Bat Ear Color
Tadarida brasiliensis - Mexican Free-tailed Bat 4a. If ears proportionally large relative to body, more than 25mm from notch to tip, color black with three large white spots on back, one just behind each shoulder and the other at the base of the tail, then: Euderma maculatum. The Purpose of Bat Coloration Bat coloration primarily serves as an adaptive advantage, offering camouflage against predators.
During daylight hours, when bats are inactive and vulnerable, their fur color helps them blend into their roosting environments. Bats can be a range of colors, including red, tan, brown, and gray. A bat's ears are very important because bats use them to hunt for food.
Molecular evolution is echoed in bat ears | EurekAlert!
The ears tend to be large and noticeable, many times sticking up on the side of the head. The Allen's big. Big brown bats are closely associated with humans, often roosting in human-made structures and commonly using buildings as hibernacula.
It is the 3rd largest bat in SC. Big brown bats have a relatively heavy body, black ears and wing membranes, and a large head with a broad nose and powerful jaw. The pelage (fur) is dark above and light below and varies from glossy dark brown to pale.

Bat Ears Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock
The ears. Final Tools Available The Service developed final tools and guidance documents for the endangered northern long-eared bat (NLEB) and the proposed endangered tricolored bat (TCB). In the event that the tricolored bat is listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Act, these tools would be applicable to both species.

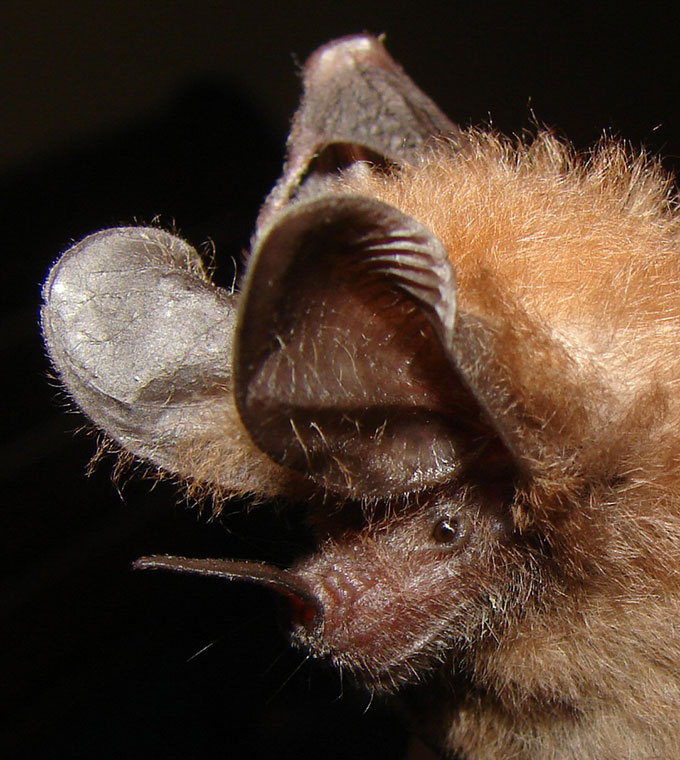
The shape of the ear, particularly the external pinnae, amplifies these high-frequency sounds. Some species, like the greater mouse-eared bat, even possess additional ridges on their ears to enhance sound reception. This adaptation not only aids in hunting but is also vital for navigating complex environments like dense forests.

Best Bat Ears Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock
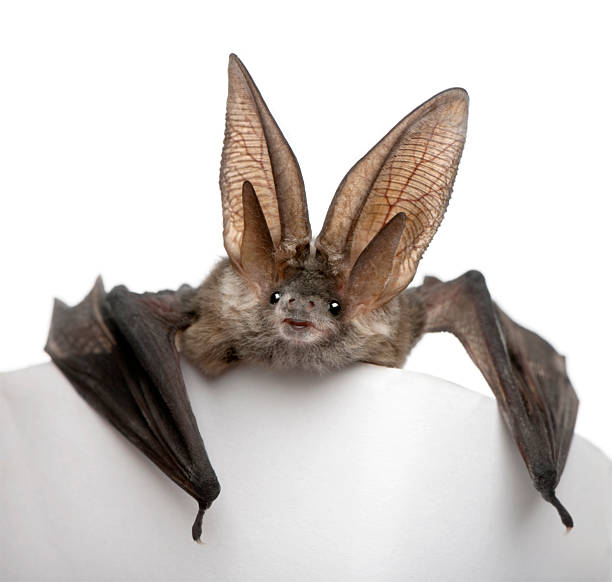
Bat (Common Long-Eared) - Appearance - The common long-eared bat is the second most common bat in the UK and is a highly agile hunter, using its unusually large ears to listen for prey. The adult bat has brown fur with a pale underside and a pink-brown face, while juveniles are more gray in color overall. P.

auritus have relatively large eyes, and slit-shaped nostrils that open laterally. The most distinguishing features are the animalπs ears, which are nearly the length of its whole body. It is named for its large ears, which have a role in thermoregulation.

It is a small canid, being of comparable size to the closely related cape fox and common raccoon dog. Its fur varies in color depending on the subspecies, but is generally tan-colored and has guard hairs of a grey agouti color. The bat-eared fox is found in Southern and East Africa, though the two subspecies are separated.

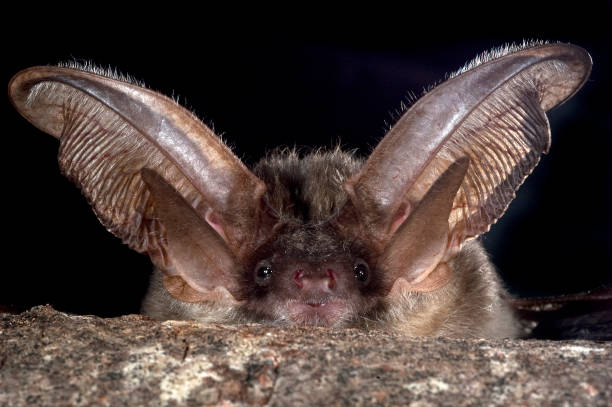
Introduction Brown long-eared bats are medium-sized. Their ears are nearly as long as their body but not always obvious: when at rest they curl their ears back like rams' horns, or tuck them away completely under their wings leaving only the pointed inner lobe of the ear (the tragus) visible. Brown long-eared bats feed in large gardens, along hedgerows, in parks and in woodlands.





