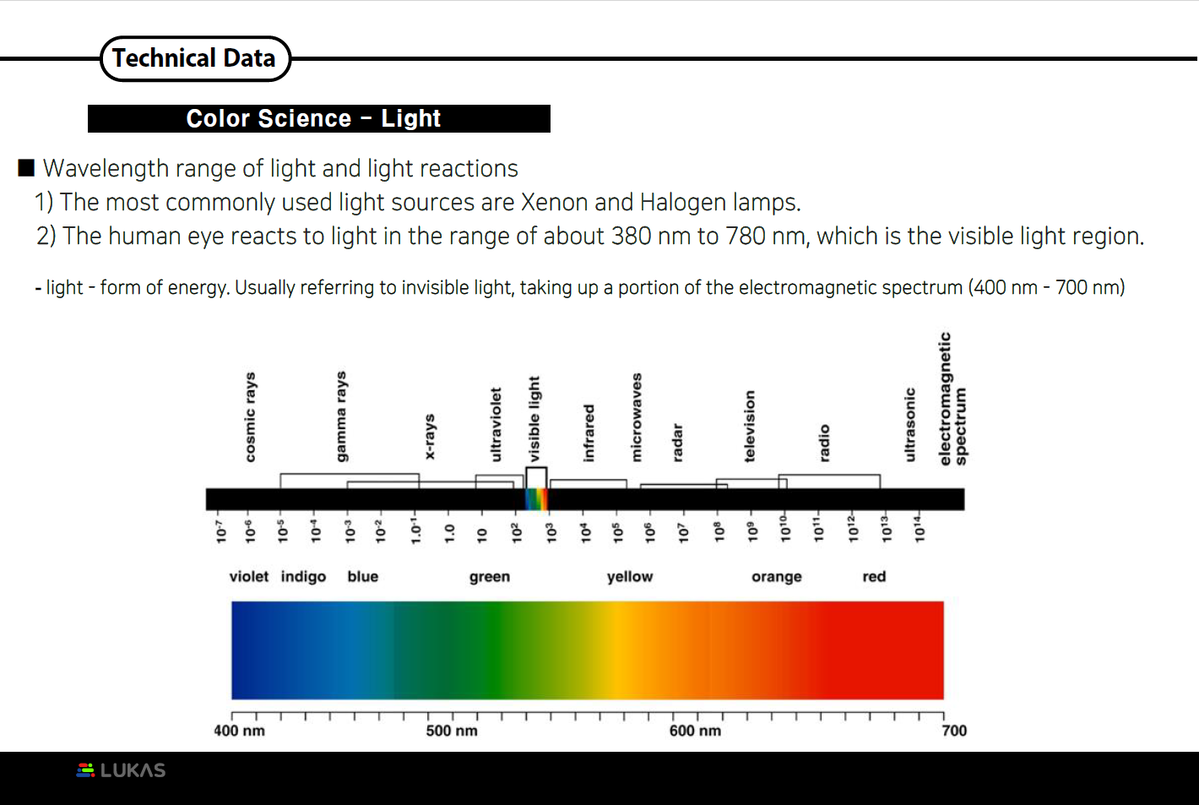
Color Science Light
He demonstrated that clear white light was composed of seven visible colors. By scientifically establishing our visible spectrum (the colors we see in a rainbow), Newton laid the path for others to experiment with color in a scientific manner. His work led to breakthroughs in optics, physics, chemistry, perception, and the study of color in nature.

Color science is the scientific study of color including lighting and optics; measurement of light and color; the physiology, psychophysics, and modeling of color vision; and color reproduction. It is the modern extension of traditional color theory. Light is a mixture of all visible electromagnetic wavelengths; color is the sensation resulting from the eye seeing light waves of certain lengths.

RGB colour model | Description, Development, Uses, Science, & Facts ...
The earliest studies of color were done by Newton. He understood that white light was a combination of lots of wavelengths. He performed some ingenious experiments to show this, described in his book Optiks (1704).

For example, even though prisms turned white light into a rainbow, people thought that maybe the prism was producing the rainbow colors. Newton showed that this wasn't true. He.

Science: Colors
Color science serves as an underlying technical foundation for the entire lighting industry. It establishes a consistent way of thinking about light-how it is created, controlled, and delivered in real-world implementations. A core understanding of the science of color is critical to lighting professionals, who must be able to specify the right light-color, technology, luminaire, and more.

Uncover the fascinating science of color. Learn how light, chemistry, and structure interact to define everything you see. Color matching experiment: Monochromatic test light and monochromatic primary lights Spectral RGB primaries (scaled, such that Rλ=Gλ=Bλ matches spectrally flat white).

Primary Colours and Secondary Colours of Light | Light, Colour and ...
"Negative intensity": color is added to test color Standard human observer: CIE (Commision Internationale de L'Eclairage), 1931. Color perception requires a light source (such as the sun), an object (an apple) and an observer (for this example a human). As demonstrated by Newton, light from the sun contains all colors.

When sunlight illuminates an apple most of that light is absorbed by the apple's skin and only certain colors are reflected. What color is Colors are the sensations that arise from light energy of different wavelengths. The different colors in visible light and how they relate to its wavelength, and how a prism separates visible light into its different colors.

Colors of objects, the colors we see and what pigments are.