Snake Color Genetics
The genetics of snake color morphs work through simple genetic principles where mutations affect pigment production and distribution. You'll find that most morphs follow dominant-recessive inheritance patterns - recessive traits like albinism require two copies to express, while dominant ones need just one. Color mutations in snakes arise from genetic alterations that affect pigment production, distribution, or expression, resulting in snakes with extraordinary appearances that rarely occur in nature.

Beyond their aesthetic appeal, these mutations offer valuable insights into reptile genetics and inheritance patterns. The Basics of Snake Genetics Image Source If you are into snake breeding, it is important to understand its genetics, especially if you like to produce patterns and color morphs. Most snakes are popular when it comes to morphs because each snake species has unique attributes, may it be physically or behaviorally.
Colorful Snake Species
Basic Reptile Genetics 101 A look at mutations and how they are reproduced Over the last 15 years or so the practice of breeding snakes exhibiting various mutations of color or pattern has gained wide popularity. With the influx of newcomers to the hobby, a lot of questions are generated about how these traits are inherited and a lot of misconceptions are prevalent among this group of new. A deeper understanding of adaptive features can guide efforts to maintain biodiversity, ultimately benefiting broader ecological systems.

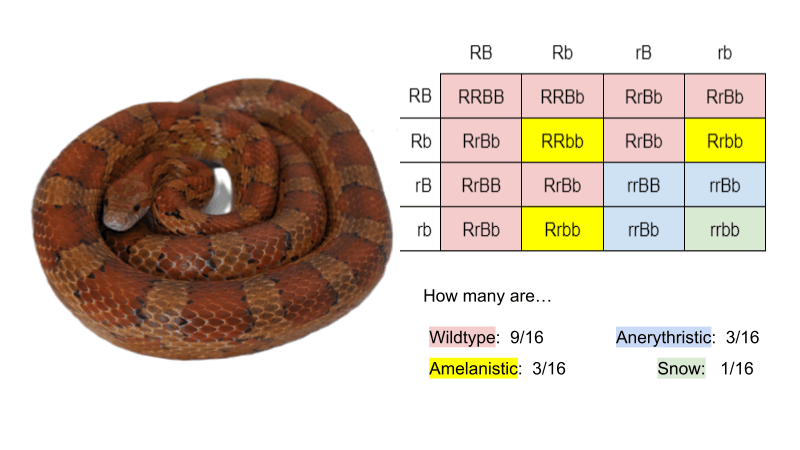
Final Thoughts on Snake Coloration and Its Genetic Underpinnings Understanding the genetic basis of snake coloration and patterning reveals a complex interplay between genetics, environment, and evolution. The color squares in that first example also show DOMINANT and recessive, but let's dig a little deeper to gain a more thorough understanding. In case you have not yet noticed.
Snakes reveal the origin of skin colours | Science Codex
Finally, we explore macroevolutionary patterns of snake coloration, including phylogenetic tests of color variation, directionality of transitions and rates of change, and ecological correlates of. Discover snake color pattern inheritance! Learn how genetics shape stunning morphs, from dominant and recessive traits to creating unique variations. In snake breeding, this is the color and/or pattern of the animal.
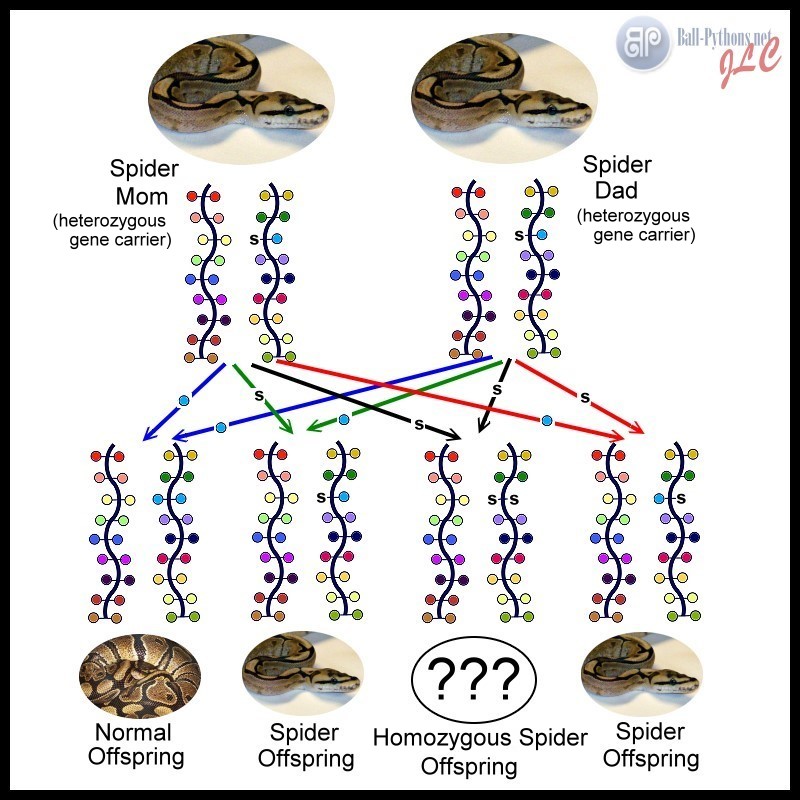
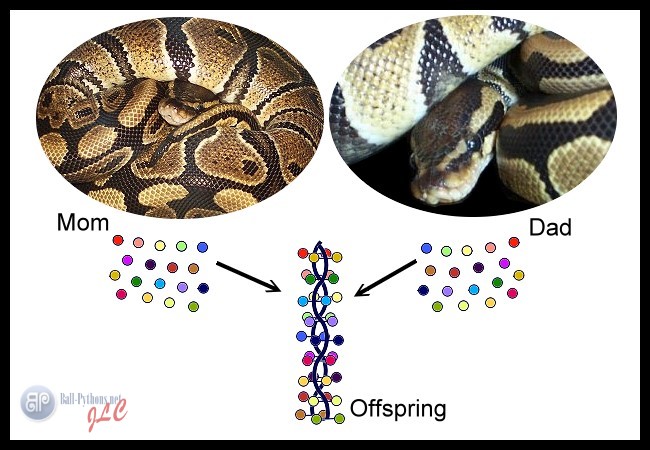
GENE INHERITANCE The genes involved in color/pattern morphs of snakes come in pairs. Genes have one spot on an animal's DNA for a pair of alleles to "sit" or be present, hence the terms heterozygous and homozygous as mentioned above. In the intricate world of animal coloration, the patterns and hues adorning skin are not merely aesthetic but serve vital functions such as camouflage, communication, and thermoregulation.
Corn Snake Color Morphs: 60+ Stunning Types, Patterns & Genetics Guide
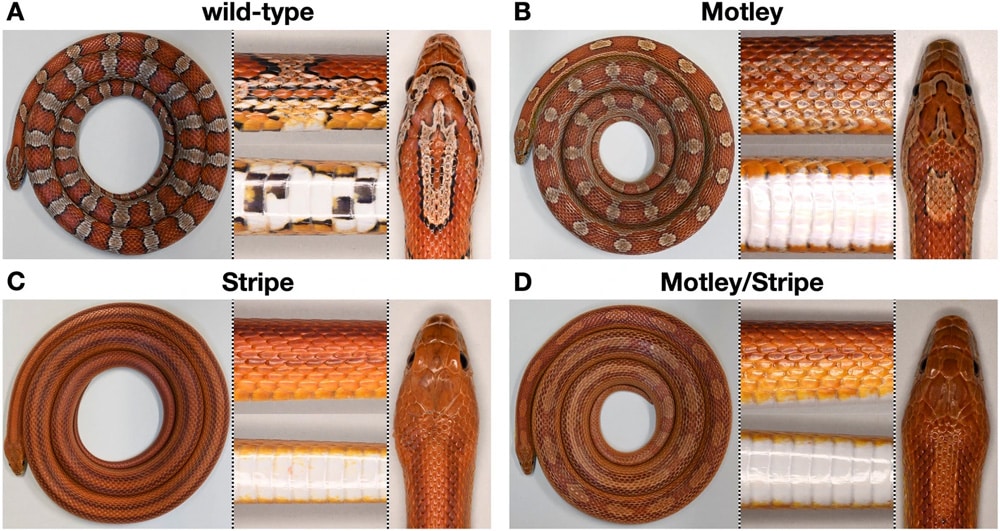
Among the dazzling variety of nature's palette, the corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) offers a striking example with its diverse color morphs that have fascinated geneticists and evolutionary biologists.








