Heart Colour Without Blood
The human heart is often depicted as a vibrant, deep red organ. However, this popular image can be misleading, as the heart's true color is revealed when it is deprived of blood. This article explores the heart's intrinsic color, why blood makes it red, and how various conditions can alter its hue.

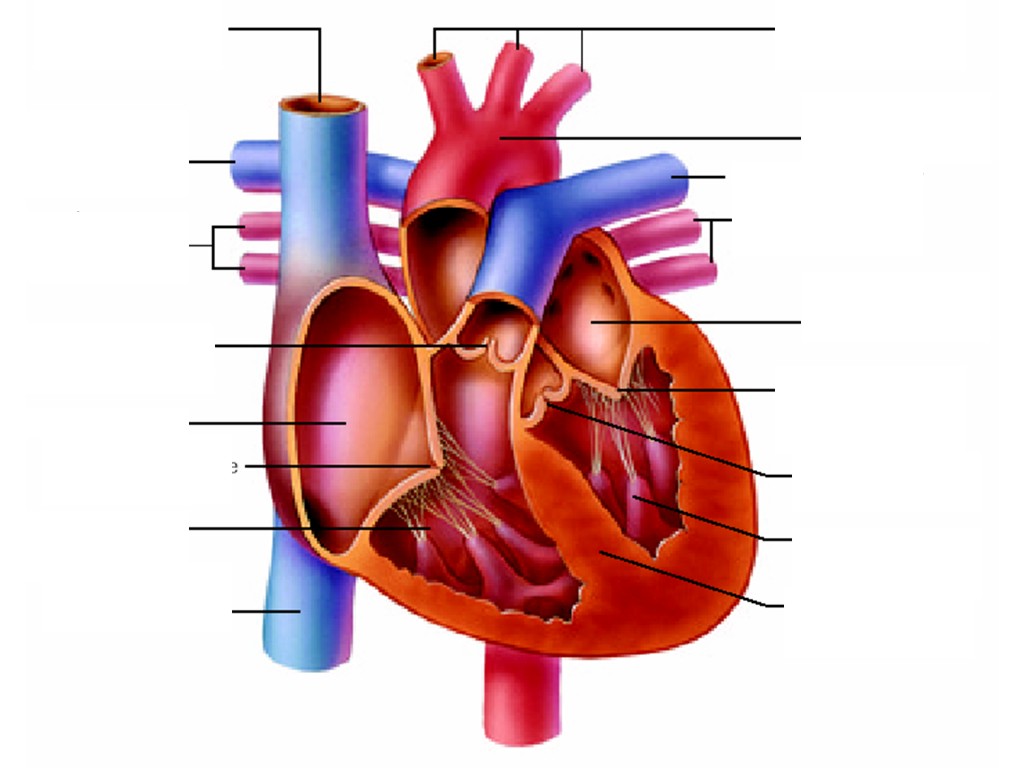
The Heart's Intrinsic Color Without the presence of blood, the human heart typically. Without blood, the true color of the heart muscle and tissues is revealed. This color results from the intrinsic coloration of the cardiac cells themselves without the red of blood obscuring it.

What is the color of the heart without blood?
The human heart is a complex organ that serves as the center of the cardiovascular system. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body via a vast network of blood vessels. But what happens when you remove the blood from this vital organ? What color does the heart become without the red oxygenated blood flowing through it? In this article, we will examine the anatomy of the heart.

In summary, a heart without blood appears pinkish-beige in color. This is because the absence of blood causes the myocardium to appear pale, rather than the vibrant red color it exhibits when full of blood. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.

What Color is Your Blood? - YouTube
Without blood, the heart appears pale or light pink in color. This is because the color of the heart is mainly attributed to the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood present within its chambers and vessels. Oxygenated blood appears bright red due to its interaction with oxygen, while deoxygenated blood is darker in color.

The in-question ghost heart was described in a 2019 blog published by the Texas Heart Institute, for whom Taylor was a researcher, as being "void of color, drained of blood and cells," and with. How does your heart look without blood? This skeletal tissue, when drained of blood, is white and is what gives a "ghost heart" its name. By removing the blood vessels, she also removed the antigens that the organ recipient's body might reject.

Human Heart Color
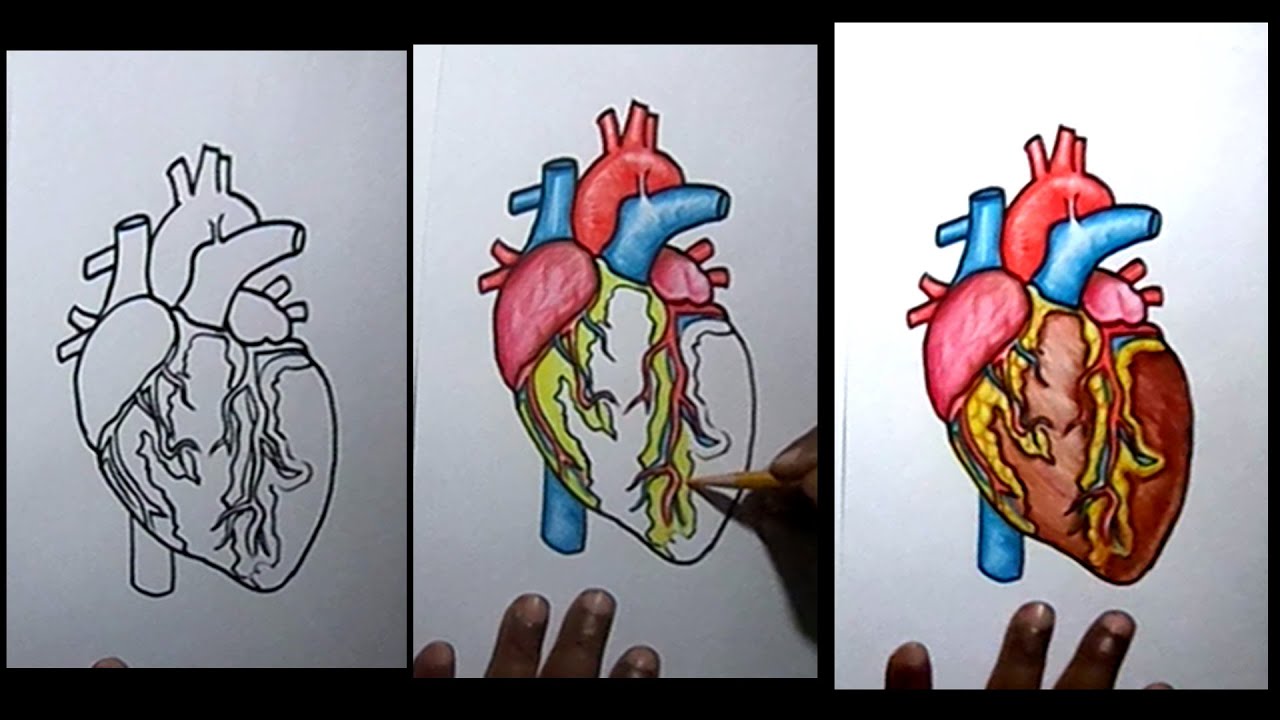
However, there is another problem: a heart cannot function without cells. The real human heart is generally a deep red, reddish-brown color. This is due to the muscle tissue, blood vessels, and connective tissues that often form the organ's visible surface.

The color of a healthy heart may range from a bright, dark red to a dark brown, depending on the age, sex, and race of the individual. What is the real color of the heart without blood? The heart will appear white if it has been drained of blood. The heart itself possesses a consistent, darker hue.
This appearance reflects its dense muscular composition and constant engagement with blood. Biological Basis of Color The characteristic dark reddish.