What Causes Fall Leaves To Change Color
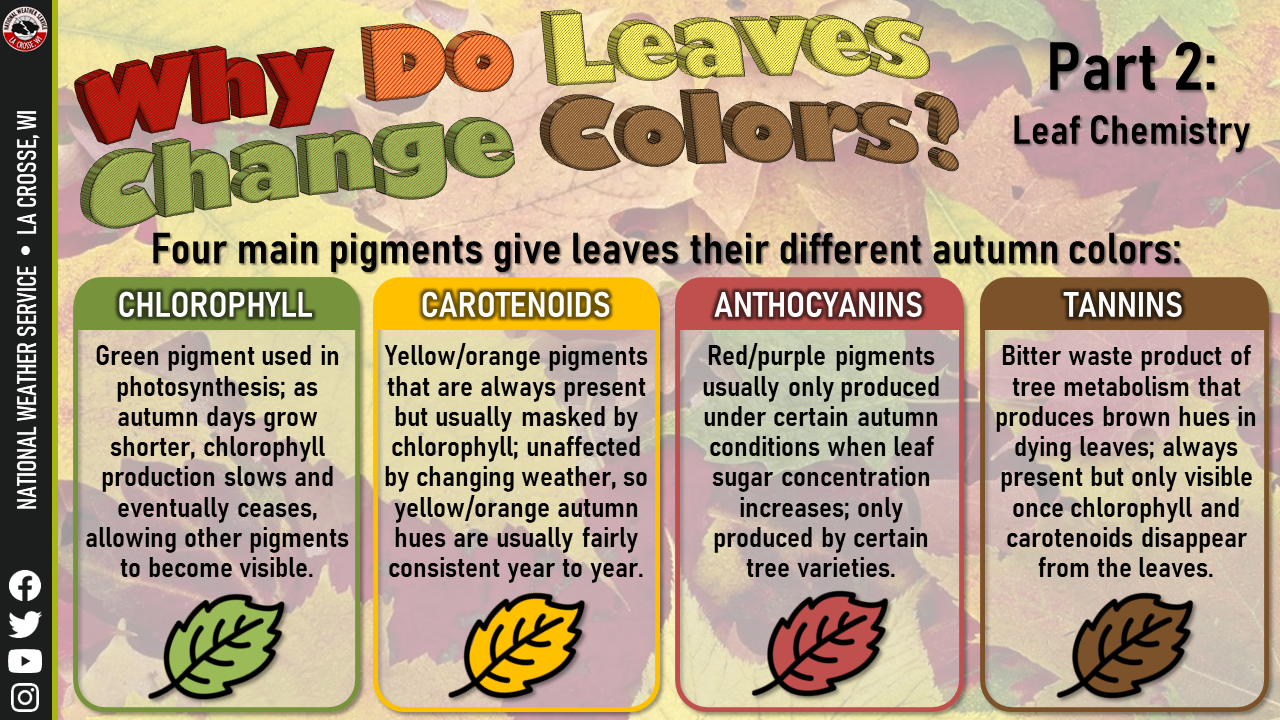
Darker red leaves are the result of a chemical change: Sugars that can get trapped in the leaves produce new pigments (called anthocyanins) that weren't part of the leaf in the growing season. Some trees, like oaks and dogwoods, are likely to produce red leaves. Explore why leaves change color in fall, the role of sunlight and pigments, and top tips for spotting the brightest autumn foliage this season.

Brilliant Fall leaves on the Superior National Forest. (Forest Service photo) Certain colors are characteristic of particular species: Oaks: red, brown, or russet Hickories: golden bronze Aspen and yellow-poplar: golden yellow Dogwood: purplish red Beech: light tan Sourwood and black tupelo: crimson The color of maples leaves differ species by species: Red maple: brilliant scarlet Sugar maple. The peak dates for fall foliage in the U.S.

Why Leaves Change Color in the Fall - Chemistry
vary from region to region. Colors change first in the North and in higher elevations, then spread south and to lower elevations. Admiring the vibrant red leaves that add so much color to Acadia's fall landscape.

NPS Photo/Hadley Seymour When the temperature drops and there is less daylight, the tree begins to conserve the energy it generated in the spring and summer months. One way trees save energy for winter is by dropping their leaves. As autumn progresses, a tree will send a substance to each leaf called an enzyme.

Science Sundays: Why Do Leaves Change Color in Autumn
Moderate drought stress in the fall can enhance red pigment production, provided the stress is not severe enough to cause premature leaf drop. The Final Act: Leaf Abscission The color change culminates in leaf abscission, the shedding of leaves from the tree. This protective mechanism allows deciduous trees to conserve water and energy during.

The color change usually happens before the leaves fall off of the tree. Why might that be? It takes a lot of energy to make chlorophyll. If the plants break down the chlorophyll and move it out of their leaves before the leaves fall, plants save energy.

What causes leaves to change their color in fall? Illustrated
The plants can reabsorb the molecules that make up chlorophyll. Then, when it's warm and sunny enough to grow again, the plants can use those. Learn why leaves change color in the fall and see the chemistry of the pigment molecules responsible for different leaf colors.

What is the chemistry that causes all those beautiful hues to appear in the fall. Jason Grabosky, a professor and program director of Urban Forestry in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences, explains the process that makes leaves change color, the factors that influence the shades that. In many places around the world, autumn is marked by the slow, beautiful change of green foliage to vibrant reds, oranges, yellows, and purples.

Green leaves appear green because of the presence of the pigment chlorophyll, which is key to photosynthesis.