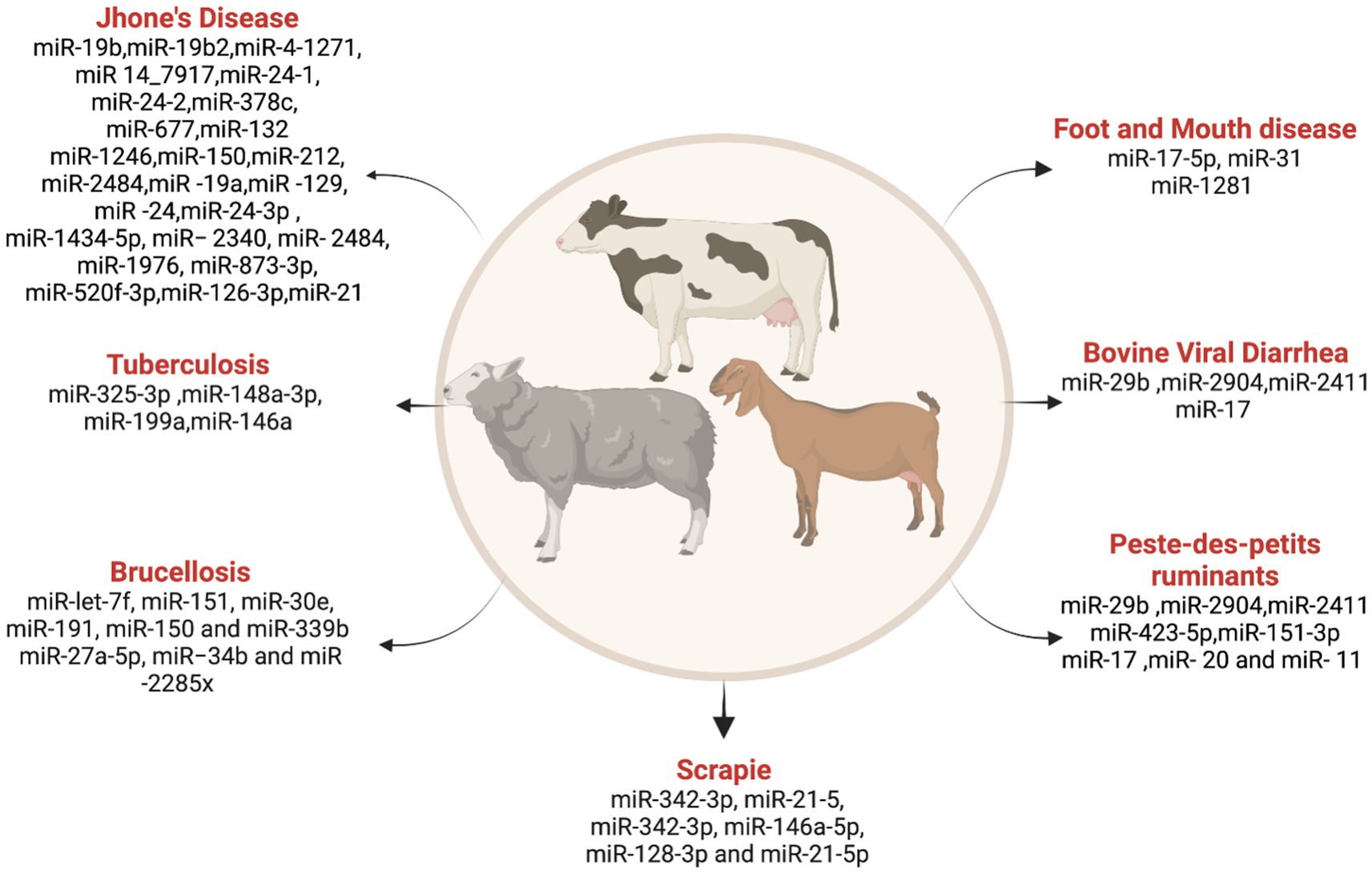
Example Of Farm Animals Disease
Explore the overview of common farm animal diseases, their impact on livestock health and productivity, and effective preventive measures to ensure animal welfare. This comprehensive guide covers zoonotic and contagious diseases, the role of proper nutrition, biosecurity, and the importance of working with veterinarians for healthier farm management practices. Understand how to mitigate risks.

Diseases contracted and spread by farm animals can impact agriculture and public health. They also negatively affect the animal's welfare. The National Agricultural Library (NAL) provides literature and other resources to help USDA agencies conduct animal health and welfare research as well as actively control and prevent the spread of disease in livestock.
Diseases Caused By Bacteria In Animals
These materials can also be useful. Human exploitation of animals has proven to be harmful to public health time and time again. While waiting for legislators to make the right decision, you can personally help prevent such diseases by reducing or eliminating animal products from your diet.

As more people take this step, animal agriculture industries take notice. The most Common Animal Diseases Animals are susceptible to a number of diseases and conditions that may affect their health. Some, like classical swine fever and scrapie are specific to one type of stock, while others, like foot.

Nuclear-Derived Techniques Help Farmers Combat Cattle Disease Outbreaks ...
The wellbeing of an animal depends on factors such as the quality and quantity of feed consumed (nutrition), water intake, parasitic infestation, predators, disease incidence as well as numerous management and environmental factors. Farm Animal Diseases: Symptoms, Causes And PreventionCan an animal live and produce forever? The answer is no! Part of the characteristics of living thing is that. Common animal diseases and their control in agriculture are crucial aspects of livestock management that directly impact productivity, food safety, and farmers' income.
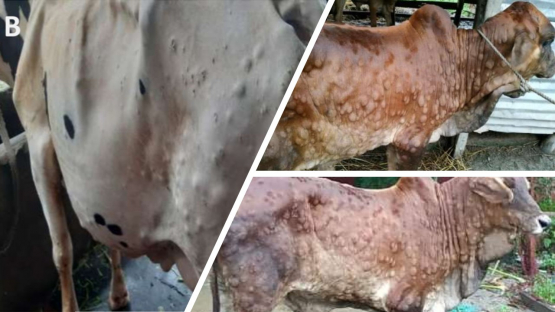
In both commercial and subsistence farming systems, animals are vulnerable to various diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, and environmental factors. The rising demand of the rapidly growing global population for animal-derived foods and other products requires intense animal farming. However, the husbandry and breeding of livestock are associated with a conflict between the economic requirements.

Disease Prevention - Teagasc | Agriculture and Food Development Authority
Different types of farm animals can carry different diseases. For example, cows and calves can carry the bacterium Escherichia coli O157:H7, often called E. coli.
-720x542.png)
This germ can cause bloody diarrhea in people. In addition children can develop kidney failure due to coli 0157:H7 infection. Pigs can carry the bacterium Yersinia enterocolitica which causes the disease yersiniosis.

Chickens can. These are the common zoonotic diseases that are passed from farm animals like cattle, poultry birds, pigs, goat and sheep to the farmer when poorly handled. Farm Animals: Diseases and common illnesses Livestock diseases occur when animals' standard bodily functions alter and cause adverse effects, such as infections, damaging their physical well-being.

To keep you informed, here are the most common animal diseases you should be cautious of.