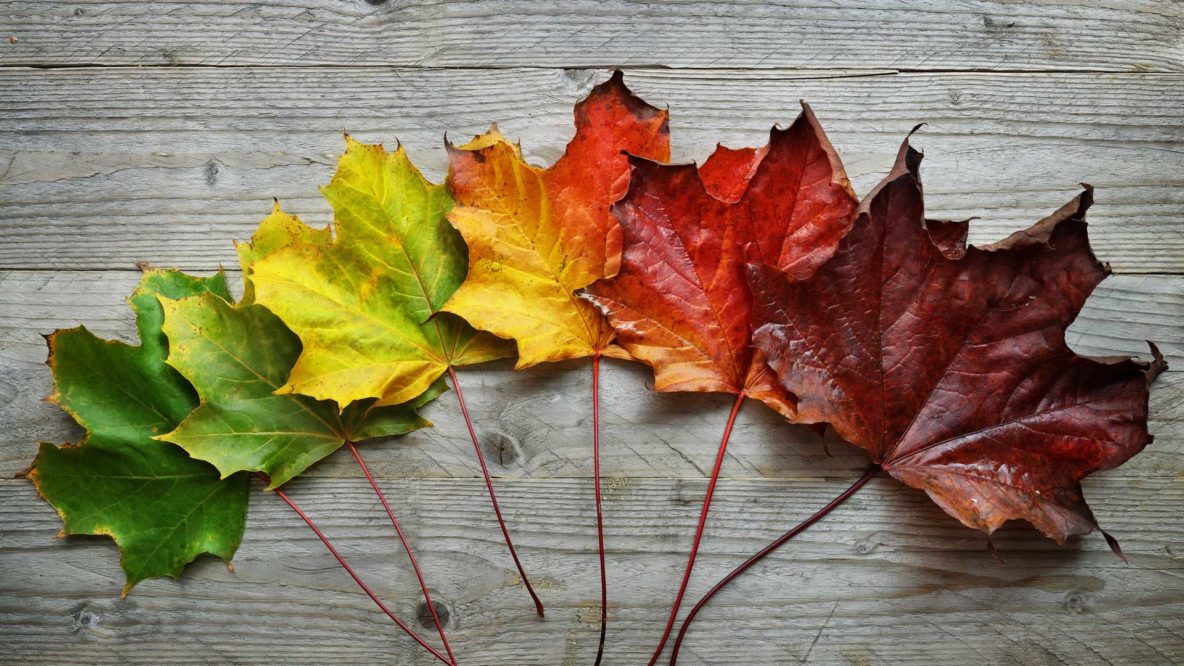
What Holds The Key To What Color A Leaf Will Change To In The Fall
Brilliant Fall leaves on the Superior National Forest. (Forest Service photo) Certain colors are characteristic of particular species: Oaks: red, brown, or russet Hickories: golden bronze Aspen and yellow-poplar: golden yellow Dogwood: purplish red Beech: light tan Sourwood and black tupelo: crimson The color of maples leaves differ species by species: Red maple: brilliant scarlet Sugar maple. Explore why leaves change color in fall, the role of sunlight and pigments, and top tips for spotting the brightest autumn foliage this season.

In the fall, trees put on a pretty impressive fashion show. Leaves that were green all summer long start to turn bright red, orange, and yellow. But where do these colors come from? It all starts inside the leaf.

How Do Leaves Change Color
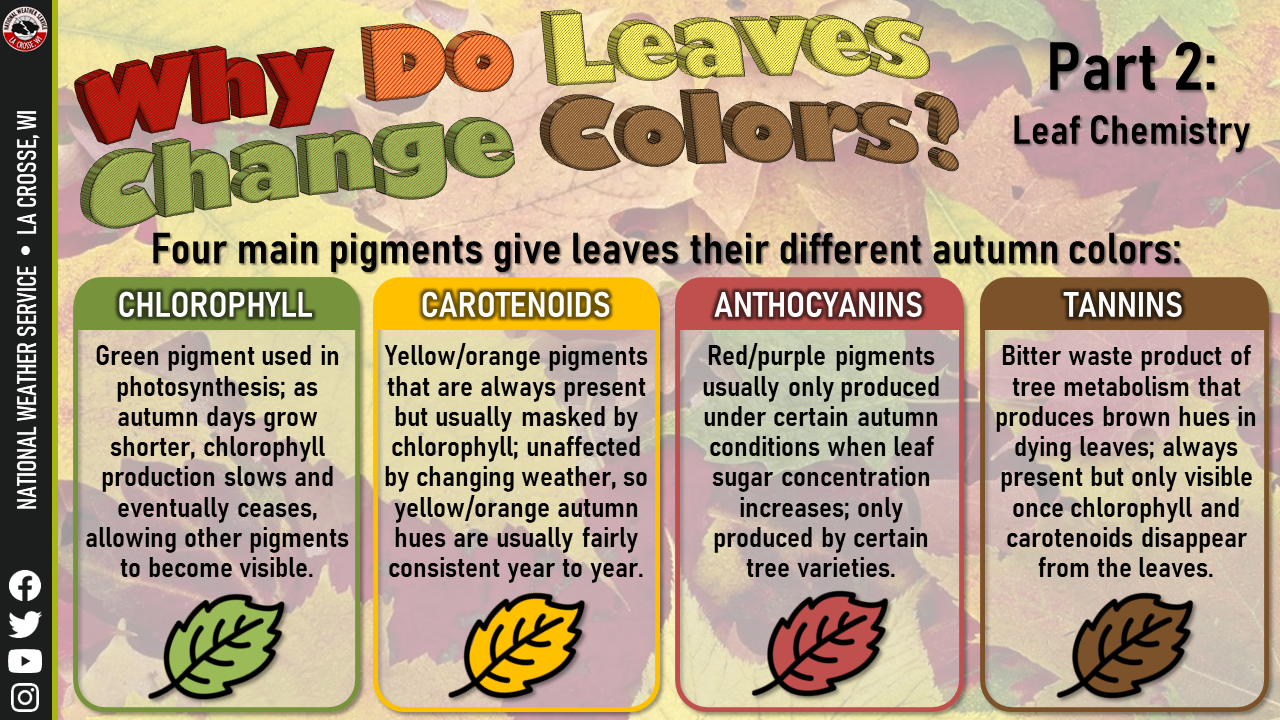
Leaves have color because of chemicals called pigments, and there are four main types of pigment in each leaf: Leaves are green in the spring and summer because that's when they are. The peak dates for fall foliage in the U.S. vary from region to region.

Colors change first in the North and in higher elevations, then spread south and to lower elevations. Leaves change color during the autumn because the amounts of pigments change as the leaves prepare to fall from the trees. All leaves gradually lose chlorophyll during the growing season, and this loss accelerates before leaf fall.

Why Leaves Change Color | Fall Science Worksheets
Under optimal conditions this process of chlorophyll loss is very orderly and allows the plants to resorb much of the nitrogen in the structure of the pigment. Ever since the leaves on the trees bloomed in the spring, they have actively been helping the tree grow. Each leaf contains a pigment called chlorophyll.

Chlorophyll is the most common pigment in a leaf. It absorbs the sun's rays to turn sunlight into food and energy for the tree. Chlorophyll is also what gives a plant its green color.
Science Sundays: Why Do Leaves Change Color in Autumn
The Final Act: Leaf Abscission The color change culminates in leaf abscission, the shedding of leaves from the tree. This protective mechanism allows deciduous trees to conserve water and energy during winter. At the base of each leaf stem, a specialized region known as the abscission zone forms.

Within this zone, two distinct layers develop. To recap, leaves change color because of hidden pigments, and different factors like sunlight and temperature affect how vibrant those colors become in the fall. Discover why leaves reveal their inner chemistry when chlorophyll breaks down - and how to brighten your lessons on colour changes with this context Every autumn, nature swaps its coat of green for an ensemble of red, yellow, orange and brown.

Fashion followers take inspiration from this seasonal shift. During the spring and summer, however, high chlorophyll levels overpower carotenoids, and leaves stay green. In this video, we cover why leaves change color in the fall and the science behind it! What Causes Leaf Color Change? While remaining present, chlorophyll levels dip in the fall, allowing carotenoids to become more visible.




![Is Leaves Changing Color A Chemical Change? [Shocking Truth] Is Leaves Changing Color A Chemical Change? [Shocking Truth]](https://plantscraze.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Different-leaf-colors-1160x1160.png)

