Pandas Style Color Map
pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.map # Styler.map(func, subset=None, **kwargs) [source] # Apply a CSS-styling function elementwise. Updates the HTML representation with the result. Parameters: funcfunction func should take a scalar and return a string.

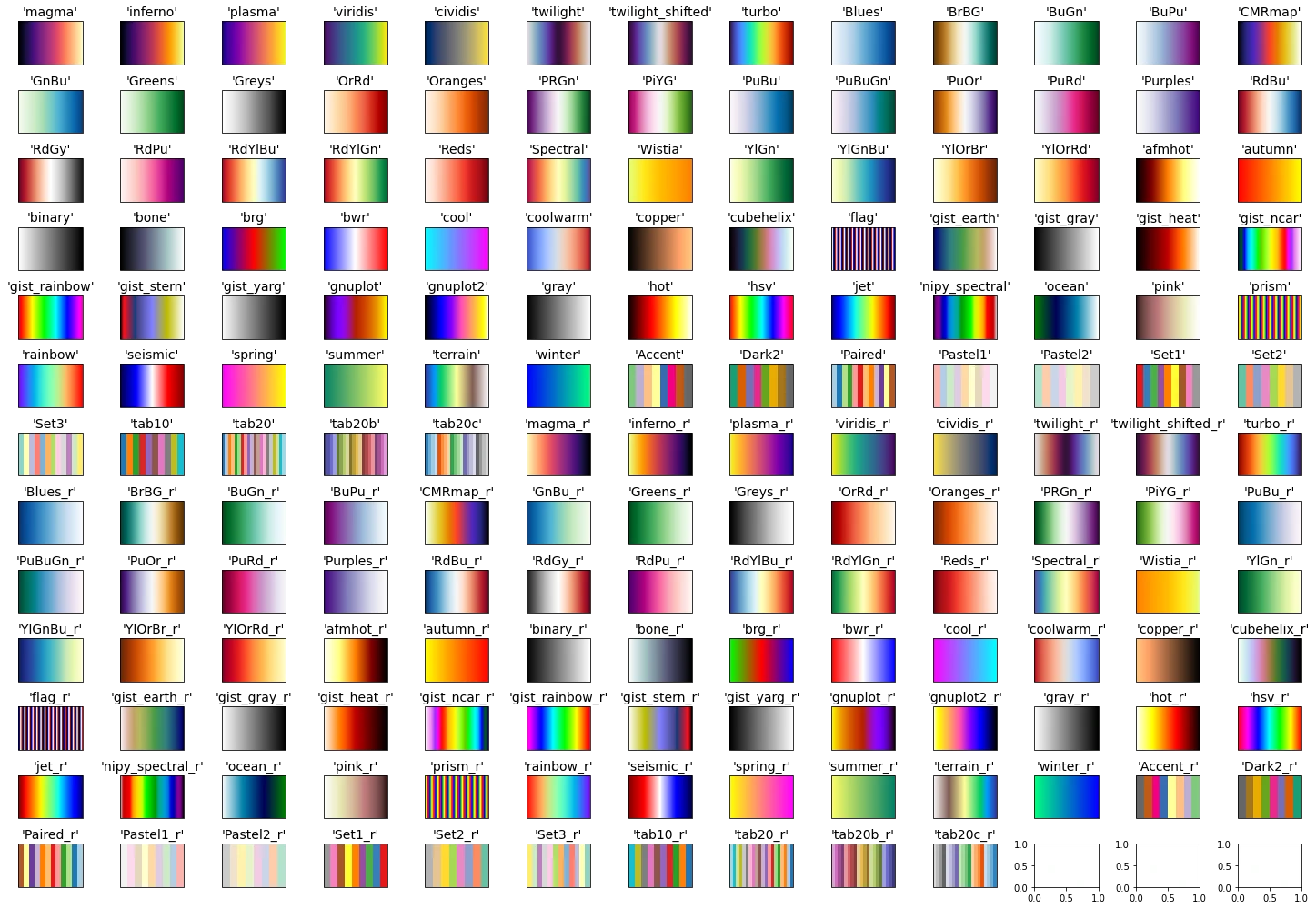
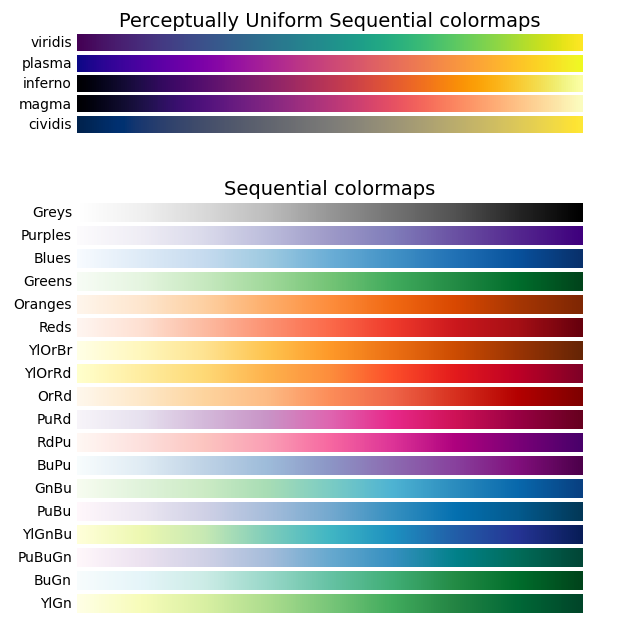
subsetlabel, array-like, IndexSlice, optional A valid 2d input to DataFrame.loc [], or, in the case of a 1d input or single key, to. Choosing Colormaps in Matplotlib # Matplotlib has a number of built-in colormaps accessible via matplotlib.colormaps. There are also external libraries that have many extra colormaps, which can be viewed in the Third-party colormaps section of the Matplotlib documentation.
Python数据可视化(二):Pandas和Seanborn-CSDN博客
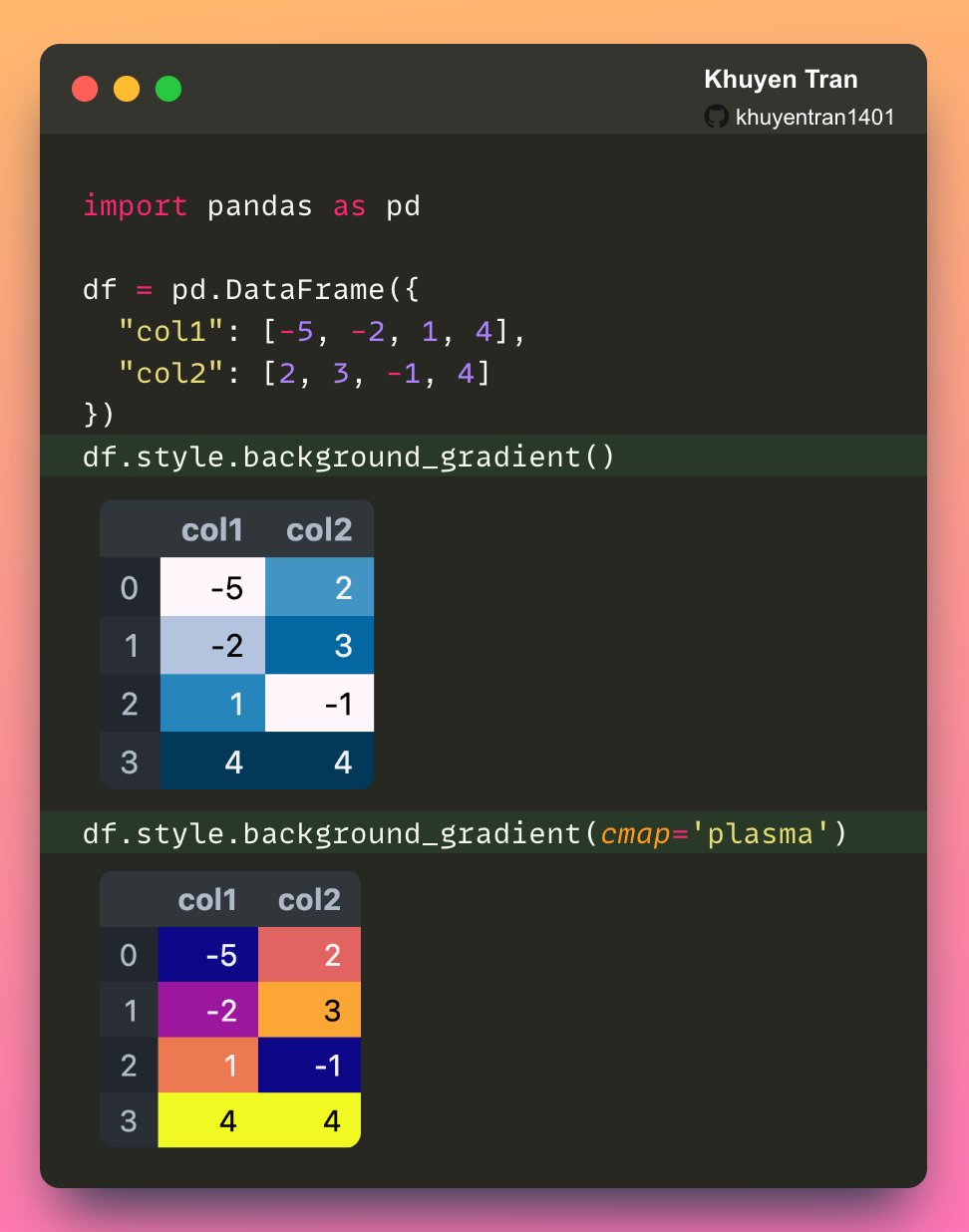
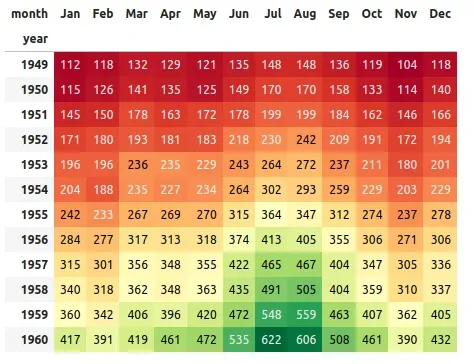
Here we briefly discuss how to choose between the many options. For help on creating your own colormaps, see Creating. I have a dataframe (df) like this, using color map for styling: #create random 30 x 30 frame df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, (5, 20))) df.style.background_gradient(cmap='RdYlGn_r') The above code colors the dataframe over all the numbers (5 x 20 cells - smaller numbers in green, bigger numbers in red).

How can I color the small to big for each row considered individually (NOT as a. Let us see how to gradient color mapping on specific columns of a Pandas DataFrame. We can do this using the Styler.background_gradient () function of the Styler class.
Pandas Visualization Cheat Sheet
Syntax: Styler.background_gradient (cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None) Parameters: cmap: str or colormap (matplotlib colormap) low, high: float (compress the range by these values.) axis: int or str (1 or. The DataFrame.style attribute is a property that returns a Styler object. It has a _repr_html_ method defined on it so it is rendered automatically in Jupyter Notebook.
The Styler, which can be used for large data but is primarily designed for small data, currently has the ability to output to these formats: HTML LaTeX String (and CSV by. 1. How do I style a Pandas DataFrame? To style a Pandas DataFrame we need to use.style and pass styling methods.
Unconventional Pandas: Colormaps — DUTC
This returns a Styler object and not a DataFrame. We can control the styling by parameters and options. We can find the most common methods and parameters for styling in Pandas in the next section.

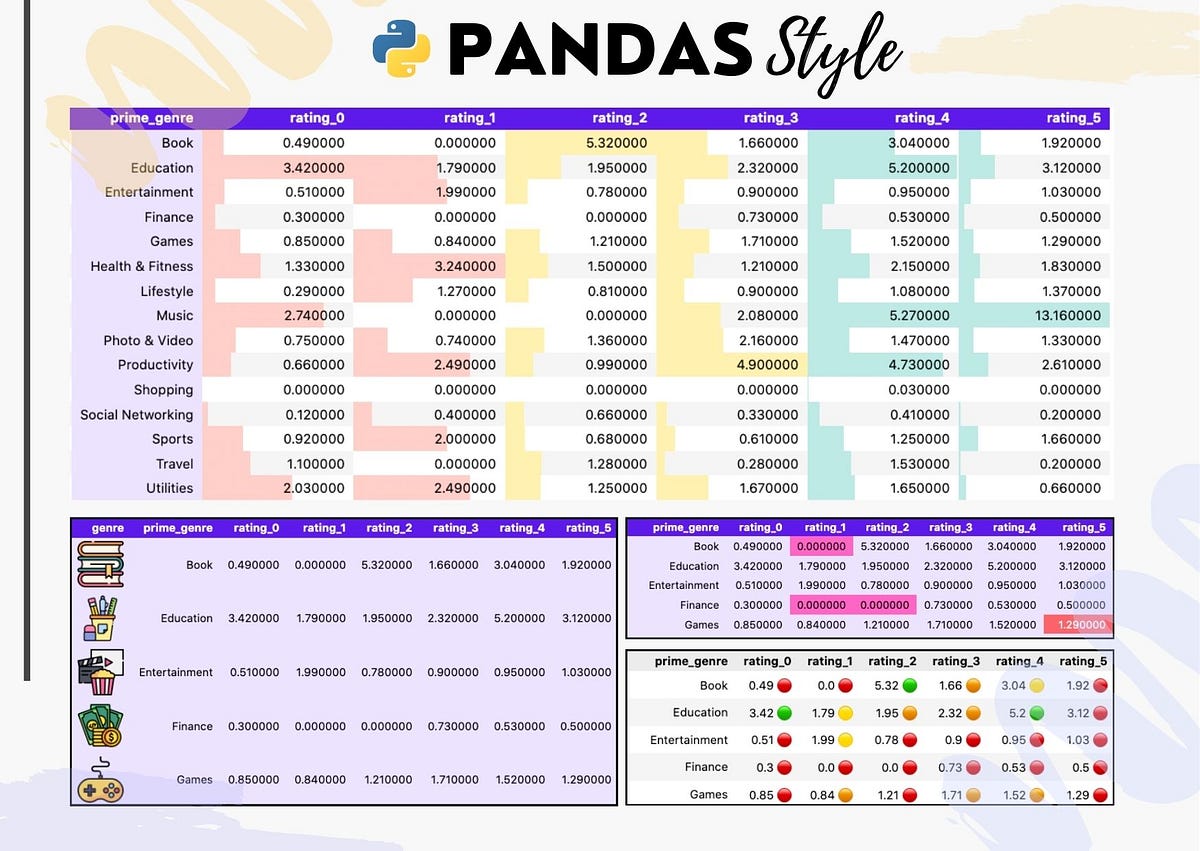
The syntax for the Pandas Styling methods is: df.style.highlight_null(null_color. In the following section of this article, we will explore a method to add colors and styles to Pandas DataFrames. Our focus will be on the application of colors and emojis, utilizing approaches.
Use Pandas Styler to Change Text and Background Color Usually, it's a good idea to highlight data points you want to draw attention to. The convenient highlight_max() function assigns a yellow color to the largest value of every cell in a DataFrame: df.style.highlight_max() Image 6 - Highlighting max values (image by author) The highlight_min() function does just the opposite: df.style. pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.background_gradient # Styler.background_gradient(cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None, text_color_threshold=0.408, vmin=None, vmax=None, gmap=None) [source] # Color the background in a gradient style.

The background color is determined according to the data in each column, row or frame, or by a given gradient map. Requires matplotlib. Parameters.
We can make changes like the color and format of the data visualized in order to communicate insight more efficiently. For the more impactful visualization on the pandas DataFrame, generally, we DataFrame.style property, which returns styler object having a number of useful methods for formatting and visualizing the data frames.