Barchart Matlab
This MATLAB function creates a bar graph with one bar for each element in y. A Bar Graph is a diagrammatic representation of non-continuous or discrete variables. It is of 2 types vertical and horizontal.
When the height axis is on the y-axis then it is a vertical Bar Graph and when the height axis is on the x-axis then it is a horizontal Bar Graph. In MATLAB we have a function named bar () which allows us to plot a bar graph. Syntax: bar (X,Y) where X and Y represent.
bar - Bar graph - MATLAB
Over 19 examples of Bar Charts including changing color, size, log axes, and more in MATLAB. Discover how to create stunning visualizations with a matlab bar chart. This concise guide walks you through the essentials for effective data display.
On execution in matlab command window the output is - Example 9: Bar Chart with Colormap Colors Generate a bar graph employing colormap colors by configuring the FaceColor property to 'flat'. Afterwards, assign an integer to the CData property for each Bar object. The code is as follows -.
Bar Chart Matlab Multiple 2023 - Multiplication Chart Printable
Guide to Bar Graph in Matlab. Here we discuss how the bar graphs are used in Matlab along with the respective examples and the advantages. Bar graphs are useful for viewing results over a period of time, comparing results from different data sets, and showing how individual elements contribute to an aggregate amount.

Bar charts are a great way to visualize data. Matlab includes the bar function that enables displaying 2D bars in several different manners, stacked or grouped (there's also bar3 for 3D bar-charts, and barh, bar3h for the corresponding horizontal bar charts). Displaying stacked 1D data bar is basically a high.
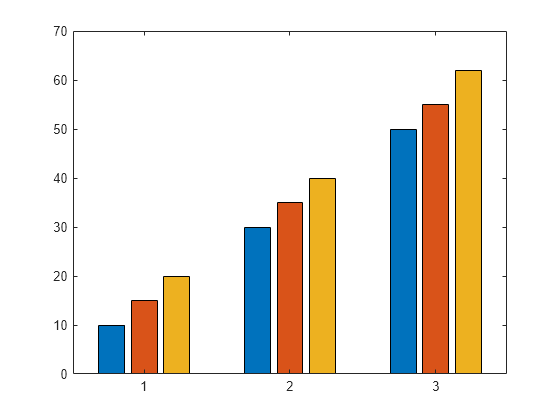
bar - Bar graph - MATLAB
In this chapter, the bar graph which is one of the plot types in MATLAB is presented and described. In this regard, several examples and exercises for each section of the chapter are presented. The exercises that include writing the codes, executing them, and.
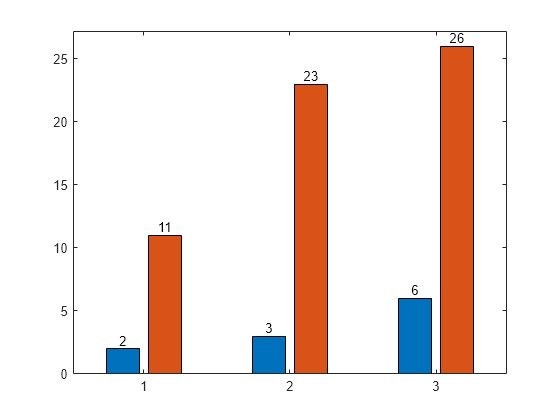
A bar chart displays the values in a vector or matrix as horizontal or vertical bars. bar (Y) draws one bar for each element in Y. If Y is a matrix, bar groups the bars produced by the elements in each row.

The x -axis scale ranges from 1 to length (Y) when Y is a vector, and 1 to size (Y,1), which is the number of rows, when Y is a matrix.