Shark Color Blind
The shark retina contains both rod cells and photoreceptor cells, which are responsible for detecting light and color. However, recent research suggests that sharks may be cone monochromats, meaning they have only one type of cone photoreceptor and are likely completely colorblind. Discover the truth about shark color vision.

Are sharks color blind? Can sharks see color? Learn how sharks see their world, and if they can distinguish colors. A single cone type means sharks are largely monochromatic, perceiving the world in shades of gray. Behavioral studies, such as those conducted on grey bamboo sharks, further support this conclusion, showing that these sharks discriminate objects based on contrast rather than color.

Are Sharks Blind? How Do Sharks See?
Sharks may be able to smell blood from miles away, but they probably don't know how red it is: New research suggests sharks are color. Sharks have long fascinated us with their sleek bodies and predatory prowess, but one question often surfaces: are sharks color blind? Understanding how these incredible creatures perceive their underwater world can shed light on their hunting strategies and behaviors. Research suggests that sharks aren't entirely color blind, but their color vision is limited compared to humans.

They. Sharks, with their sleek bodies and powerful presence, have long been considered the oceans' apex predators. Yet, the mysteries surrounding their senses, particularly their vision, have led to questions like: Are sharks blind? How do sharks see in their watery world? In this article, we dive deep into the fascinating realm of shark vision, uncovering the truth about their visual capabilities.

Are Sharks Blind? Do They Have Eyelids? Shark Sider
Sharks have limited color vision, relying on contrast and brightness to detect prey, predators, and mates in their underwater environment. In recent decades, conflicting data have sparked debate about how sharks see. New studies have shed new light on this question.

Read on to find out how sharks see and if they are in fact, blind. The Anatomy of Shark Eyes To understand if sharks are color blind, we first need to look at the anatomy of their eyes. Sharks possess a well-developed eye structure that is particularly adapted to low-light conditions found in deep waters.

Sharks Are Color-Blind, Retina Study Suggests | National Geographic
Their eyes contain a high concentration of rod cells, which are responsible for detecting light and movement, making them excellent at seeing in dark. Are sharks completely colorblind, or do they have some ability to see colors? Sharks, just like most other fish, do have some ability to see colors. However, their color vision is not as advanced as that of humans or other animals that rely heavily on color perception.
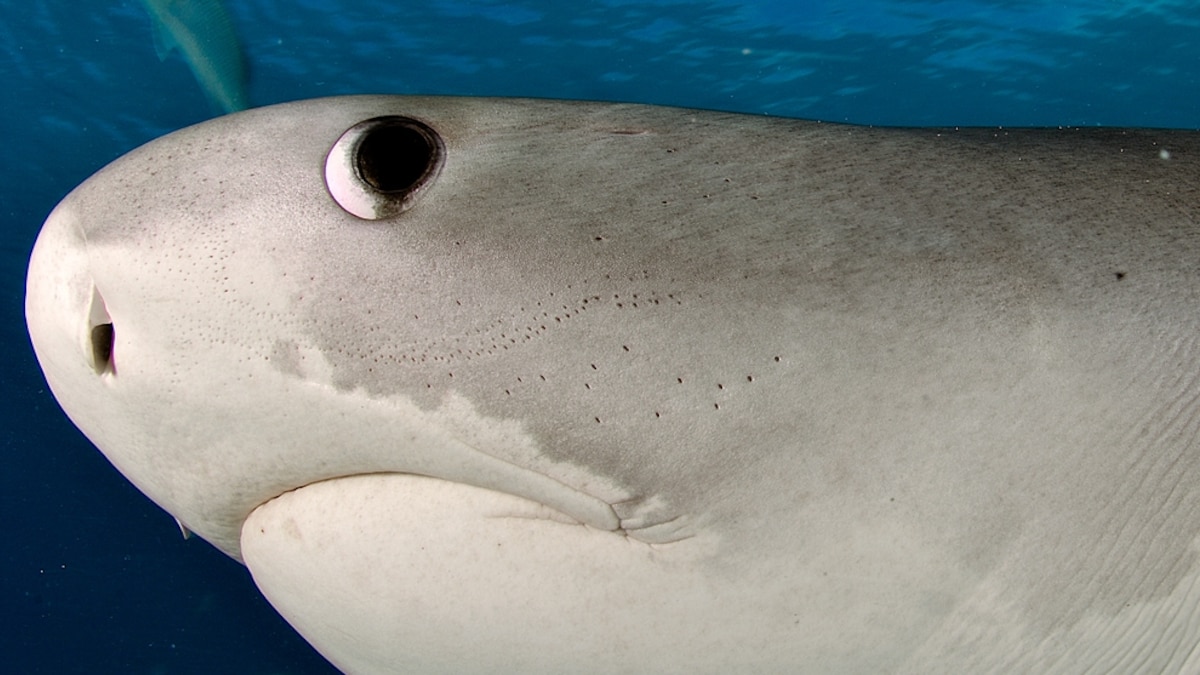

While humans have three types of color receptors called cones (red, green, and blue), sharks and most other fish only have two.