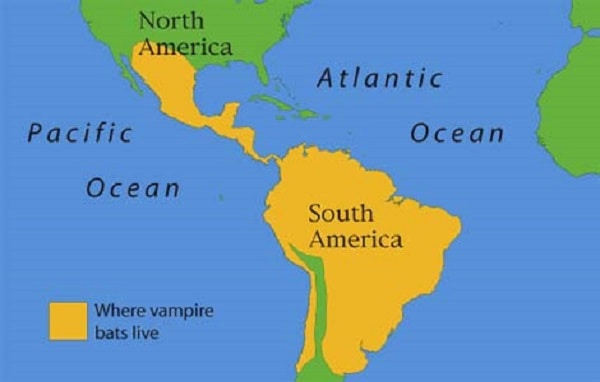
Vampire Bat Range
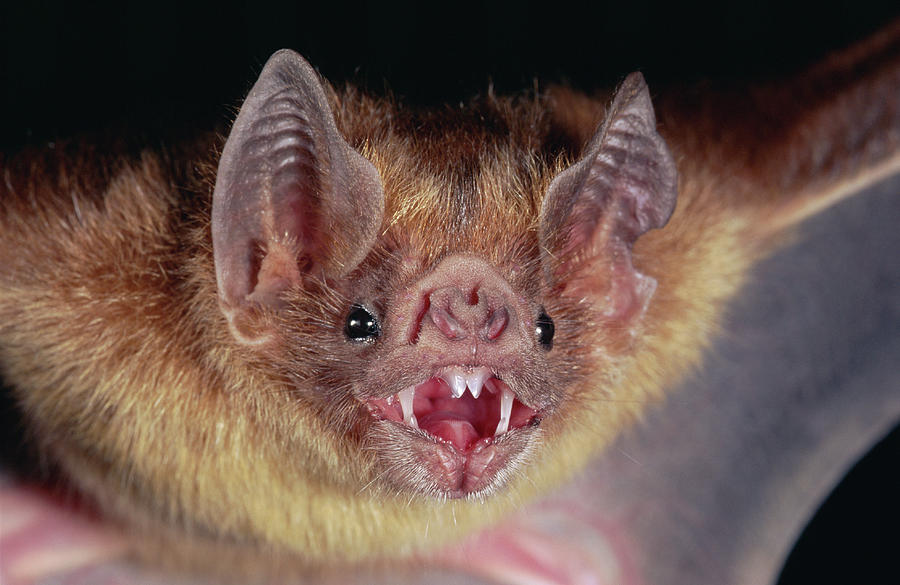
Vampire bats tend to live in colonies in almost completely dark places, such as caves, old wells, hollow trees, and buildings. They range in Central to South America and live in arid to humid, tropical and subtropical areas. Vampire bat colony numbers can range from single digits to hundreds in roosting sites.
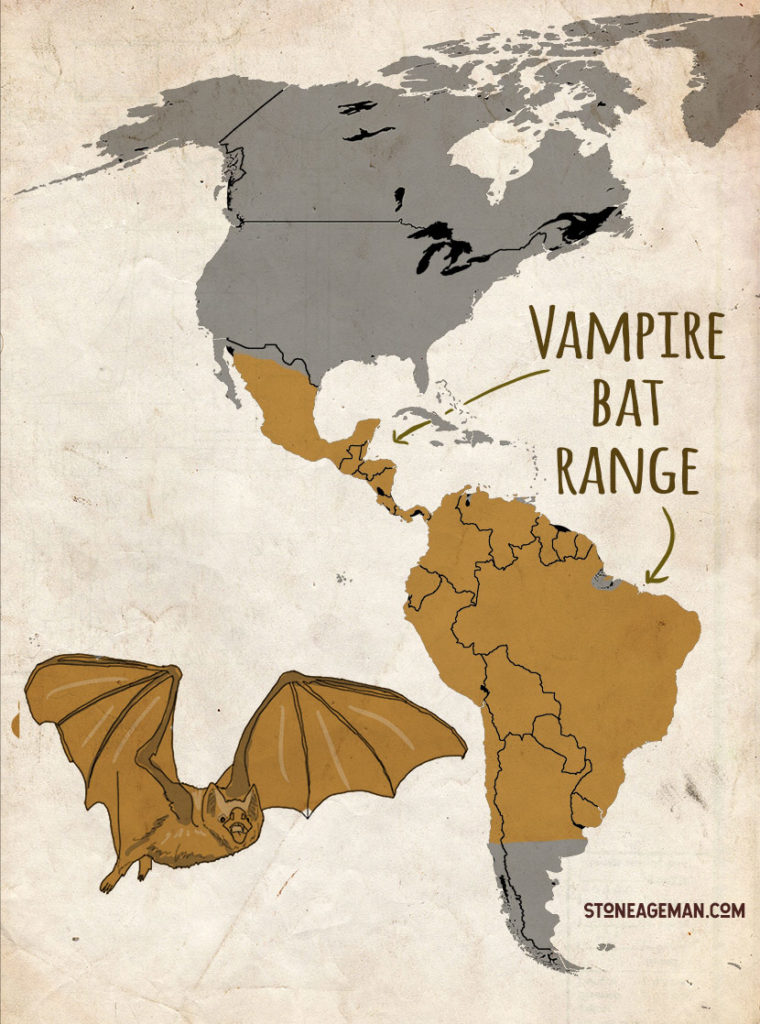
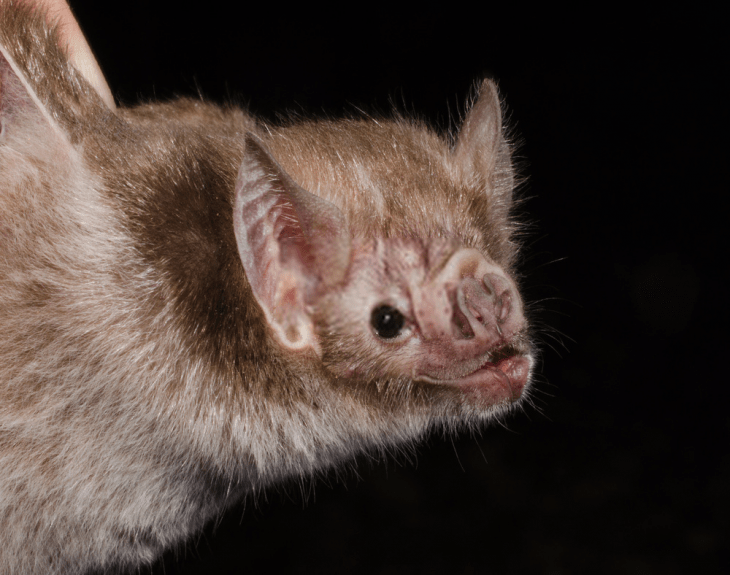
The basic social structure of roosting bats is made of female groups and their. Geographical Range Vampire bats are found exclusively in the Americas, from Mexico through Central America and into South America. The common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) has the widest distribution, from northern Mexico through Central America and much of South America, including central Chile, Argentina, and Uruguay.
Common Vampire Bat: The Animal Files
Common vampire bats are highly social and have sophisticated social organization and behaviors. Female bats form close associations with other females, observed through activities such as social grooming and sharing food. How often these bats share their food depends on a variety of factors including kinship, association, and reciprocal help.

Basic facts about Common Vampire Bat: lifespan, distribution and habitat map, lifestyle and social behavior, mating habits, diet and nutrition, population size and status. Because researchers expect vampire bats to expand their range to southern Texas, livestock producers need to be aware of the ecology of the species, its habits, potential impacts on livestock, and how to recognize the signs of vampire bat feed. Read about Desmodus rotundus (vampire bat) on the Animal Diversity Web.
Common Vampire Bat - Facts, Diet, Habitat & Pictures on Animalia.bio
Habitat The Common Vampire Bat has a wide range across Central and South America, from Mexico down to Argentina. It lives in hugely varied habitats, from desert to rainforest, and up to 2,400 metres above sea level. Like all bats, it needs a daytime roost and roost sites are usually used by 20 to 100 individuals.

Occasionally much larger roosts of up to 5000 bats are discovered. Caves and tree. Common vampire bats range from northern Mexico through Central America, and south into the South American countries of Chile, Argentina and Uruguay.
Future climate ensemble map for common vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus ...
Found in humid and arid climates, they occupy rainforests as well as deserts. RANGE AND HABITAT The common vampire bat is widely distributed throughout tropical Mexico, Central America, and South America as far south as central Chile, northern Argentina and Uruguay. It has been found at altitudes ranging from sea level to as high as 10,000 feet near the equator in the mountains of Columbia and Peru.

Vampire bats are also found on the islands of Trinidad and Margarita. A vampire bat may ingest up to 40 percent of its body weight while feeding. With such a huge increase in body weight, vampire bats would not be able to fly after a meal if it were not for their ability to rapidly process and digest the blood.

Ultrasonic Navigation Common vampire bats are active only during the darkest hours of the night.



