Jellyfish Eye Color
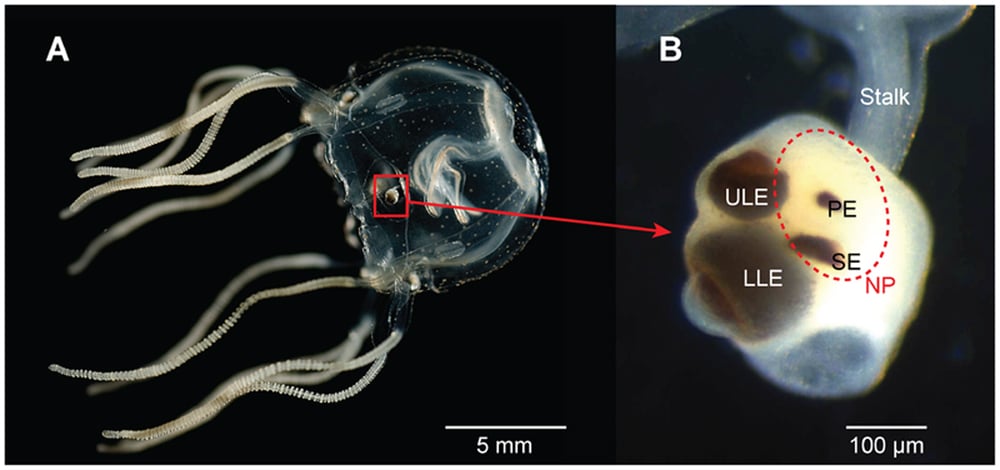
Scyphozoa (true jellyfish) and Cubozoa (box jellyfish) have a sensory structure called rhopalia that has neurons, gravity cells and light receptor (photoreceptor) cells. Eyes in these groups of jellyfish are found in the rhopalia. Their visual systems can be composed of simple eyes or even complex lens eyes, similar to humans.
11 Different Jellyfish Colors Jellyfish colors mainly come from their genes, what they eat, and where they live. Some jellyfish colors result from their pigment, while others come from bioluminescence. Let's discover the most common colors seen in different types of jellyfish and explore each one.

Premium AI Image | A blue eye with a jellyfish eye
1. Colorless. What colors do jellyfish see? Using electrophysiology, the spectral sensitivity curves of the lens eyes in Tripedalia and another box jellyfish had a peak at approximately 500 nm.

That means that these lens eyes sense blue. Understanding Jellyfish Vision Vision in the animal kingdom is remarkably diverse, ranging from simple light-dark detection to highly sophisticated color perception. For jellyfish, members of the phylum Cnidaria, their visual capabilities fall somewhere along this spectrum, primarily focused on sensing light.
Jellyfish eye genes suggest a common origin for animal eyes | National ...
Unlike vertebrates and many arthropods that possess complex camera. Do Jellyfish Have Eyes? When we think of eyes, it is natural to picture them as structures similar to our own, but the variety of eye and sight. Thus, it's another way that jellyfish eyes are resemble vertebrate eyes (camera eyes with bleaching pigments) more than most other invertebrate eyes (compound eyes with non-bleaching pigments).

A previous study had suggested that a box jellyfish might see colour, but that was a different species (Carybdea marsupialis). But did you know that these gelatinous jellies, including the moon jellyfish, immortal jellyfish, and lion's mane jellyfish, have a unique way of seeing the world around them with their lens eyes? Many species of jellies possess a form of visual perception through their lens eyes, allowing them to see and perceive color. Researchers have sequenced the genome of a unique species of jellyfish with 28 eyes to help us understand the wild evolution of vision.

Do Jellyfish Have Eyes? » ScienceABC
Introduction Do Jellyfish Change Colors: Jellyfish, those enigmatic and ethereal creatures of the ocean, have long captivated the imagination of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Beyond their graceful and often ghostly appearance, jellyfish bodies hold a fascinating secret: the ability to change colors. This remarkable phenomenon is a testament to the complexity and adaptability of.

Jellyfish don't have eyes, but they do have eyespots. A jellyfish's eyespot is a clear spot on the body that helps it sense light. Jellyfish are most comfortable in shallow water, where they can easily feel the movement of nearby fish and other animals.

Jellyfish also have small tentacles to catch small prey, such as plankton. Jellyfish don't need their eyes to see because they have no.






