Elephant Urine Color
Kidney disease is quite common in elephants. The analysis of urine is important. This page describes the routine urinalysis and some specific features related to elephant urine.

Protein detection can be done by refractometry and sulfosalicylic acid (SSA)precipitation. Comparing osmolarity in serum and urine gives an indication for the presence of kidney failure. The elephant's urinary system is designed for rapid fluid ejection, thanks to a long and wide urethra.
How elephants communicate
The urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, plays a crucial role in determining the speed and volume of urine expulsion. Urine was collected from 22 healthy female adult Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) and analyzed for the purpose of determining normal biochemical and microscopic parameters. Findings included urine that was less concentrated compared to other mammals, predominantly alkaline pH, crystalluria of varyi.

This study analyzed urine samples from 22 healthy female Asian elephants to establish normal biochemical and microscopic parameters. Findings indicated that elephant urine is less concentrated, predominantly alkaline, and contains various types of crystals, with minimal cellularity and no glucose or urobilinogen detected. Establishing baseline values for elephant urine is crucial for.

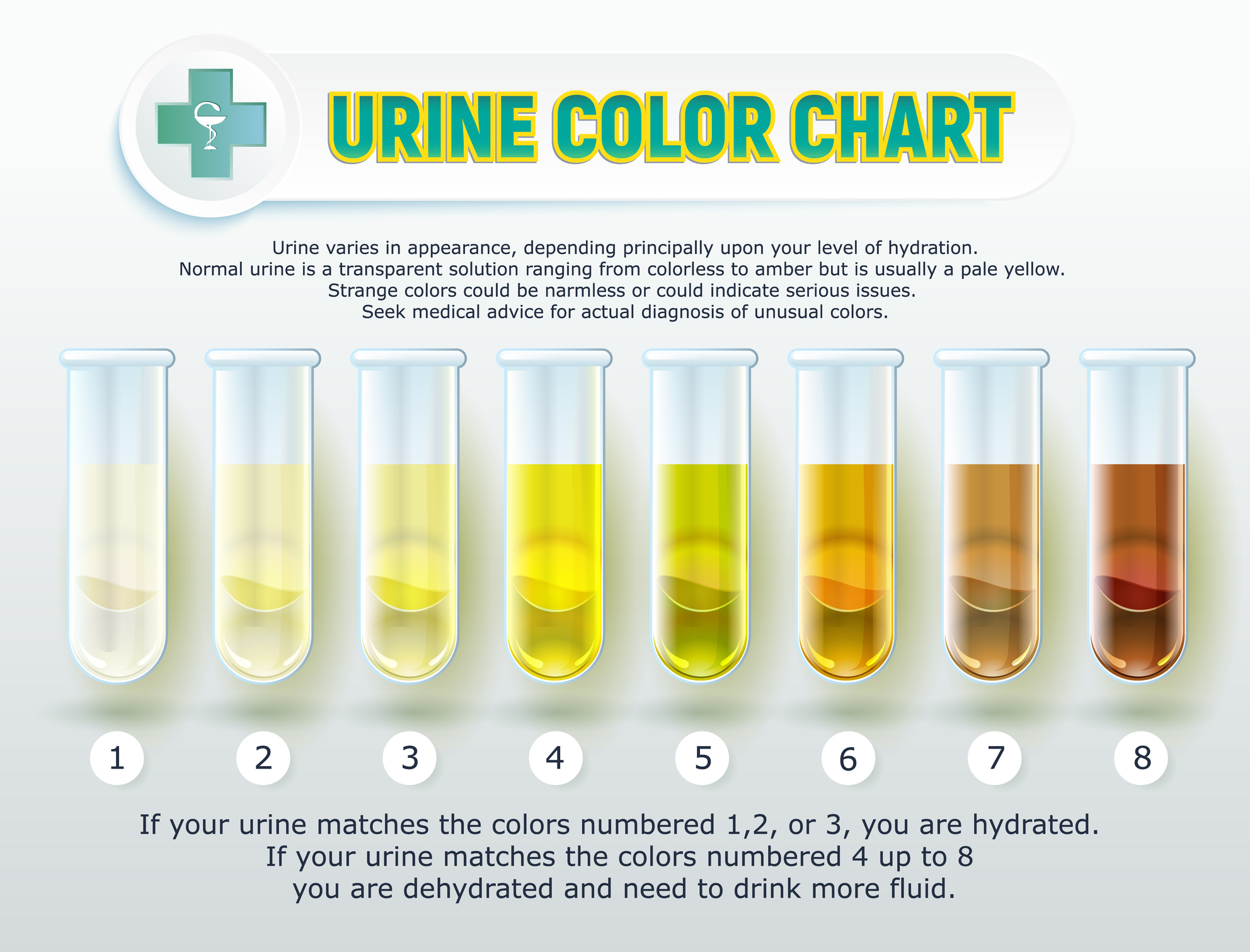
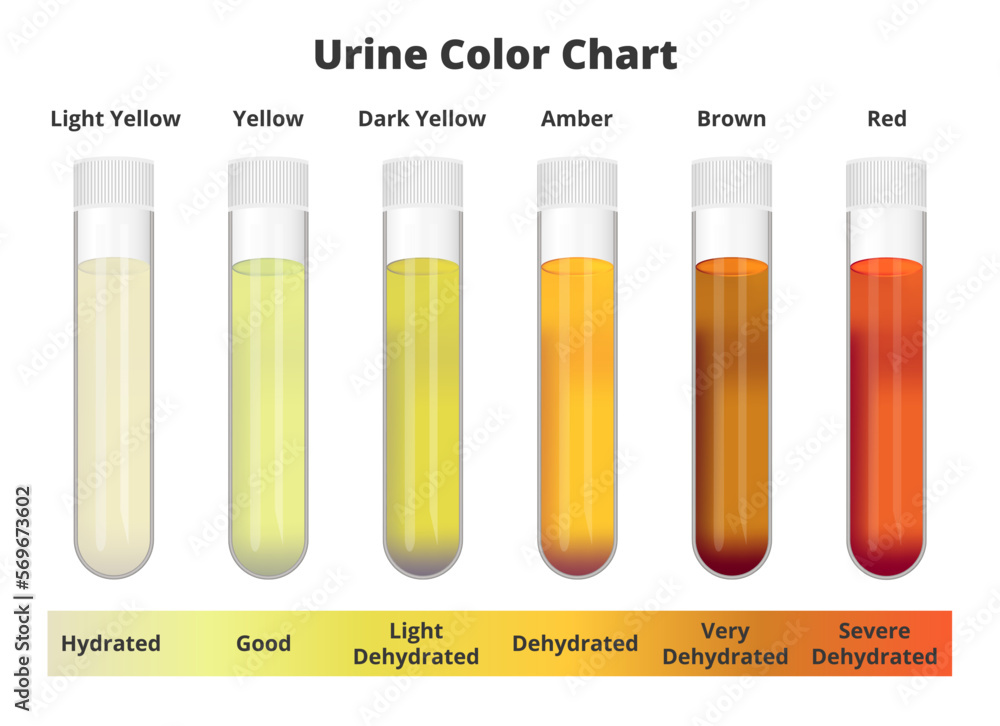
Urine color chart. Vector test tubes with different colors of urine or ...
Abstract: A 37-yr-old female Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) presented with anorexia, restlessness, and dark- colored urine. Urinalyses showed hematuria, leukocyturia, isosthenuria, proteinuria, granular casts, and no calcium oxalate crystals. Bloodwork revealed azotemia.
Urine culture revealed a pure growth of Streptococcus zooepidemicus resistant to sulfamethoxazole. Elephant urine analysis is one of the less explored arena compared to haematology and serum biochemistry of elephants. Despite of the confirmation that elephants develop urinary tract infections, data regarding the same is very limited.

80 Elephant Urinating Images, Stock Photos & Vectors | Shutterstock
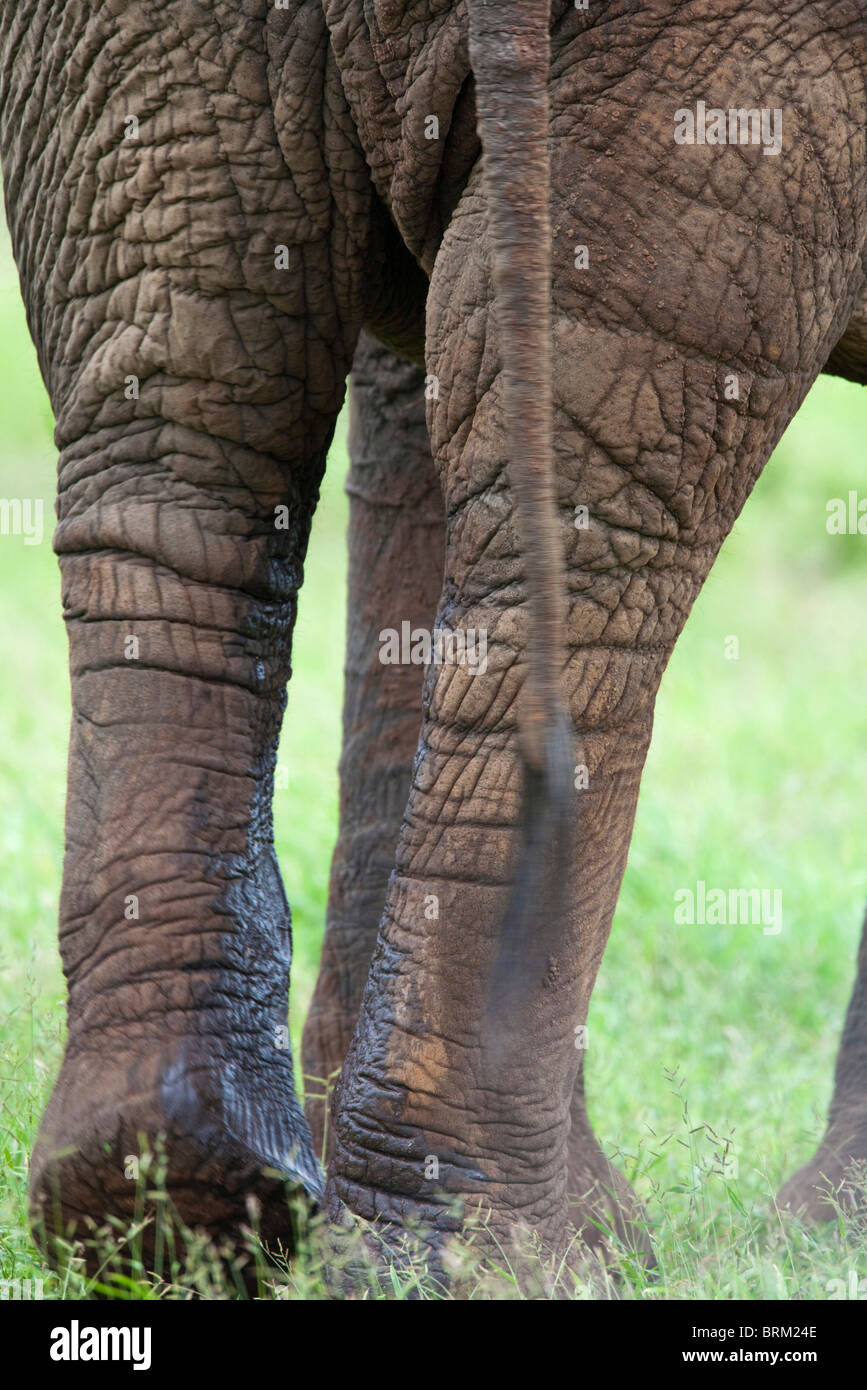
The continual dribbling of urine gives the inner hind legs black shiny appearance and may turn the sheath of the penis a light greenish coloration. The urine has a very pungent odor that can be detected downwind from the musth male and from the urine trail he deposits. The elephant also showed clinical signs of urinary incontinence and turbid urine over the previous six months.

Laboratory Tests: Blood was collected from the auricular vein for pre. Lymphoid follicu-lar vulvitis n African (Loxodonta africana) and Asian (Elephas maximus) elephants Anthrax and cow-driosis in an African elephant (Loxodonta africana) A morphologic study and diagnostic ultrasonography of Asian elephant kidney Diagnosis and treatment of presumptive pyelonephritis in an Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). Despite the alkalinity and the high amount of calcium excreted in elephant urine, 1, 2, 3 creating an opportune environment for calculi formation, urolithiasis is infrequently reported in elephants and usually accidentally found during necropsy or urogenital examination.

Two calcium carbonate stones had been found in the left ureter during necropsy of an African elephant (Loxodonta africana.






