Pandas Background Color Options
As we know, the basic idea behind styling is to make more impactful for the end-user readability. We can make changes like the color and format of the data visualized in order to communicate insight more efficiently. For the more impactful visualization on the pandas DataFrame, generally, we DataFrame.style property, which returns styler object having a number of useful methods for formatting.

Using Styler to manipulate the display is a useful feature because maintaining the indexing and data values for other purposes gives greater control. You do not have to overwrite your DataFrame to display it how you like. Here is a more comprehensive example of using the formatting functions whilst still relying on the underlying data for indexing and calculations.
Cute Panda Background Set Graphic by PKDesign · Creative Fabrica
Use Pandas Styler to Change Text and Background Color Usually, it's a good idea to highlight data points you want to draw attention to. The convenient highlight_max() function assigns a yellow color to the largest value of every cell in a DataFrame: df.style.highlight_max() Image 6 - Highlighting max values (image by author) The highlight_min() function does just the opposite: df.style. I want the background color of the index cell (and just the index cell) A,C in blue and B,D in red.

I looked at the styling documentation but I could not find an example that matches this case. In this article, you'll learn how to add colours to a pandas dataframe by using pandas styling and options/settings. The Pandas documentation is rather extensive, but if you're searching for a.

Premium Vector | Three pandas with different colors and one has a ...
1. How do I style a Pandas DataFrame? To style a Pandas DataFrame we need to use.style and pass styling methods. This returns a Styler object and not a DataFrame.

We can control the styling by parameters and options. We can find the most common methods and parameters for styling in Pandas in the next section. The syntax for the Pandas Styling methods is: df.style.highlight_null(null_color.

Colorful Panda Wallpaper
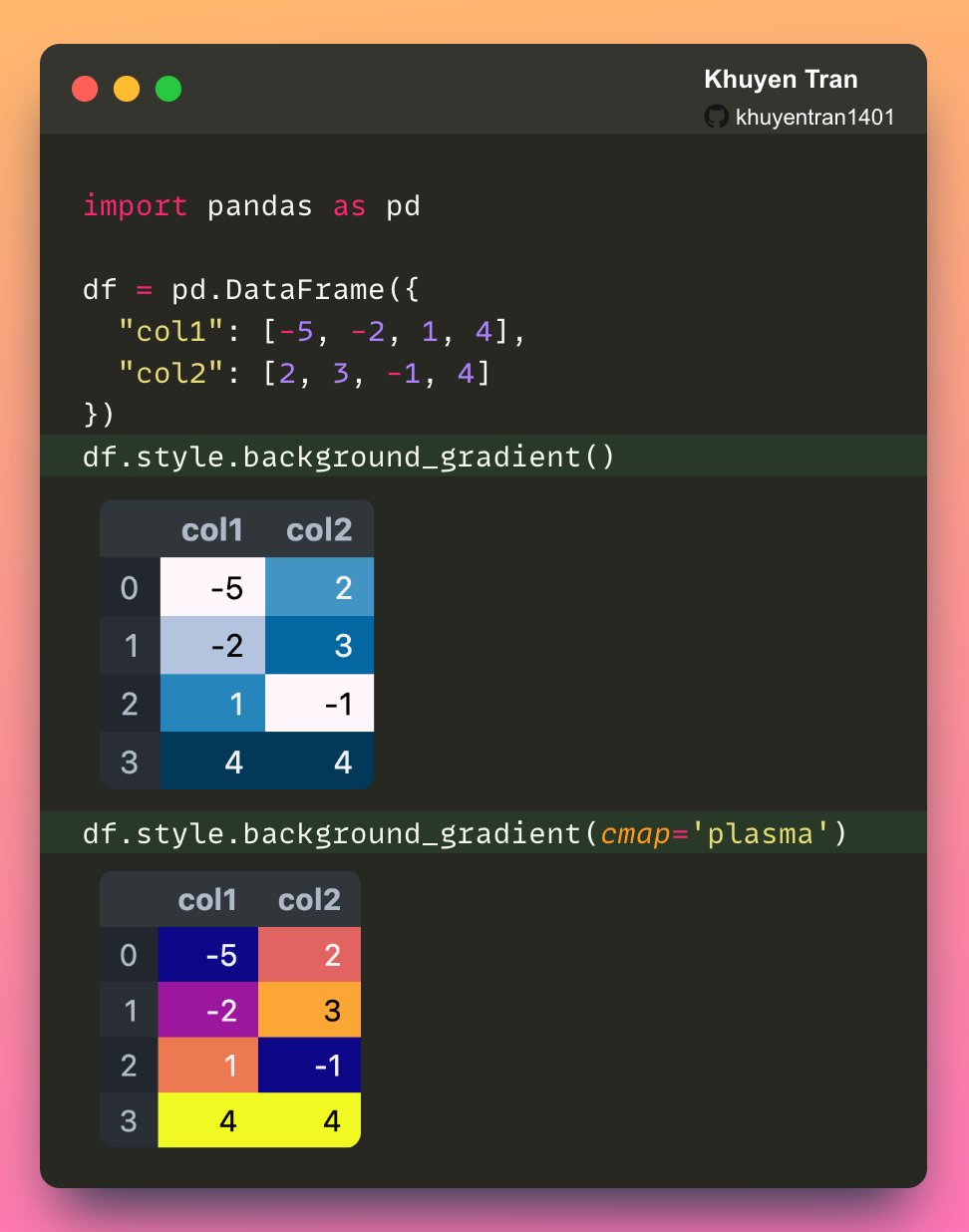
pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.background_gradient # Styler.background_gradient(cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None, text_color_threshold=0.408, vmin=None, vmax=None, gmap=None) [source] # Color the background in a gradient style. The background color is determined according to the data in each column, row or frame, or by a given gradient map. Requires matplotlib.

Parameters. The following line of code i=0 and the lines i= not i and return x can be thought of as the start and stop buttons for the function "format_color" we just created. "For factor in factors" calls on the previously defined list, then asks it to assign the sheets background colors based on the rules defined in "factor.".

Mastering DataFrame Styling in Pandas: Enhancing Data Visualization with Custom Formats Pandas is a powerhouse for data analysis in Python, offering robust tools for manipulating and analyzing datasets. Beyond its computational capabilities, Pandas provides a powerful styling API to enhance the visual presentation of DataFrames, making it easier to interpret and communicate insights. DataFrame.

Pandas is a widely-used data science library that presents data in table format, similar to Excel. Just like in Excel, you can customize tables by adding colors and highlighting important values. The Pandas Style API allows for similar styling within dataframes to enhance presentation and make data more visually appealing.

This article covers the features of Pandas styling, built.




