Abc Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet (Hebrew: אָלֶף־בֵּית עִבְרִי, [a] Alefbet ivri), known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is a unicameral abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, Judeo-Arabic, and Judeo-Persian. In modern Hebrew, vowels are increasingly. Hebrew (and Yiddish) uses a different alphabet than English.

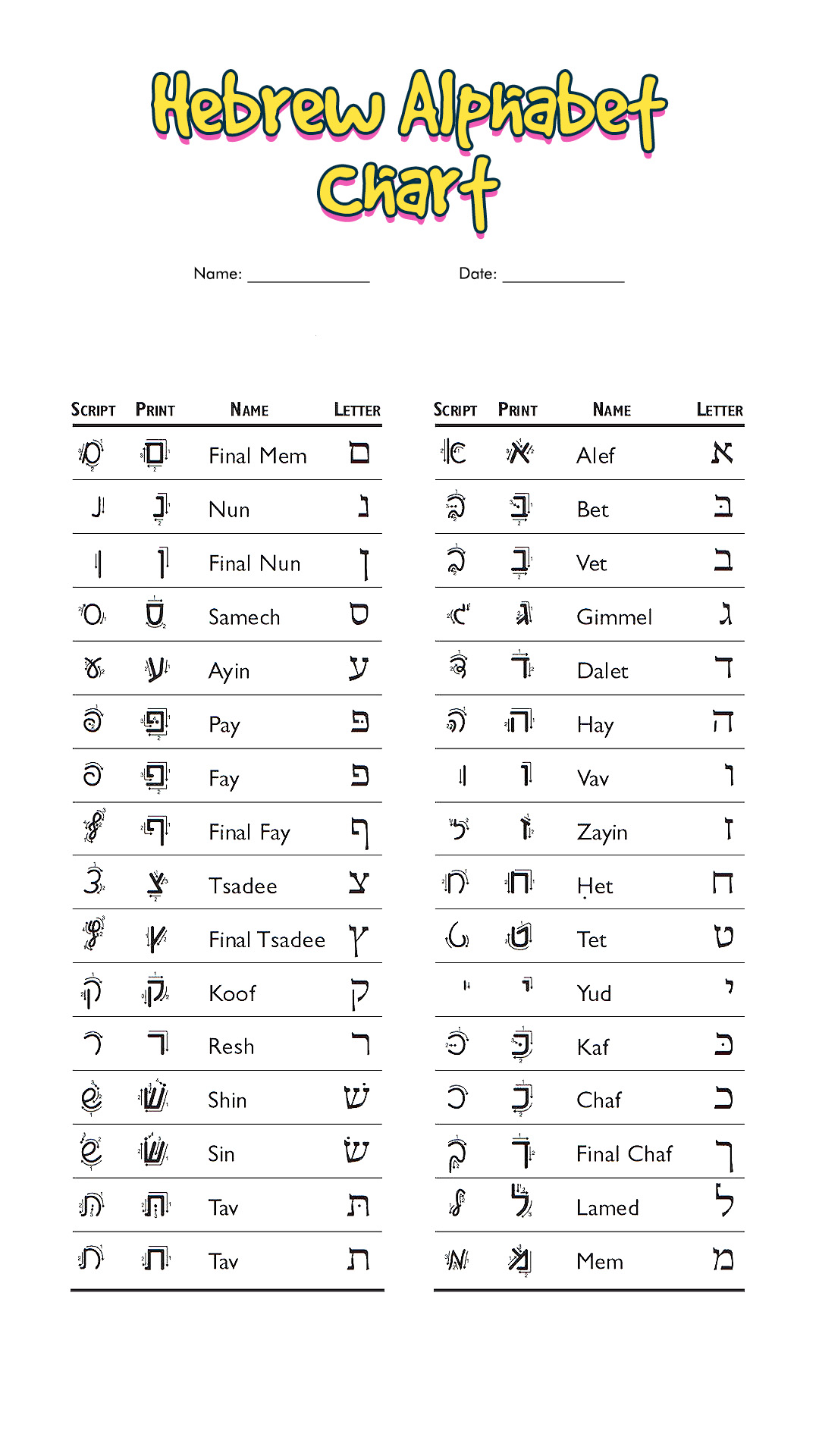
The picture to the right illustrates the Hebrew alphabet, in Hebrew alphabetical order. Note that Hebrew is written from right to left, rather than left to right as in English, so Alef is the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet and Tav is the last. The Hebrew alphabet is often called the " alef-bet," because of its first two letters.

Printable Beginner Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet, the holy language of the Bible, is used for biblical Hebrew, Modern Hebrew, Jewish Aramaic, Yiddish, and Ladino. It consists of 22 letters, all consonants, none of which are lowercase. Learn Hebrew Audio Tanakh Hebrew Training Printer-Friendly Version The Hebrew Alphabet Learning the Hebrew Consonants To begin studying Hebrew, you must begin with its character set or script.

Click on a letter below to begin studying how to pronounce, read, and write the letter (start with Aleph and proceed right. Interesting Facts About The Hebrew Alphabet Ancient Origins: The Hebrew alphabet, also known as the Aleph-Bet, dates back to around 1000 BCE. It is derived from the Phoenician alphabet and is one of the oldest writing systems still in use today.

Hebrew Alphabet Chart: Learn Each of the Hebrew Letters - B'nai Mitzvah ...
22 Letters: The Hebrew alphabet consists of 22 consonants. Discover the Hebrew Alphabet Chart at Easy Learn Hebrew! Our comprehensive guide covers the Aleph-Bet, pronunciation tips, final forms, and essential resources to help you master Hebrew effortlessly. The Hebrew Alphabet To begin learning Hebrew, you must start with the Alephbet, or learning the consonants.
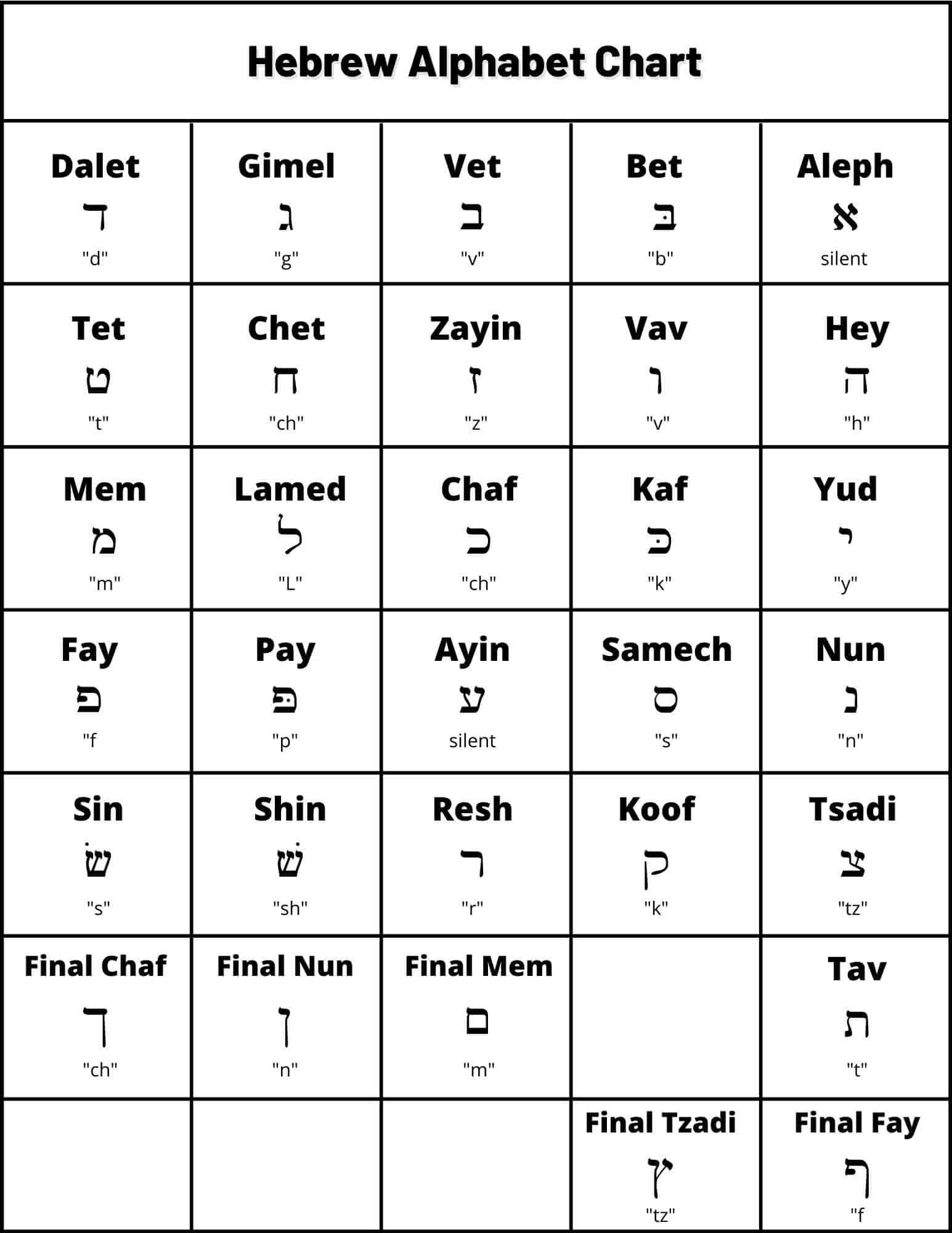
HebrewEasy's chart differs from most Hebrew charts because it is created for English speakers as an introduction to memorizing the letters. Mentally recalling the ABCs to help recognize your newly learned Hebrew letters makes memorizing easier. Remember, Hebrew.

The Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew and Yiddish languages use a different alphabet than English. The picture below illustrates the Hebrew alphabet, in Hebrew alphabetical order. Note that Hebrew is written from right to left, rather than left to right as in English, so Alef (א) is the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet and Tav (ת) is the last.
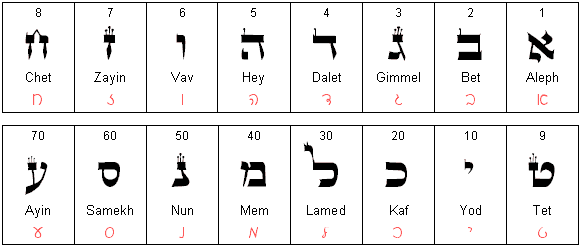
The Hebrew alphabet, or the Aleph Bet, consists of 22 letters. The Aleph Bet is also used to write other Jewish languages, like Yiddish, Ladino, Aramaic, Judeo-Persian and Judeo-Arabic. In Hebrew, the letters are all consonants and the language is comprehensible when written without vowels.

The Hebrew language is written from right to left, using the distinctive and ancient Hebrew alphabet, known as the אָלֶף-בֵּית עִבְרִי (Aleph-Bet Ivri). This alphabet consists of 22 consonantal letters, each with its own unique shape, name, and historical significance. Unlike many other alphabets, the Hebrew script does not inherently include vowels; instead, a system of.