Fish Color Eyes
These eyes are specialized for sensitivity rather than detailed color vision, as many deep-sea species primarily perceive blue-green light. Conversely, some cave-dwelling fish, like the Mexican cavefish, have evolved greatly reduced or even absent eyes because vision is unnecessary in their perpetually dark habitats. Fish are peculiar creatures with exceptional abilities, despite their limitations compared to humans.

Because of their environment and need to survive, questions arise on their senses, particularly the eyes. For instance, can they see color? If they do, what colors do they see? How well do they see? It turns out fish have a different view of the world than us humans, maybe even better. Vision in fish An oscar, Astronotus ocellatus, surveys its environment Vision is an important sensory system for most species of fish.
How and What Fish See Underwater | Sport Fishing Mag
Fish eyes are similar to the eyes of terrestrial vertebrates like birds and mammals, but have a more spherical lens. The Science Behind Color Vision in Fish The Anatomy of a Fish's Eye Fish eyes are composed of several parts that work together to create clear images. The cornea and lens focus light onto the retina, which contains photoreceptor cells called rods and cones.

Rods help fish see objects in low light conditions, while cones enable color vision. What do fish eyes look like? Fish eyes are similar to the eyes of terrestrial vertebrates like birds and mammals, but have a more spherical lens. Birds and mammals (including humans) normally adjust focus by changing the shape of their lens, but fish normally adjust focus by moving the lens closer to or further from the retina.

What do fish eyes look like?
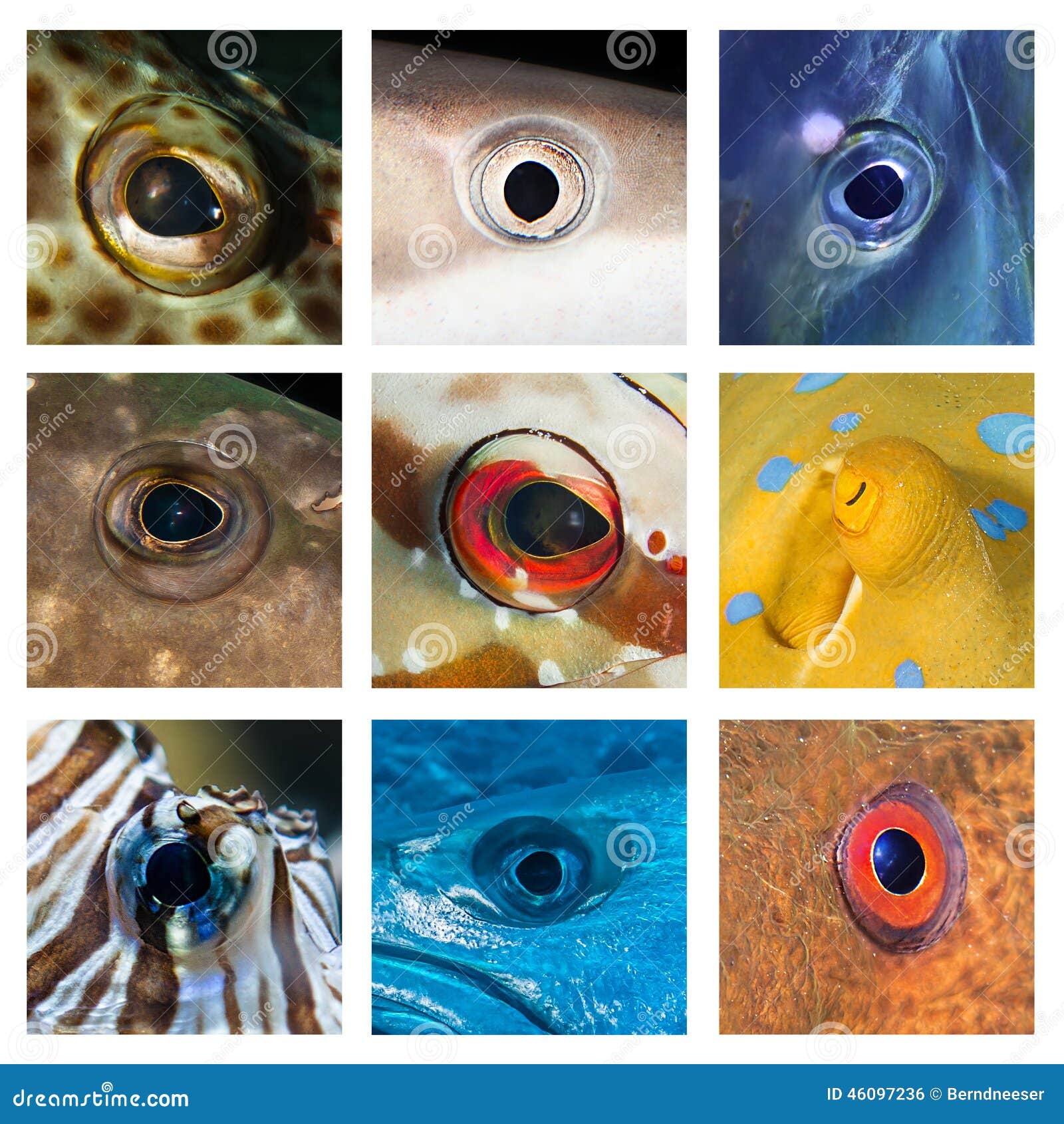
Explore the fascinating world of fish vision and learn about the physiology of their eyes, types of photoreceptor cells, color perception, and factors influencing their ability to see in color. Other fish have spots of color in their eyes. The striped mullet, for example, has a bright yellow splotch in its iris, while specks of blue-green decorate the pupils of the balloonfish.

And still other fish have colorful irises. They're usually in shades of yellow, orange, or red. The eyes of the striped burrfish, though, are bright green.

Vibrant colors of a tropical fish eye in extreme close up 24617181 ...
What do fish eyes look like? Fish eyes come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors depending on the species. Like human eyes, fish eyes contain specialized cells and structures that allow them to see clearly underwater. But fish eyes are also uniquely adapted to the marine environment and the fish's lifestyle.
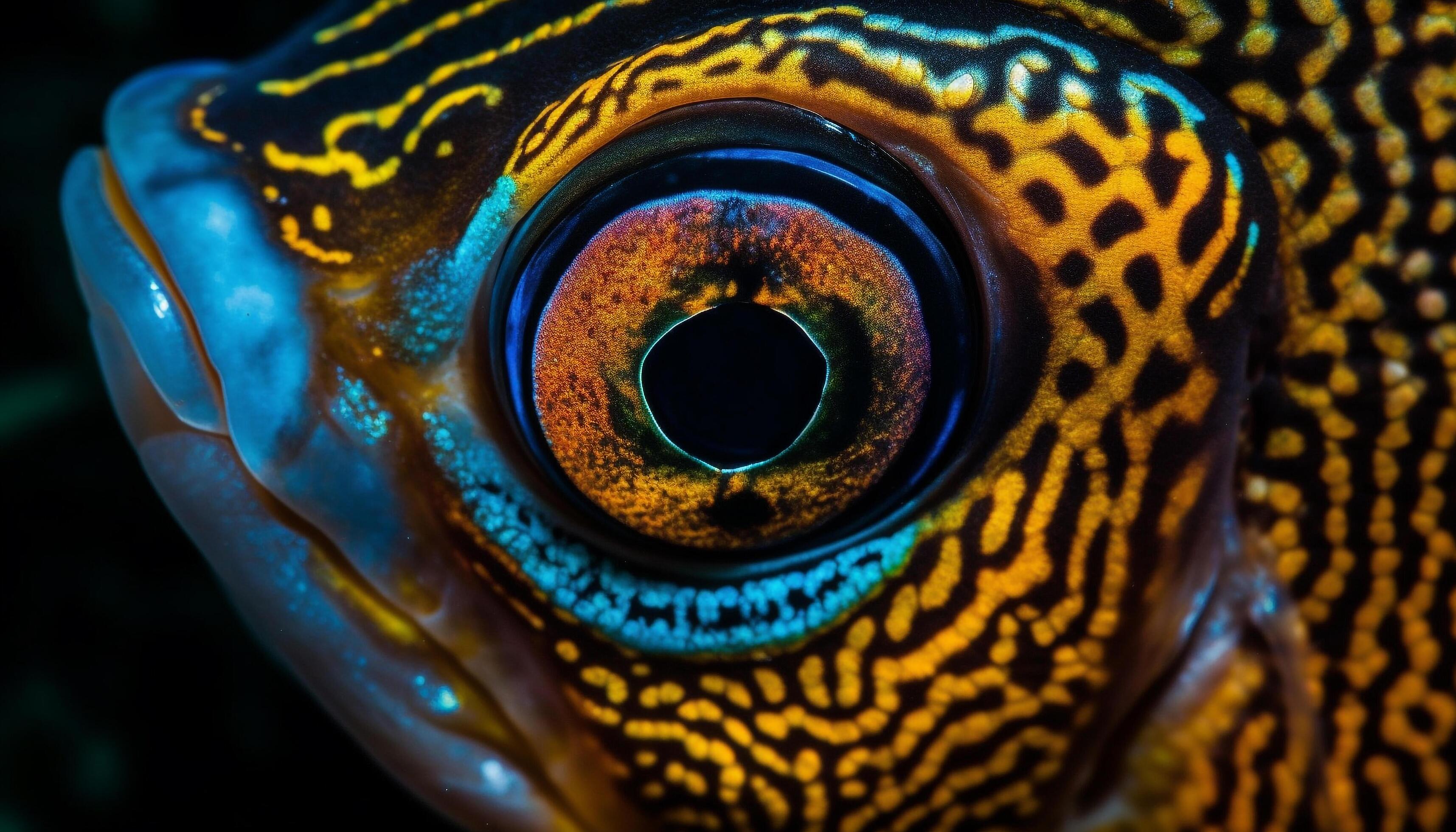

The majority of fish have developed eyes that will detect the type of colors typical of their environment. For example, inshore fish have good color vision, whereas offshore pelagic fish have limited color vision and detect only a few if any colors other than black and white. In fact, to the eyes of a fish, yellow is perhaps an effective colour to camouflage with.
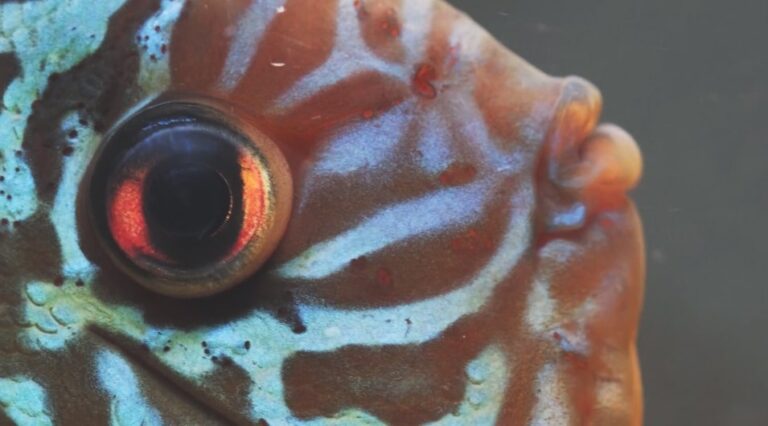

For example, some fish like the regal angelfish are coloured in closely spaced yellow and blue stripes.






