Apple Colour Change Due To
This explains why apples from the same tree can show color variations depending on their position in the canopy and light exposure. Ripening's Role in Color Transformation As an apple matures and ripens, a series of biochemical changes occur that profoundly alter its color. The level of anthocyanins that accumulate in a plant depends on the environmental conditions.

For example, light exposure influences anthocyanins to accumulate rapidly in apples (Malus domestica cv. "Red Fuji"), prompting a color change. However, the molecular mechanism that causes light.

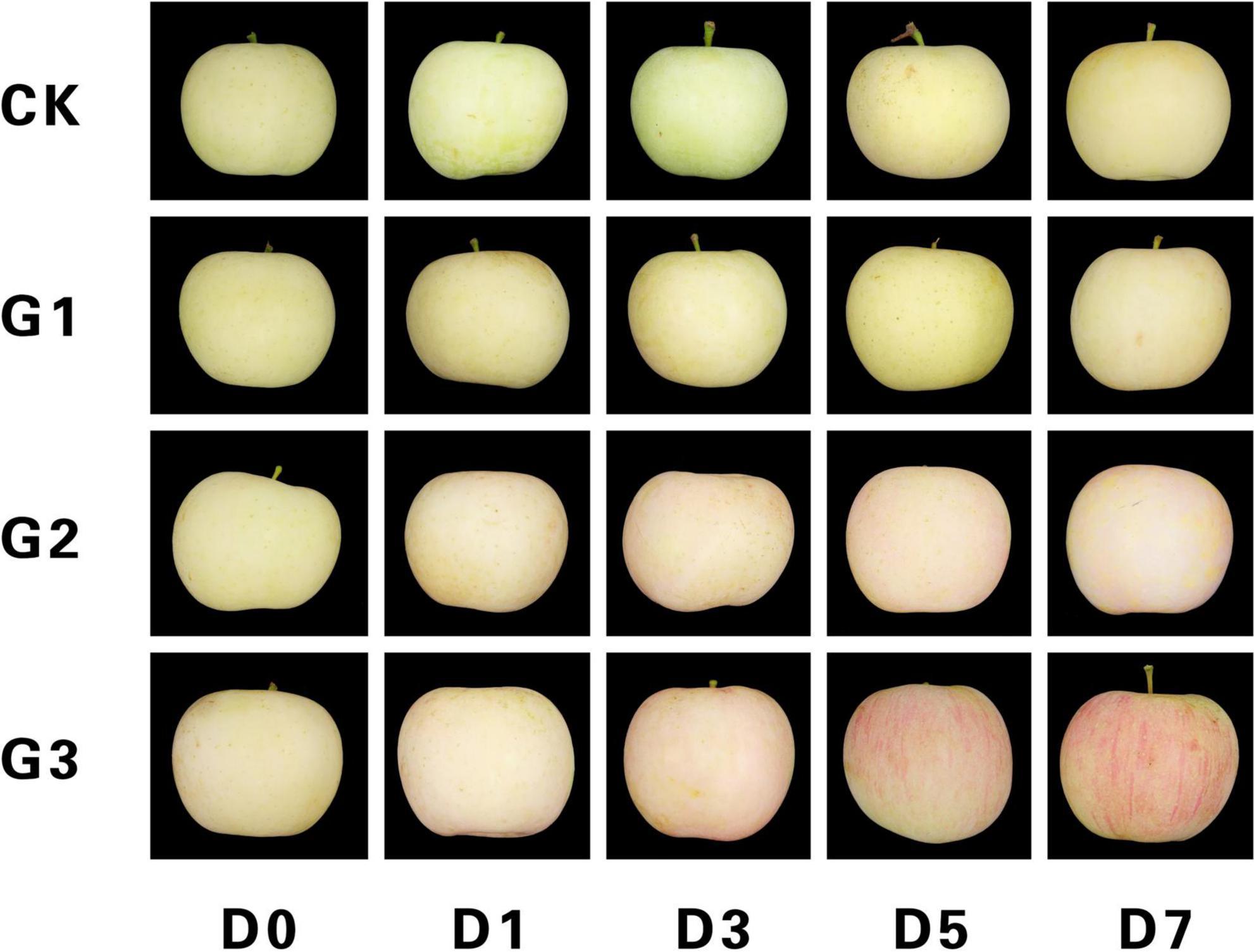
Color change on dried apple slices subjected to dipping pre-treatments ...
O-quinones then produce the well documented brown color by reacting to form compounds with amino acids or proteins, or they self. Why do apples change color? In summary, apples experience major pigment alterations as they ripen: Chlorophyll levels decrease due to shading, chloroplast breakdown, conversion into other pigments, and unmasking by anthocyanins. Anthocyanin pigments already present become visible as chlorophyll declines.

Apples are among the most consumed fruits worldwide, appreciated not only for their taste but also for the variety of colors they exhibit, primarily green and red. But what determines an apple's color? And why are some green while others are red? This article explores the biological and environmental factors that influence the coloring of apples. Fruit surface color is complex due to genetics and mutations, environmental factors, crop load, plant nutrition, plant stresses, and plant growth regulators.
Apple Color - Western Agricultural Research Center | Montana State ...
Have you ever been wandering through an apple orchard or the produce section of your grocery store and wondered why apples are different colors? If you have, today is your lucky day. We did the research so you don't have to. Keep reading to learn why apples are different colors.
The most common apple colors are red, green, and yellow. Anthocyanin concentration is an important determinant of the colour of many fruits. In apple (Malus × domestica), centuries of breeding have produced numerous varieties in which levels of anthocyanin pigment vary widely and change in response to.

An apple with a distinct colour change : r/mildlyinteresting
Apple also undergoes a colour change as a result of the reduced production of chlorophyll and its degradation causing the unmasking of pigments that were already previously formed and synthesis of new pigments (carotenoids or anthocyanins) (Ferrer et al., 2005). What makes an apple change color?Plant Cell. 2021 Oct 11;33 (10):3185-3186.

doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab197.