Science Line Graphs
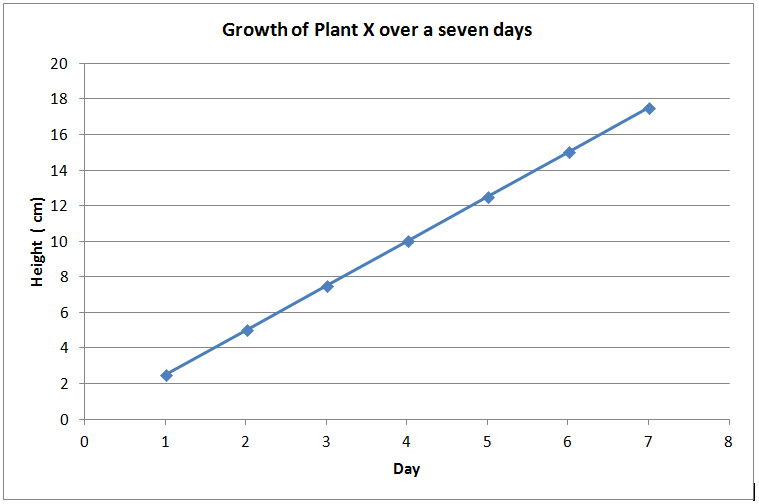
Use a line graph when you want to show how something changes over time or with different amounts. For example, you can use a line graph to show how tall a plant gets each day or how much a rubber band stretches with different weights. Line graphs help you see patterns and trends in your data.
Drawing and interpreting graphs and charts is a skill used in many subjects. Learn how to do this in science with BBC Bitesize. For students between the ages of 11 and 14.

Ms. Robinson's Super Scientists: Unit 1: Day 6 - Types of Graphs
Students will review the various types of graphs used in sharing results of an experiment: bar graph, line graph, pie charts and more. Students get practice creating graphs, and interpreting and analyzing graphs in this scientific method and nature of science lesson. This product includes:* Engaging 14 slide PowerPoint complete with instructions and student examples * 4 Pdf student pages * 3.

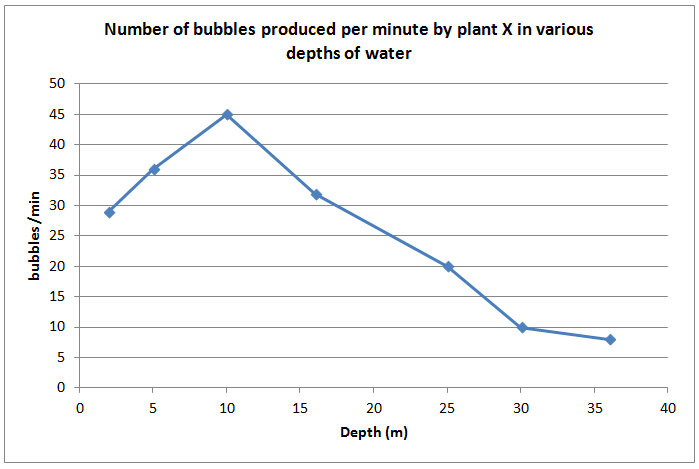
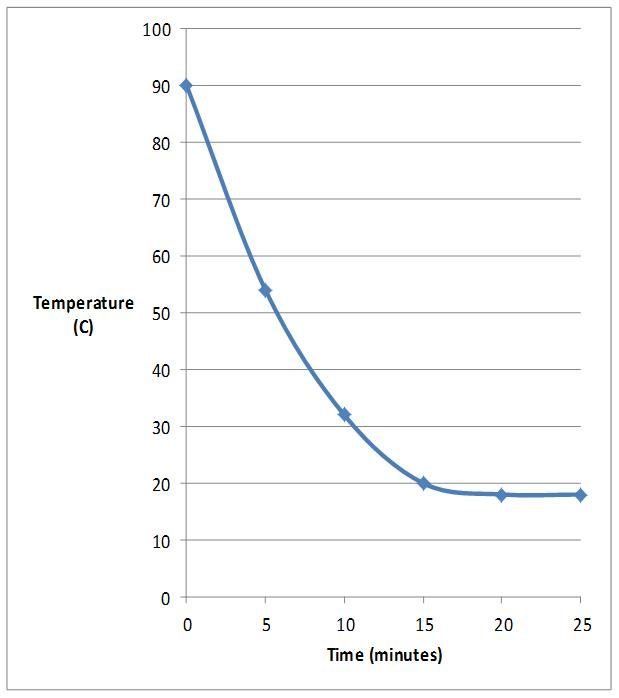
What a Line Graph Shows A line graph is a visual tool designed to display continuous data and illustrate trends or changes over a period. It shows how one variable influences another or how a variable evolves. This type of graph connects individual data points with straight lines.

Line Graphs | Western Sydney University
This is a straightforward guide to drawing graphs in KS3 and GCSE science coursework and exams. It points out common pitfalls and shows a step. Line graphs are the Swiss army knives of data visualisation.
They can be almost anything which is both good and bad. Line graphs are slow to interpret Many graphs serve one clear purpose. Ta.
Line Graph For Science
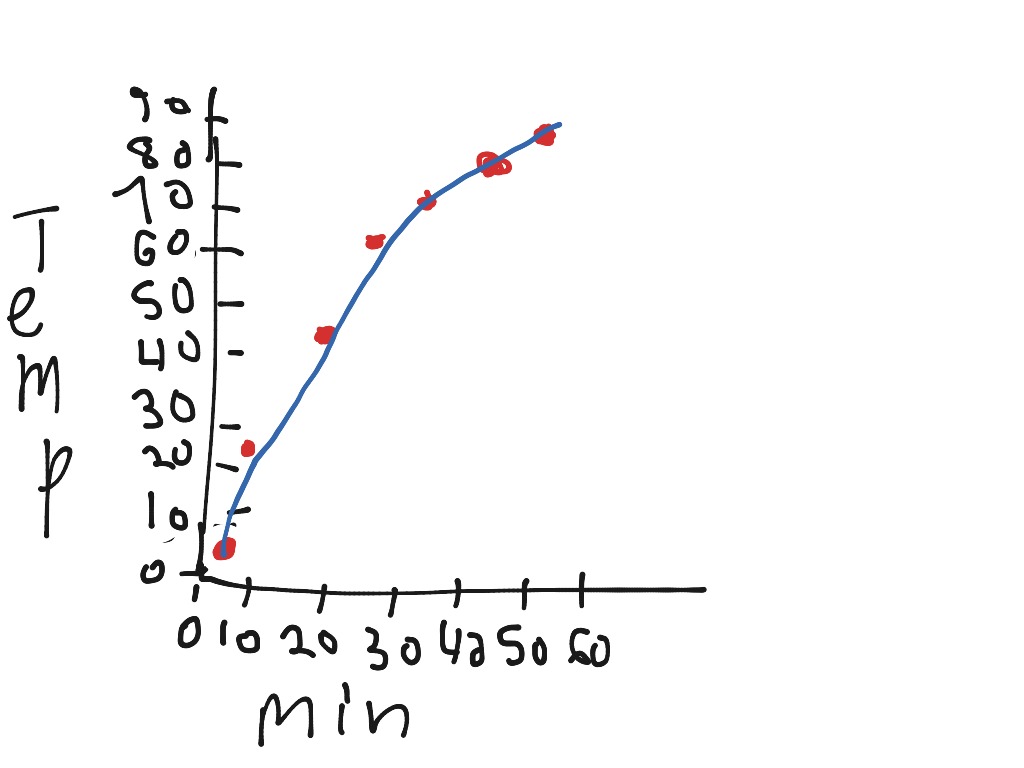
Line Graphs Graphing is an important procedure used by scientists to display the data that is collected during a controlled experiment. The most common type of graph used in biology is a line graph. A graph contains five major parts: A title.

How to Make a Line Graph Use graph paper (1) Choose the size graph paper that best fits the data Number the X-axis (the horizontal one)- Independent Variable (2) Start numbering at your lowest value (if the lowest value is 23, you don't need to start num-bering at zero-start numbering at 20!). A look into line graphs, eigenvalue multiplicity, and related graph theory concepts. Imagine a graph as a collection of points (called vertices) connected by.

A line graph shows the relationship between independent and dependent values of data, and are usually used to show trends over time. In the graph each data value is represented by a point in the graph that are connected by a line.