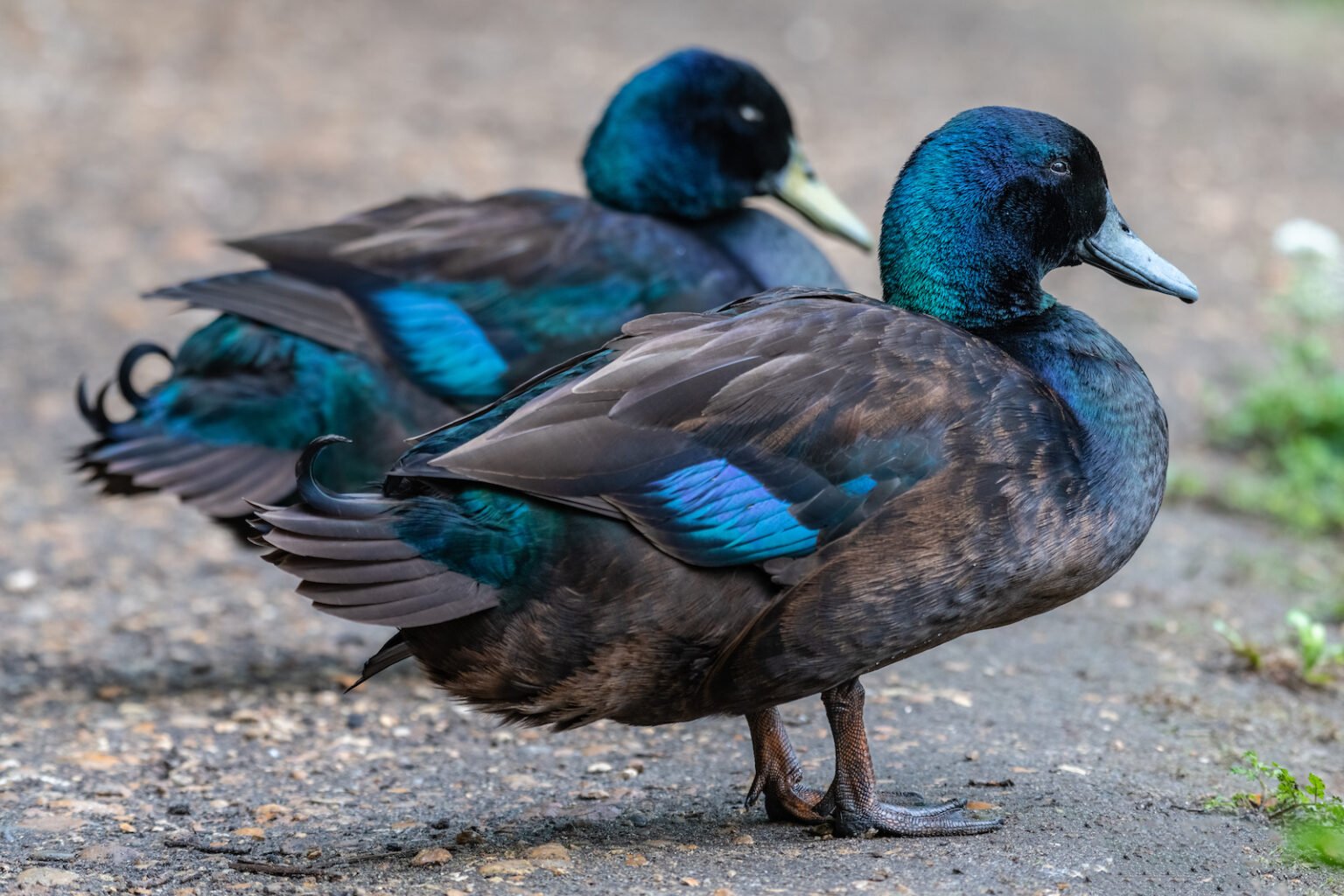
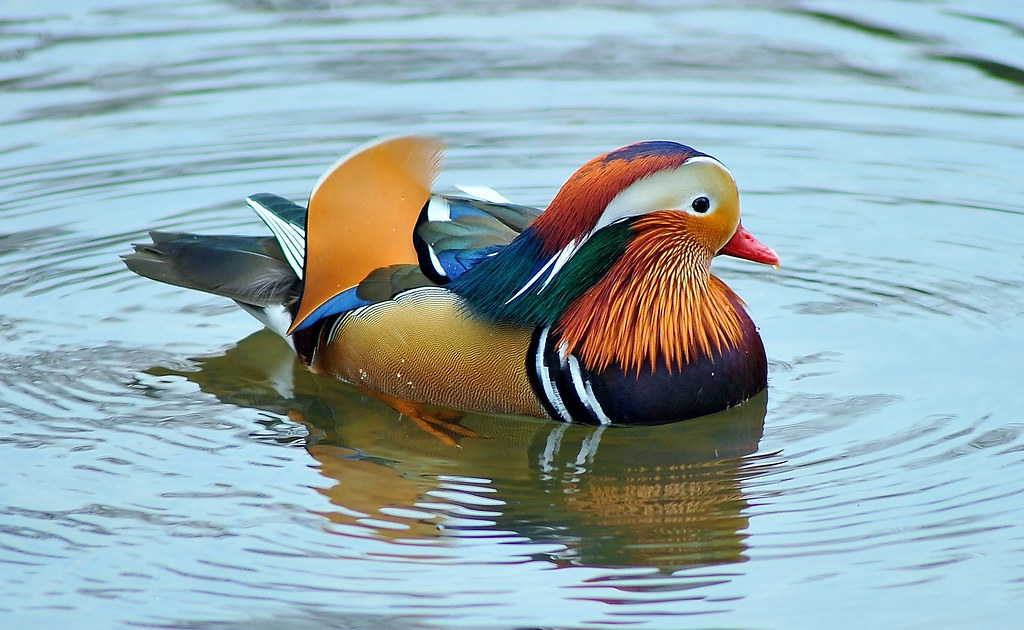
Duck Colour Real
Why do ducklings sometimes hatch in unexpected colors? Learn how duck color genetics work and what makes duckling appearances so surprising! Duck color genetics can be quite complex, with dilution factors affecting brown feathers and the ability to create lavender and lilac feathers. Understanding these genetic variations can give you insight into the diverse plumage of ducks. Mallard Derived Duck Color Genetics Basics Ducks have come a long way since they were first domesticated from mallards and now come in many beautiful colors.

This article will explore how the genetics behind these colors work, and how a duck. The color of a duck's feathers is determined by two main factors: its internal structure and the presence of melanin. The internal structure of a duck's feather consists of a central shaft (rachis), a series of barbs, and tiny hooks that secure them in place.
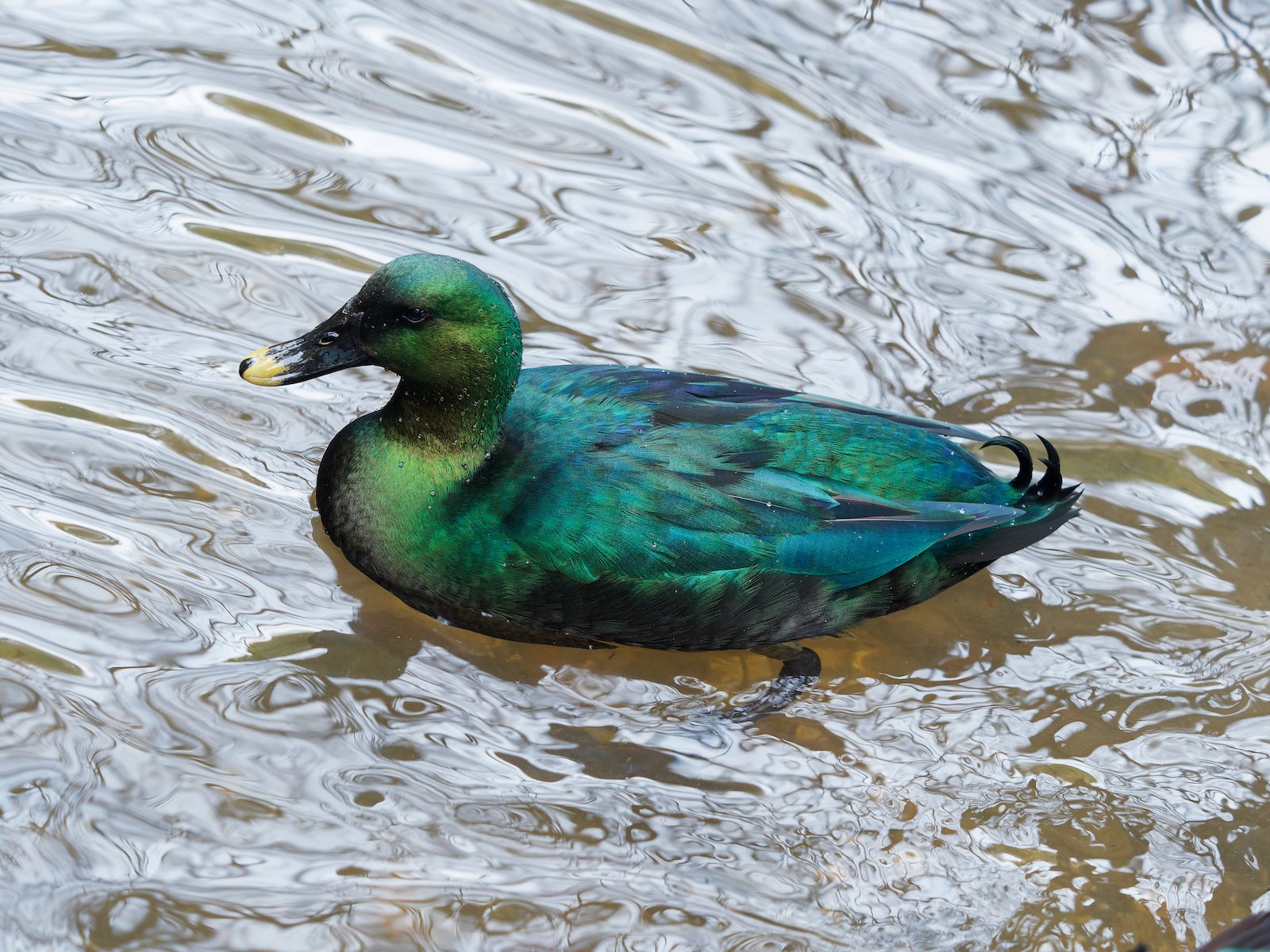

51 of the Most Colorful Ducks in the World | Color Meanings
It's this intricate arrangement that gives feathers their strength and flexibility. Colorful feature: The striking laced feathers of the flying steamer duck are somewhat uncommon in the duck world. Most of these ducks are pale gray-brown with darker brownish-black "lacing" around the feathers.

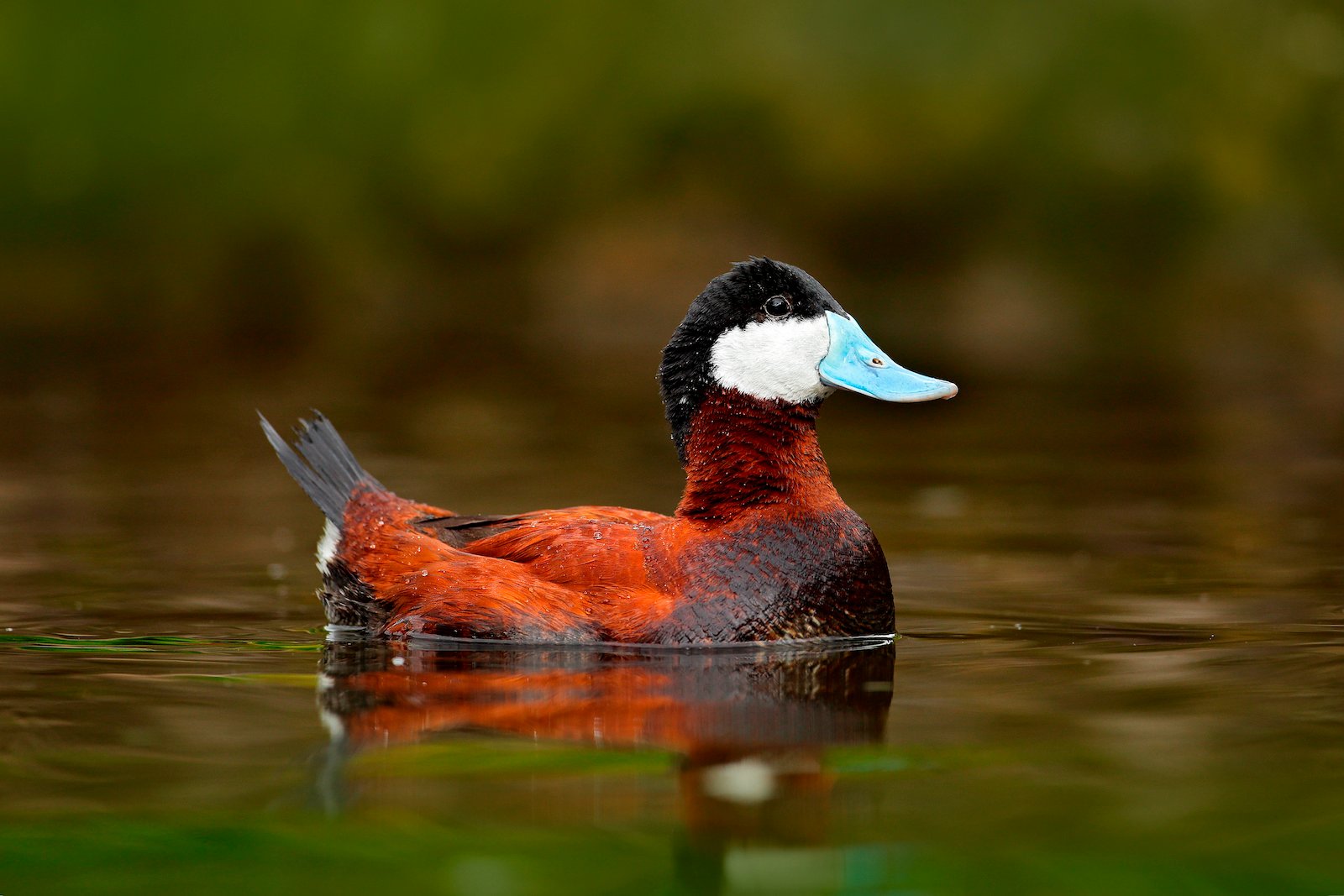
They also have a few white patches that stand out against the cool. This comprehensive guide explores 49 of the most popular types of ducks found in North America, highlighting their unique features, habitats, and behaviors. What is the Color of the Duck? There are many different species of ducks, and as a result, they come in a wide variety of colors.
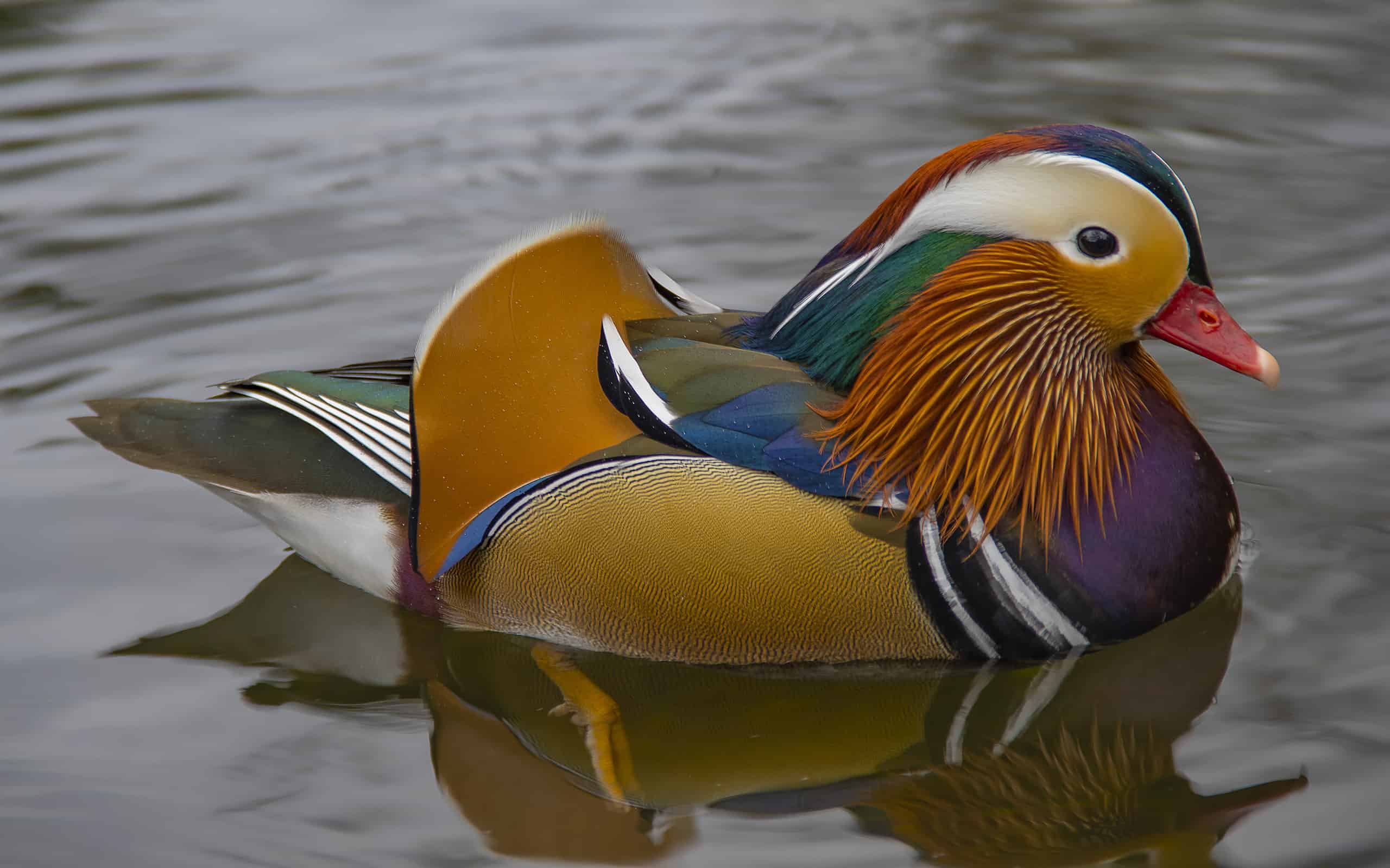

51 of the Most Colorful Ducks in the World | Color Meanings
The most common duck colors are brown, black, white, and gray. When it comes to ducks, breeding season males are usually the most colorful. Here are 15 most colorful wild ducks from around the world.

What colour is a real duck? Male ducks have red, white, and blue-gray plumage with white crescents, spots, and lines, while females are a plainer brown but still have distinctive white markings on the head. Are mallard ducks yellow? Male Mallards have a dark, iridescent. Duck Colour Genetics An introduction to duck colour genetics was published in 'The Domestic Duck' (2001, reprinted in paperback 2008).

51 of the Most Colorful Ducks in the World | Color Meanings
This analysis was based on the work of F M Lancaster and R G Jaap, and also took into account colours developed subsequent to 1963.