Democracy Vs Authoritarian
The debate over democracy vs authoritarianism is crucial because the type of government a country has shapes the lives of its people. It affects education. To better safeguard democracy, we have to understand the foundations of the surge in authoritarian leadership - we needs answers to fundamental questions like why authoritarian leaders gain support and how democracy becomes authoritarian.
Above all, we need to understand what an authoritarian government is and how different it is from democracy. Can a Democracy be Authoritarian? There are democratic authoritarian regimes that exist around the globe. This terms used to describe this form of government are "competitive authoritarianism" or "illiberal democracy.".
Democracy VS Authoritarianism - YouTube
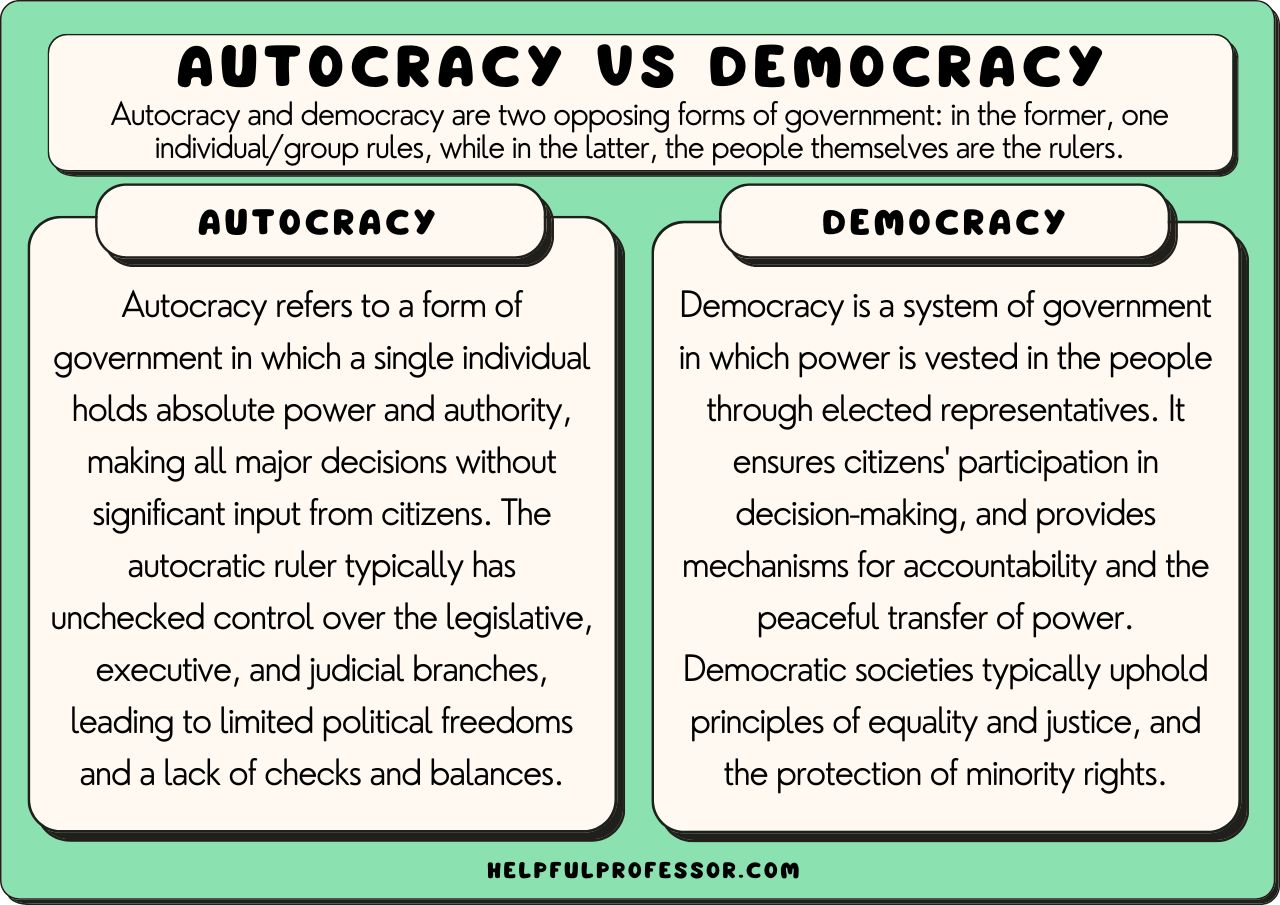
Authoritarian vs. Democracy What's the Difference? Authoritarian and democracy are two contrasting forms of government. Authoritarianism is characterized by a single leader or small group of individuals holding all the power and making decisions without input from the general population.

Similarly, Democracy and Authoritarian were established. So, what exactly is the difference between Democracy and Authoritarian? These two types of government are differentiated based on factors like definition, ideologies, characteristics, structure, etc. Economic Performance: Democracy vs.

Difference Between Authoritarian and Democracy | Difference Between ...
Authoritarianism Many studies show that democracies often have better long. Both the erosion of democracy and dictatorial drift are underpinned by the emergence of conservative and reactionary civil society, which mobilize and channel the demand-side anti-liberal and authoritarian preferences (see Youngs 2018; Ekiert 2019, 2021; Atalay 2021; Platek 2023). 1.
1.3 - Democracy vs. Authoritarianism In this topic we will explore how we can define political regimes. As a reminder, political regimes defines the set of rules and norms that determine the political system.

Authoritarian vs. Democratic by Meredith Bagnell on Prezi
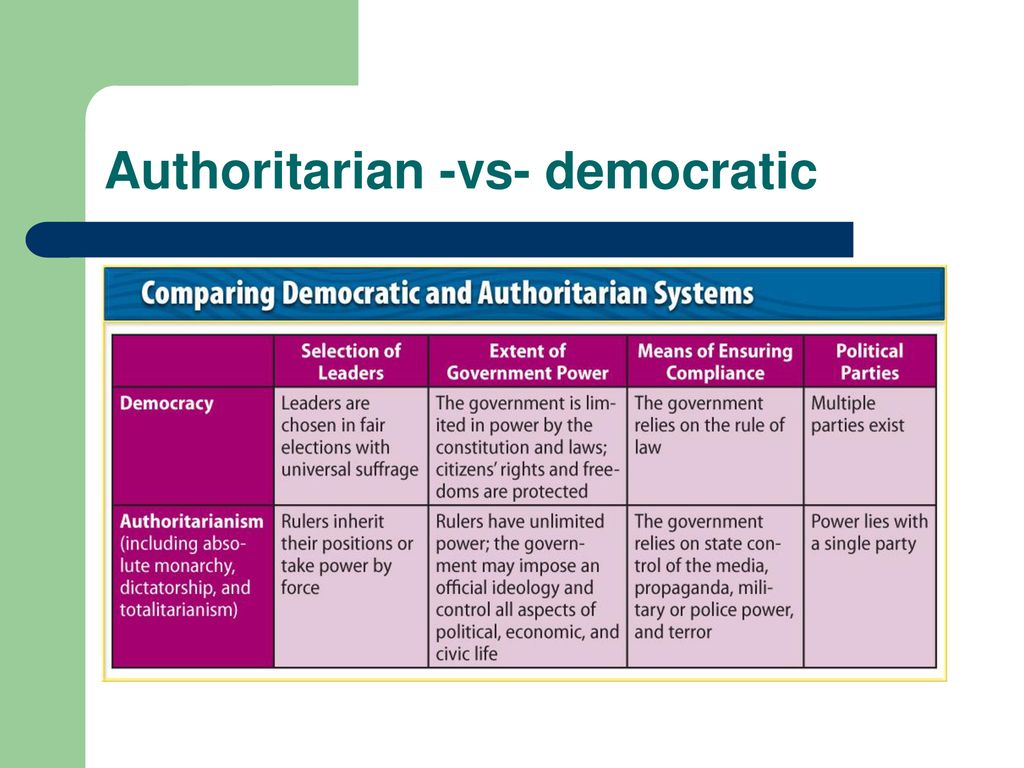
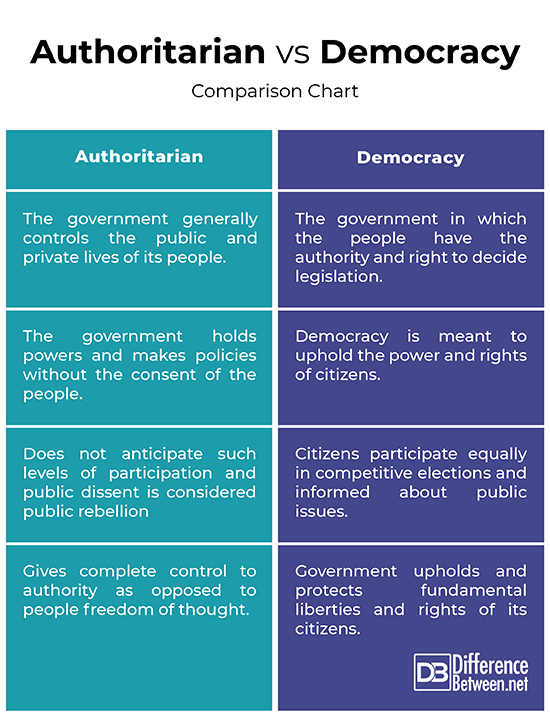
The regime defines who has the power, and that has significant implication in the lives of the citizens of a nation. 👥. Authoritarian regimes are characterized by concentrated power and limited freedoms.
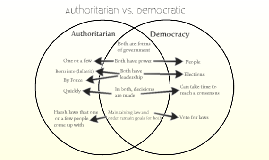
Democracies prioritize individual rights, political freedoms, and power diffused among citizens. Choice depends on values regarding freedom, equality, and governance structure. Democracy vs.

Authoritarianism Democracies, like the U.S., operate on systems of checks and balances in which power is distributed among elected officials, independent courts and a free press.