Pandas Style Color Gradient
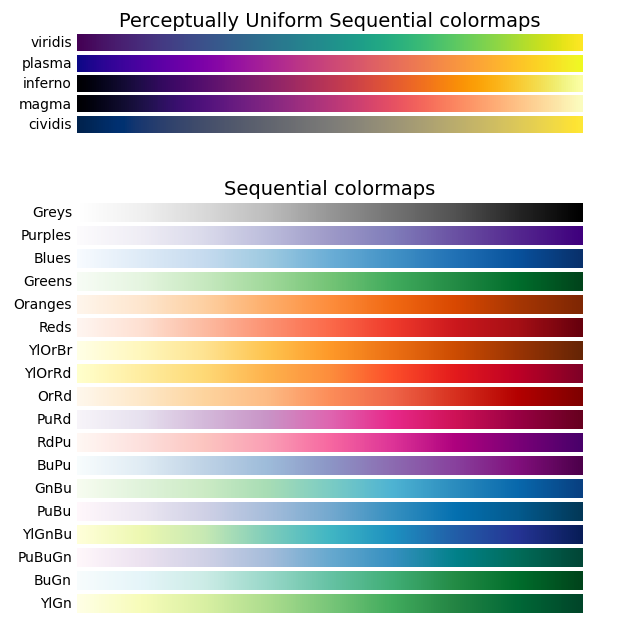
pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.background_gradient # Styler.background_gradient(cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None, text_color_threshold=0.408, vmin=None, vmax=None, gmap=None) [source] # Color the background in a gradient style. The background color is determined according to the data in each column, row or frame, or by a given gradient map. Requires matplotlib.
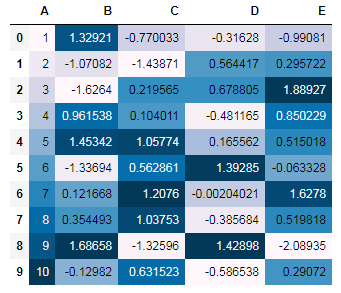
Parameters. Let us see how to gradient color mapping on specific columns of a Pandas DataFrame. We can do this using the Styler.background_gradient () function of the Styler class.
Premium Vector | Vector illustration logo panda color gradient colorful
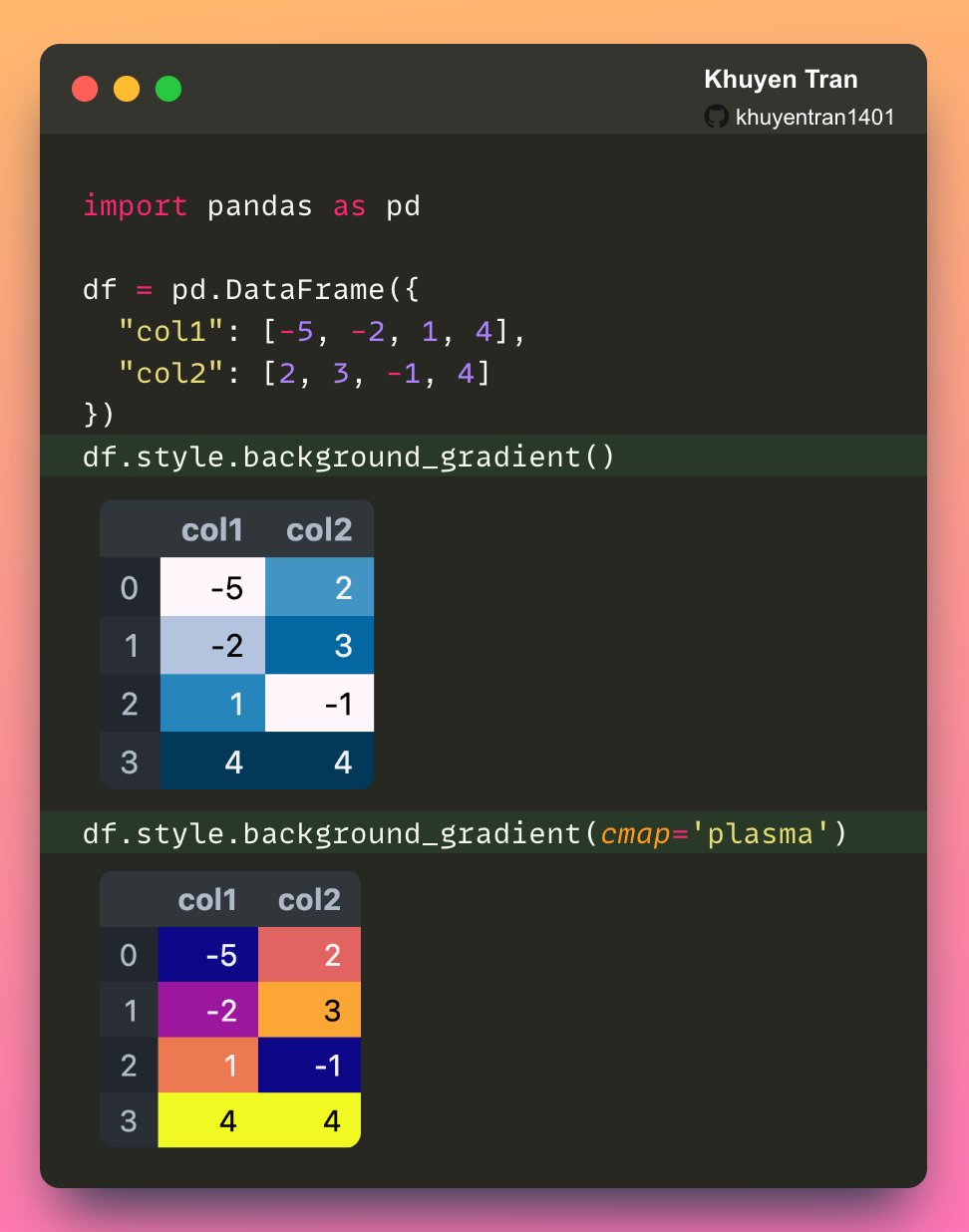
Pandas' Styler.background_gradient function is used to apply a color gradient to each cell of the data frame. In the code you entered, with the axis=None parameter, the gradient is applied to the entire DataFrame (both along rows and columns) and the vmin and vmax values are fixed for the entire DataFrame. That's why it's better to color the entire cell, and not only the text: df.style.background_gradient(subset=["C"], cmap="RdYlGn", vmin=0, vmax=2.5) Image 13 - Using a custom gradient palette to change the background color (image by author) Now let's get into the really exciting stuff.

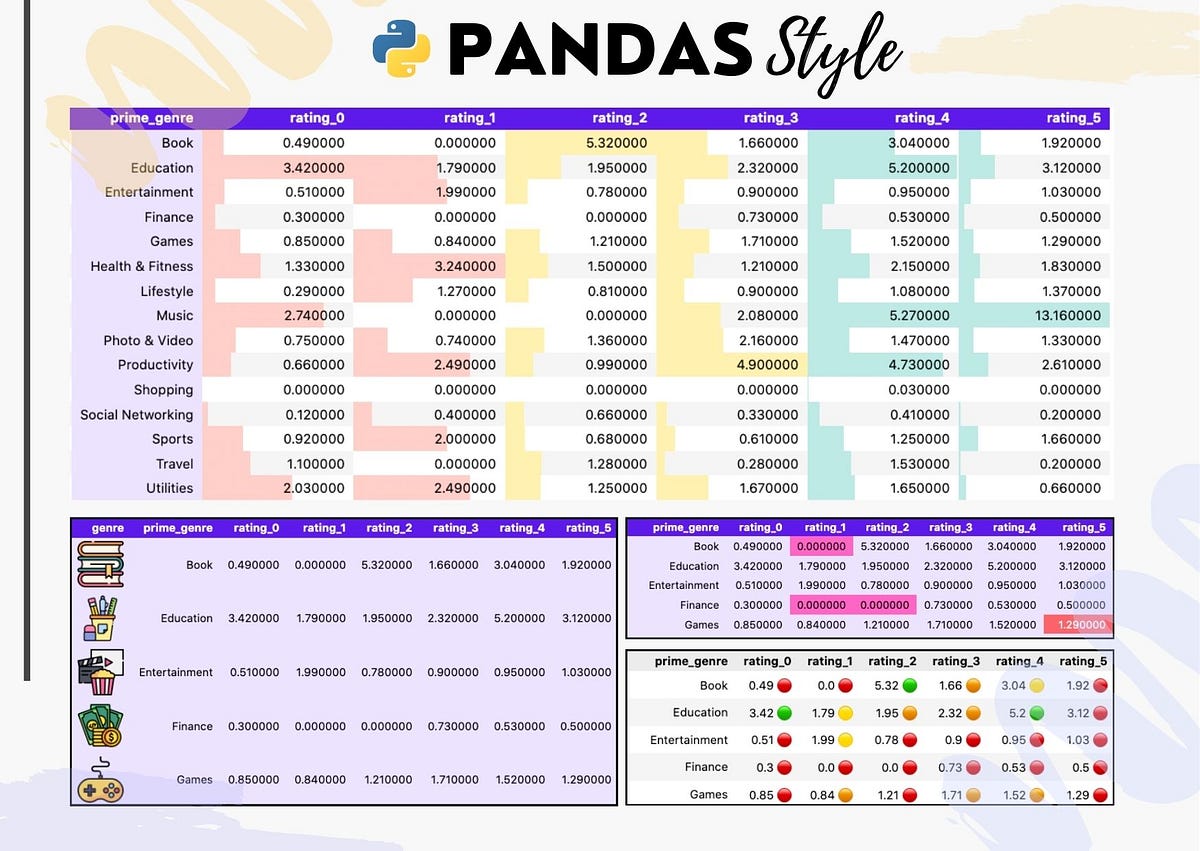
We'll explore the coloring of each cell as a bar. For example we can build a function that colors text if it is negative, and chain this with a function that partially fades cells of negligible value. Since this looks at each element in turn we use map.

Vector Illustration Panda Gradient Colorful Style Stock Illustration ...
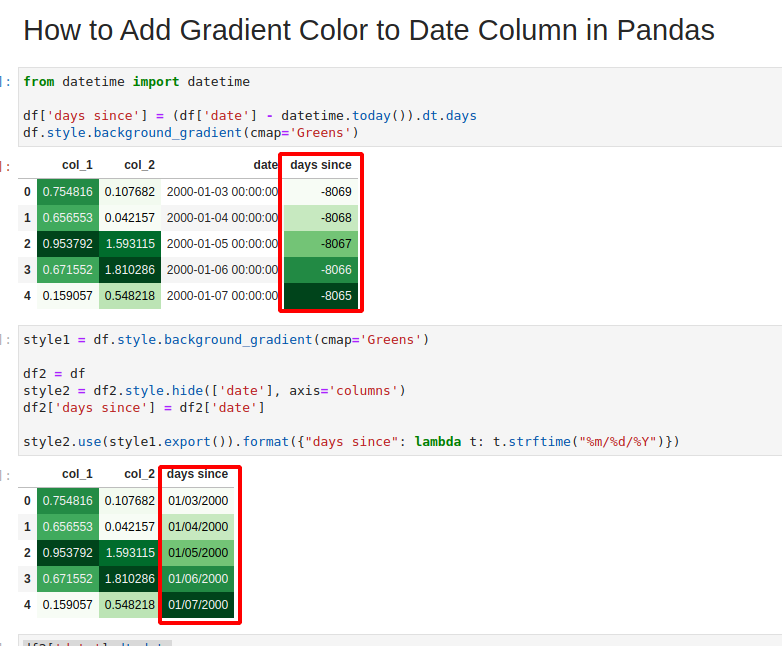
Pandas styling exercises, Practice and Solution: Create a dataframe of ten rows, four columns with random values. Write a Pandas program to make a gradient color mapping on a specified column. Conclusion DataFrame styling in Pandas transforms raw data into visually appealing, insightful outputs, enhancing both analysis and communication.

By leveraging the Styler API, you can apply formatting, conditional highlighting, gradients, and custom properties to create professional tables. Color the background in a gradient style. Notes When using low and high the range of the gradient, given by the data if gmap is not given or by gmap, is extended at the low end effectively by map.min - low * map.range and at the high end by map.max + high * map.range before the colors are normalized and determined.
Create Stunning Data Visualization with Pandas Style Background ...
pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.text_gradient # Styler.text_gradient(cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, gmap=None) [source] # Color the text in a gradient style. The text color is determined according to the data in each column, row or frame, or by a given gradient map. Requires matplotlib.
Parameters: cmapstr or colormap Matplotlib colormap. lowfloat. .hide_index().background_gradient(cmap='Blues') One can even use styler.set_properties when the style doesn't actually depend on the values.
In this example, we will render our dataset with a black background and with green color for the text itself. Pandas code to render the formatted dataframe in the same way for each cell.