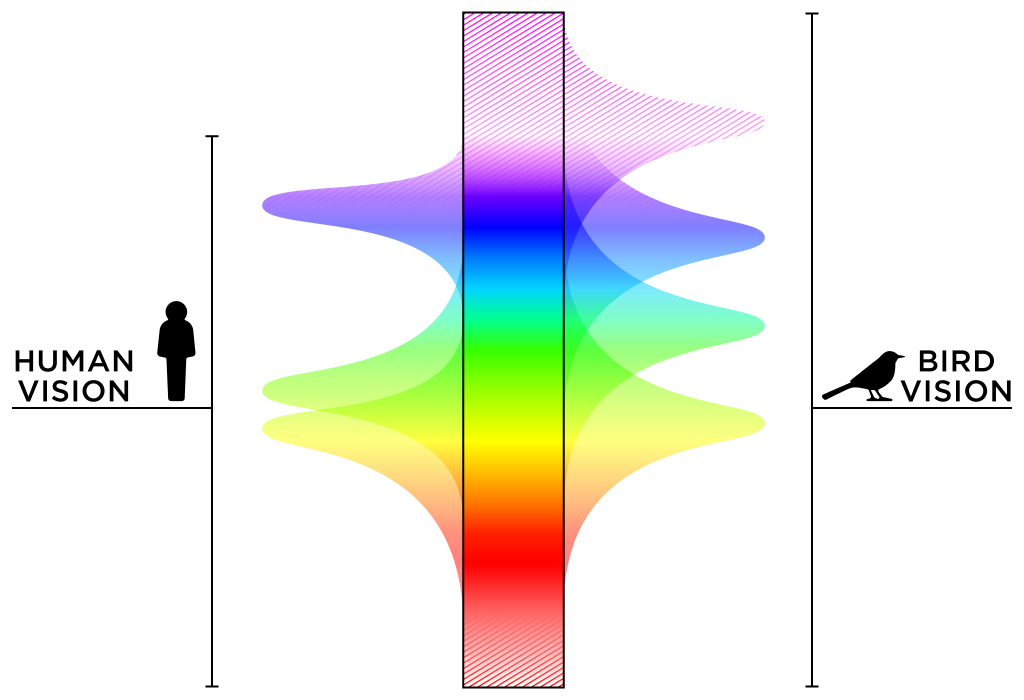
In this exploration of "What Color. Birds have an extensive range of color vision that differs from humans. They can see ultraviolet (UV) light which helps them detect food sources, navigate long distances and identify conspecifics more easily than we do.

Many bird species' feather structures reflect light in the ultraviolet range, giving them the ability to perceive a wider range of colors than humans. The most spectacular feather pigmentation in birds typically serves to impress members of the same species.