What Is It Called When Leaves Change Color In The Fall
Japanese maple autumn leaves Autumn leaf color is a phenomenon that affects the normally green leaves of many deciduous trees and shrubs by which they take on, during a few weeks in the autumn season, various shades of yellow, orange, red, purple, and brown. [1] The phenomenon is commonly called autumn colours[2] or autumn foliage[3] in British English and fall colors, [4] fall foliage, or. Brilliant Fall leaves on the Superior National Forest.

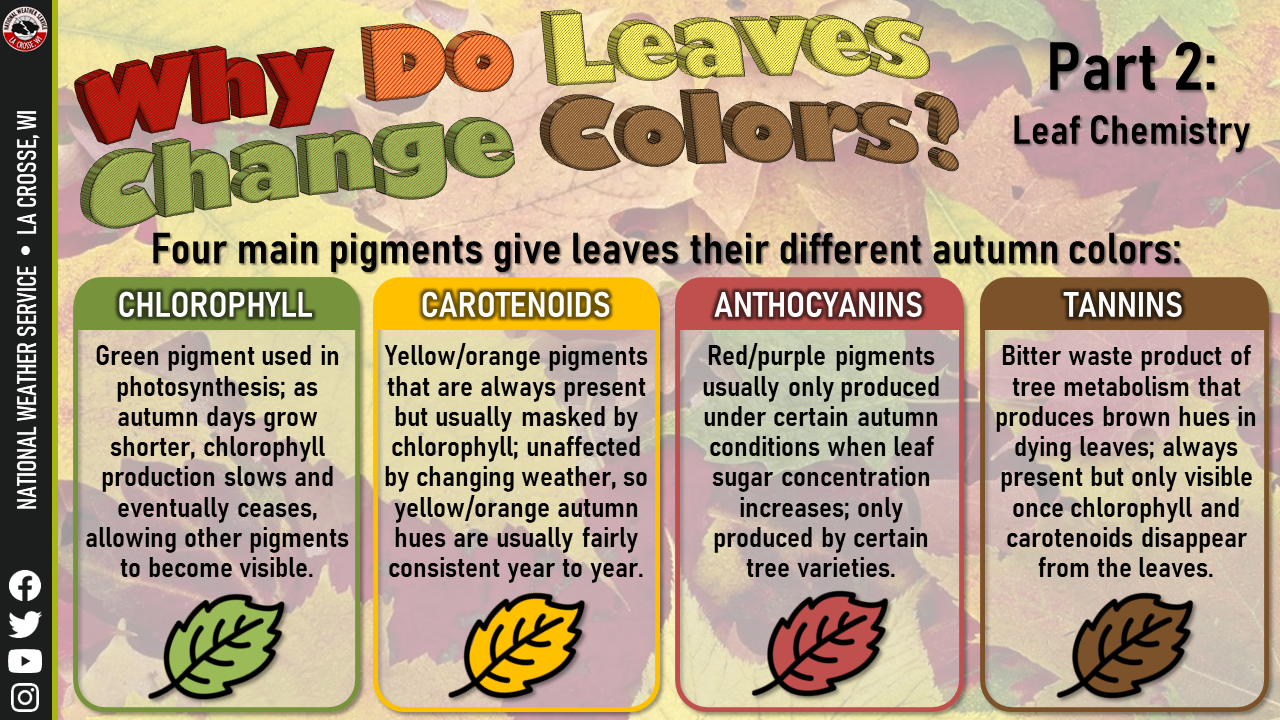
(Forest Service photo) Certain colors are characteristic of particular species: Oaks: red, brown, or russet Hickories: golden bronze Aspen and yellow-poplar: golden yellow Dogwood: purplish red Beech: light tan Sourwood and black tupelo: crimson The color of maples leaves differ species by species: Red maple: brilliant scarlet Sugar maple. Darker red leaves are the result of a chemical change: Sugars that can get trapped in the leaves produce new pigments (called anthocyanins) that weren't part of the leaf in the growing season. Some trees, like oaks and dogwoods, are likely to produce red leaves.

How Leaves Change Color In The Fall at tanzaynblog Blog
In other plants, pigments called anthocyanins accumulate in the leaves at this time, giving them shades of red and purple. Some of the most beautiful fall foliage features both types of pigments, often with one color giving way to the next as the season progresses. The weather plays a major role in the vibrancy and timing of the peak of fall foliage, but the process starts with a part of the leaf itself called the abscission layer.

Have you ever wondered how, or why the leaves on the trees start to change from green to all sorts of colors in the fall? And why do we call it "Fall Foliage"? "Foliage" is just a fancy term meaning plant, or leaves from a tree. We refer to the term "Fall Foliage" when referencing the changing of the leaves on the trees. Explore why leaves change color in fall, the role of sunlight and pigments, and top tips for spotting the brightest autumn foliage this season.

Why Do Leaves Change Color in the Fall? - O'Toole's Garden Centers
Carotenoids are present in the leaves throughout the growing season. Additionally, some trees produce pigments called anthocyanins, which create striking red, purple, and crimson colors. Anthocyanins are typically produced in the fall in response to bright light and accumulated sugars within the leaves.
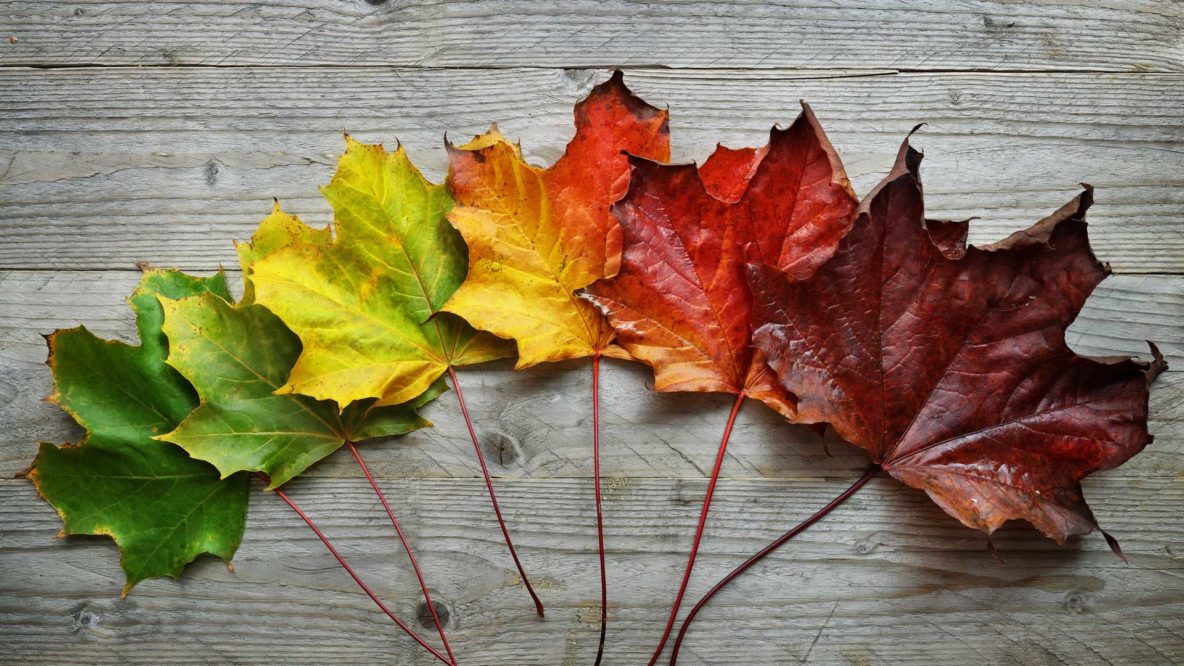

To recap, leaves change color because of hidden pigments, and different factors like sunlight and temperature affect how vibrant those colors become in the fall. Leaves change color during the autumn because the amounts of pigments change as the leaves prepare to fall from the trees. All leaves gradually lose chlorophyll during the growing season, and this loss accelerates before leaf fall.
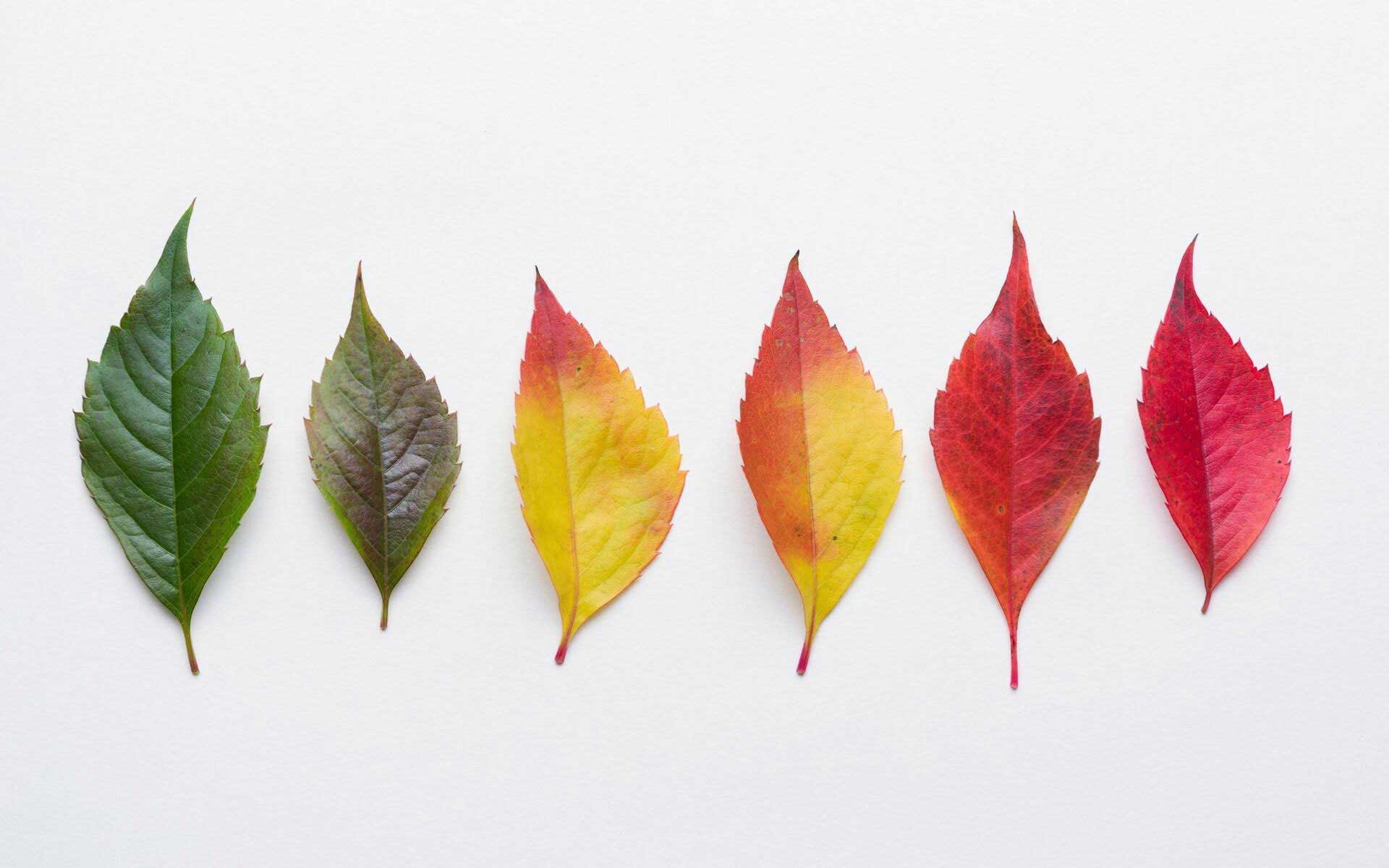


![Is Leaves Changing Color A Chemical Change? [Shocking Truth] Is Leaves Changing Color A Chemical Change? [Shocking Truth]](https://plantscraze.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Different-leaf-colors-1024x1024.png)
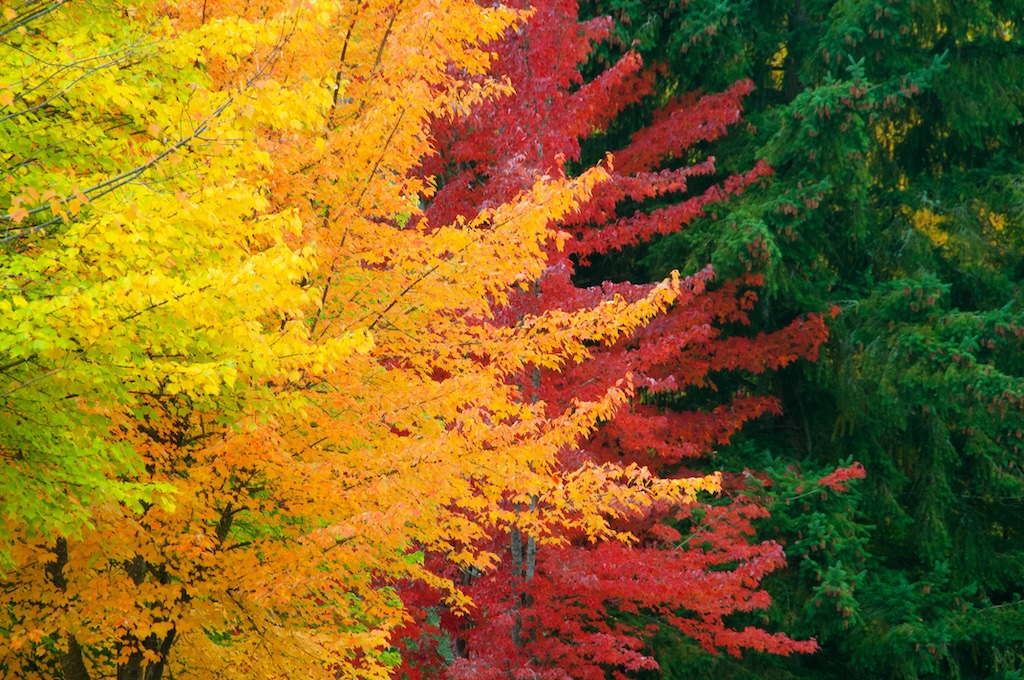





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/color-gradients-of-autumn-leaves-on-rustic-wooden-table-1221763874-d512677676604249af93204a8f53d2b1.jpg)