Double Line Graphs
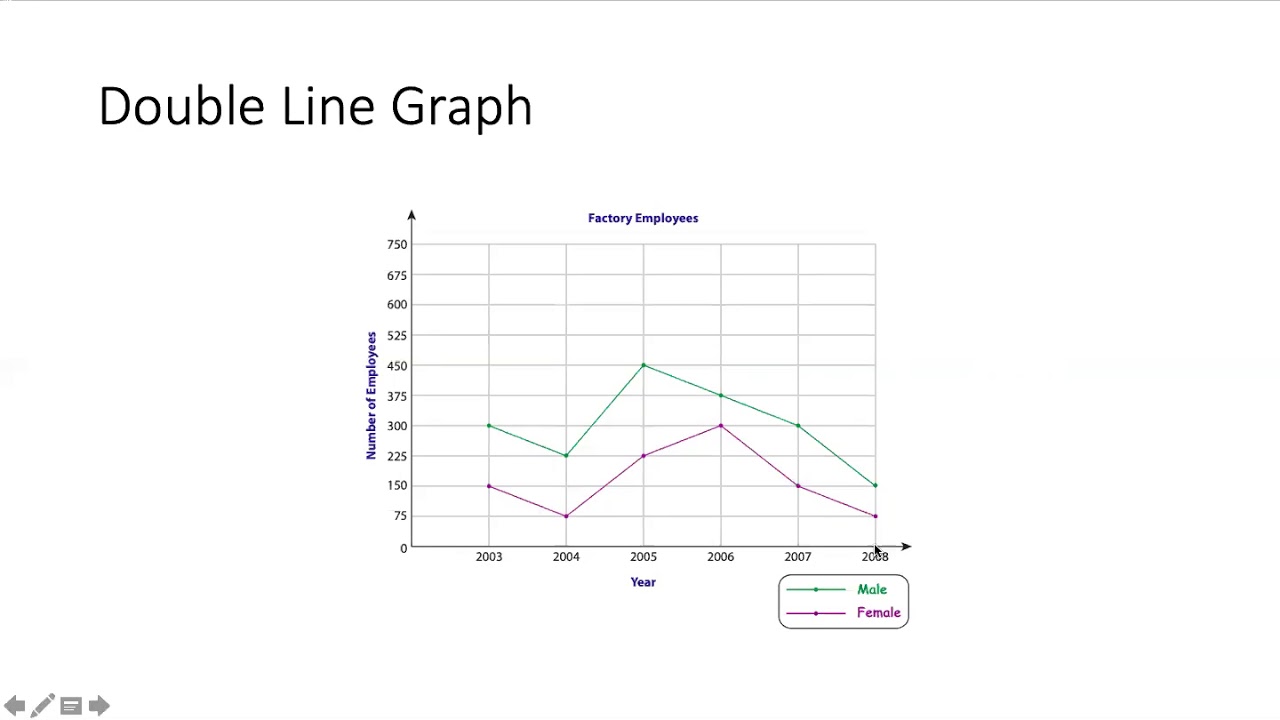
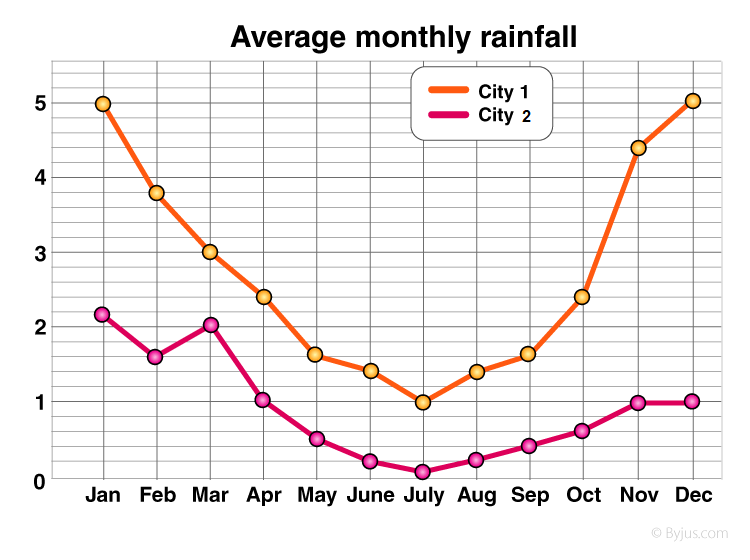
Compare two data sets over time Double line graphs compare how two data sets change over time; data is presented as continuous (joining the data points) rather than discrete, as in a bar graph. In these worksheets, students make and analyze double line graphs. A double line graph is a type of line chart that uses two separate lines to compare changes in two sets of data over the same time period or category.

It helps you visualize the relationship or differences between two variables in one easy. Understand what a double line graph is. See some real.

Double Line Graphs | K5 Learning
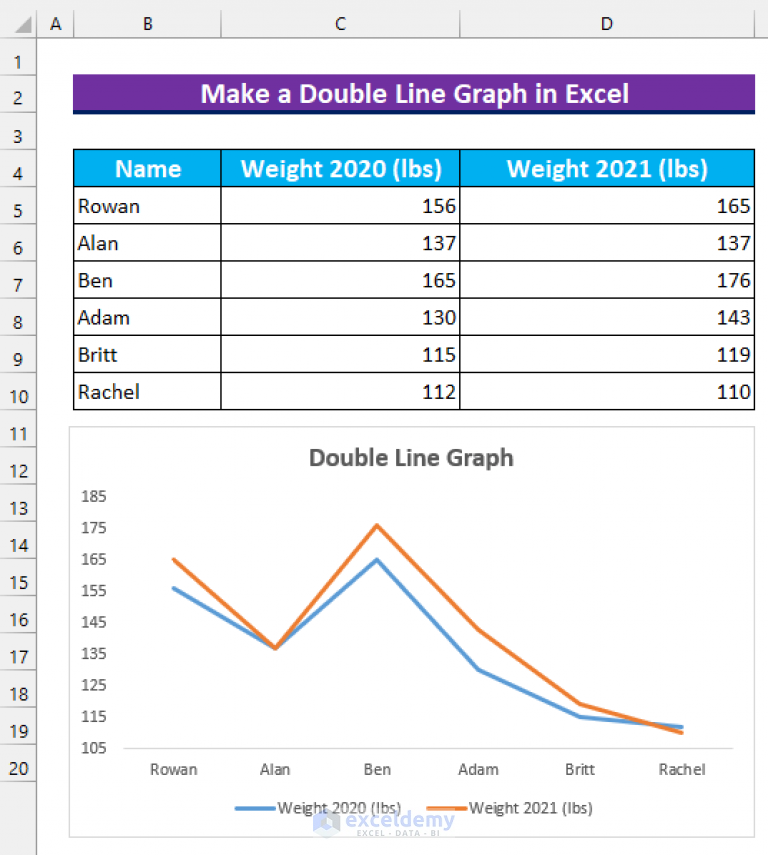
This tutorial explains how to create a double line graph in Excel, including a step. Double line graphs, as with any double graphs, are often called parallel graphs, due to the fact that they allow for the quick comparison of 2 sets of data. In this chapter, you will see them referred to only as double graphs.

Example 1 Christopher and Jack are each opening businesses in their neighborhoods for the summer. Double Line Graph Maker The Double Line Graph Maker is a specialized visualization tool built for scenarios where only two datasets need to be compared. Unlike multi-line graphs that often show multiple series (which can become cluttered), this tool is optimized for clarity and focus.

Double Line Graphs ( Read ) | Statistics | CK-12 Foundation
Graph Worksheets Double Line Graphing Worksheets This Graph Worksheet will produce a chart of data for two lines and a single coordinate grid to graph the data on. You may select the difficulty of the graphing task. The double line graph is a versatile and powerful tool for data visualization, offering a unique way to compare and contrast trends over time or across different variables.

This type of graph, often overlooked in favor of more traditional charts, provides a rich visual experience that can reveal hidden patterns and relationships in your data. Navigating Double Line Graphs: Step. Double Line Graphs Remember a line graph, by definition, can be the result of a linear function or can simply be a graph of plotted points, where the points are joined together by line segments.

Navigating Double Line Graphs: Step-by-Step Guide
Line graphs that are linear functions are normally in the form y=mx+b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. The graph below is an example of a linear equation with a slope of 2 / 3 and a y.