Autumn Leaves Changing Colors
Aspen leafs: fall colors. Beaver Ranger District, Fishlake National Forest. (Forest Service Photo by Scott Bell) Science of Fall Colors For years, scientists have worked to understand the changes that occur in trees and shrubs during autumn.

Although we don't know all the details, we do know enough to explain the basics to help you enjoy nature's multicolored display. Three factors influence. See when fall leaves will peak in 2025! View our U.S.

Why Leaves Change Color in the Fall - Chemistry
fall foliage map, find top leaf-peeping spots, and get tips for the best autumn color viewing. Frederic Edwin Church, "Autumn Woods," ca. 1870, Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum, gift of Louis P.

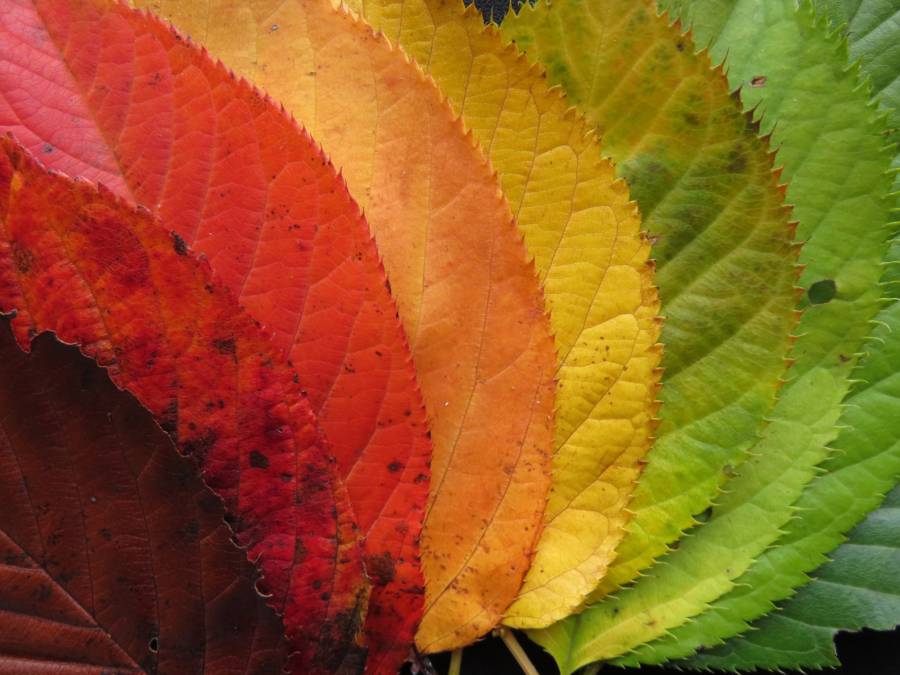
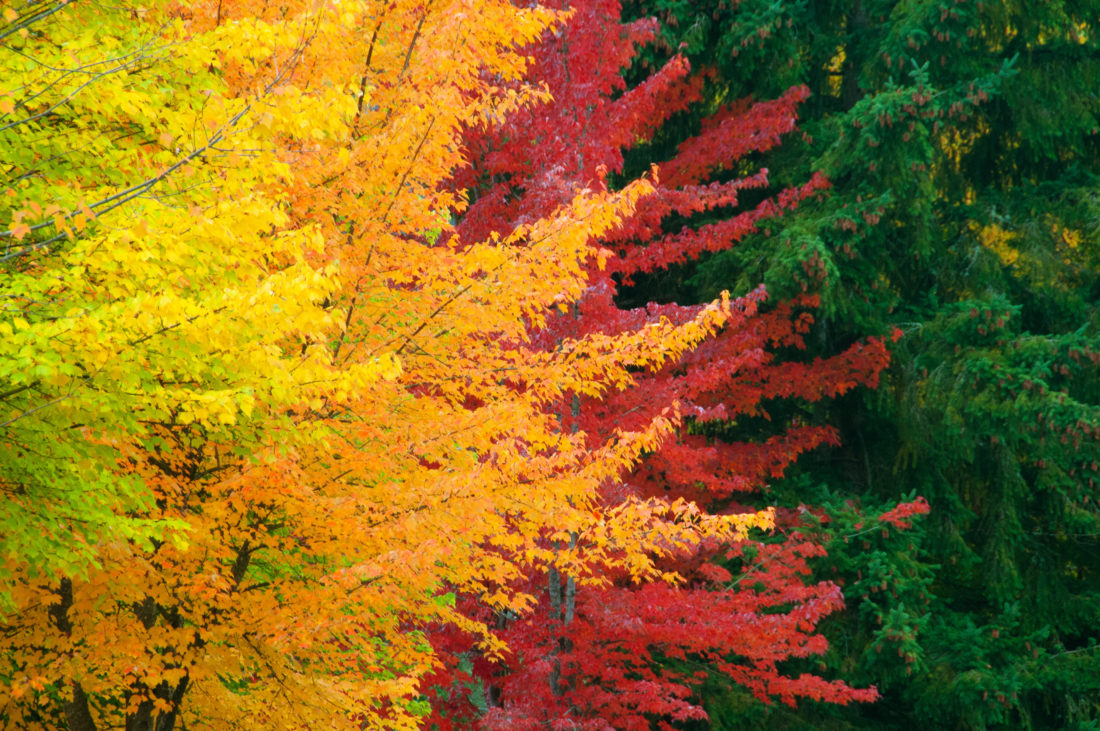
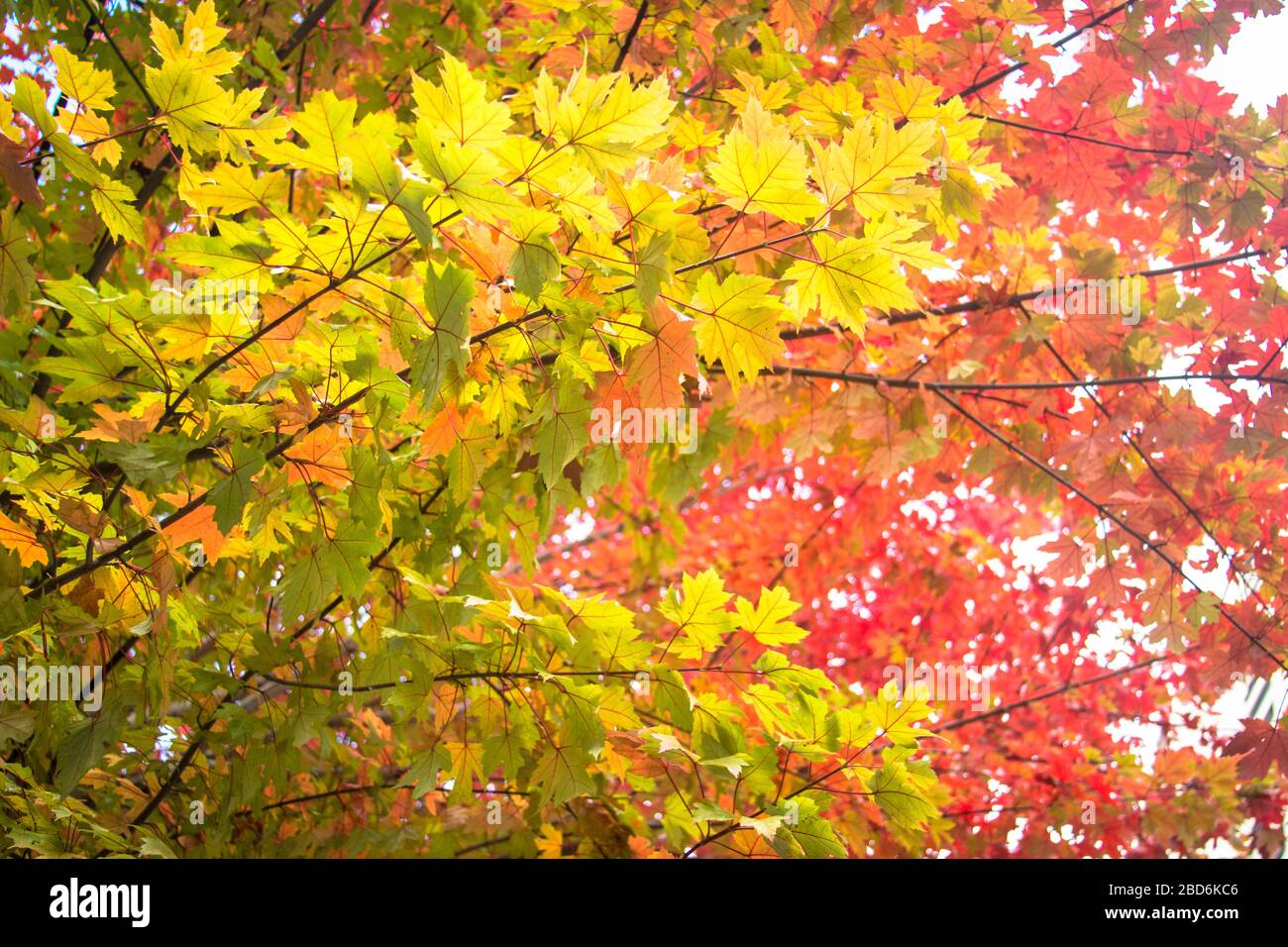
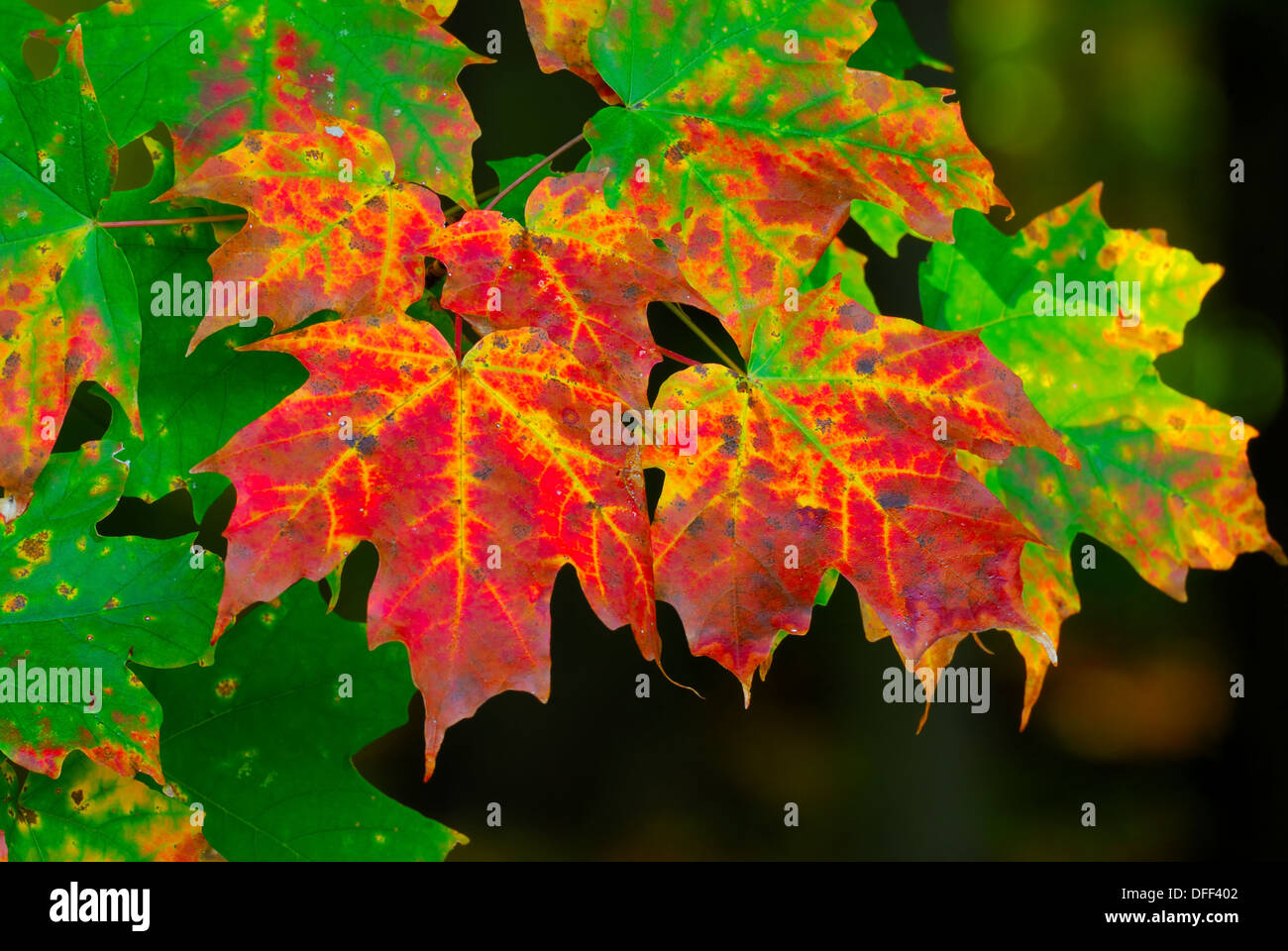
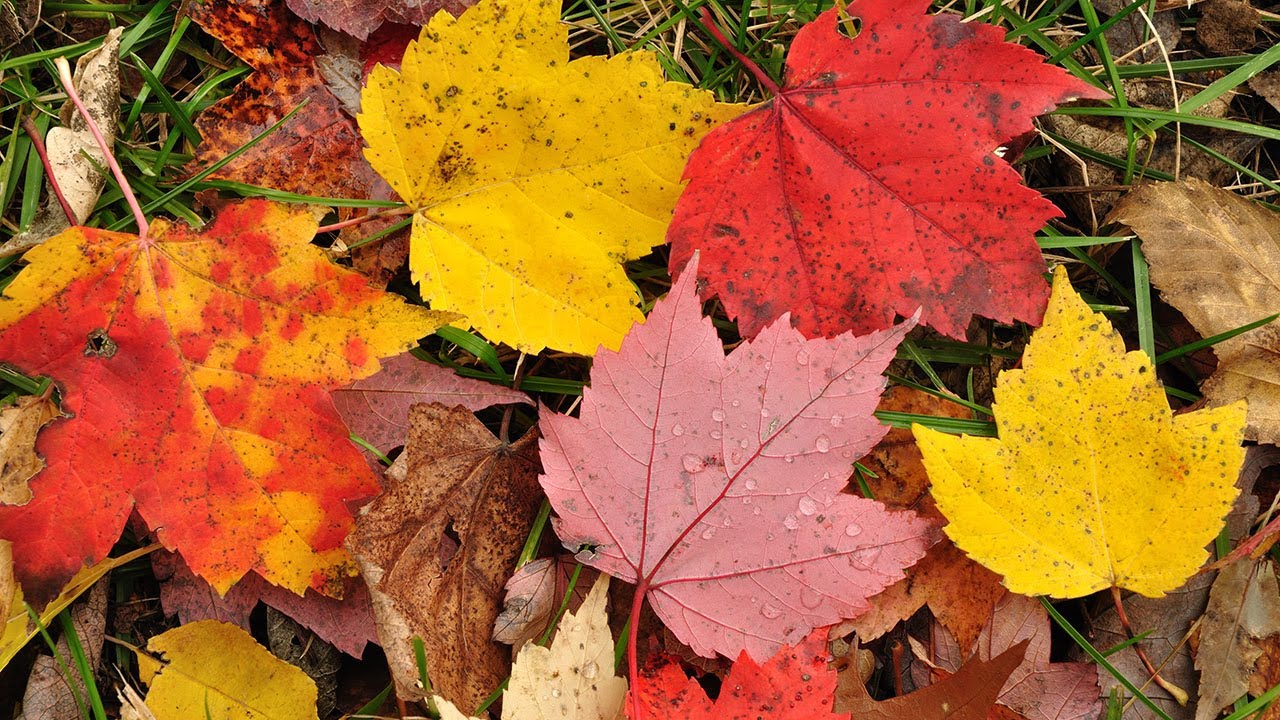
Church Autumnal leaves in vibrant hues are a beautiful part of the season, but those leaves are also a vital part of keeping trees alive. Trees that have leaves that change color in fall. Japanese maple autumn leaves Autumn leaf color is a phenomenon that affects the normally green leaves of many deciduous trees and shrubs by which they take on, during a few weeks in the autumn season, various shades of yellow, orange, red, purple, and brown.

Why Do Leaves Change Color in the Fall? - O'Toole's Garden Centers
[1] The phenomenon is commonly called autumn colours[2] or autumn foliage[3] in British English and fall colors, [4] fall foliage, or. From vivid reds to golden yellows, the science behind autumn's colors reveals how weather, tree species and chemistry combine to create the seasonal spectacle. Leaves change color during the autumn because the amounts of pigments change as the leaves prepare to fall from the trees.
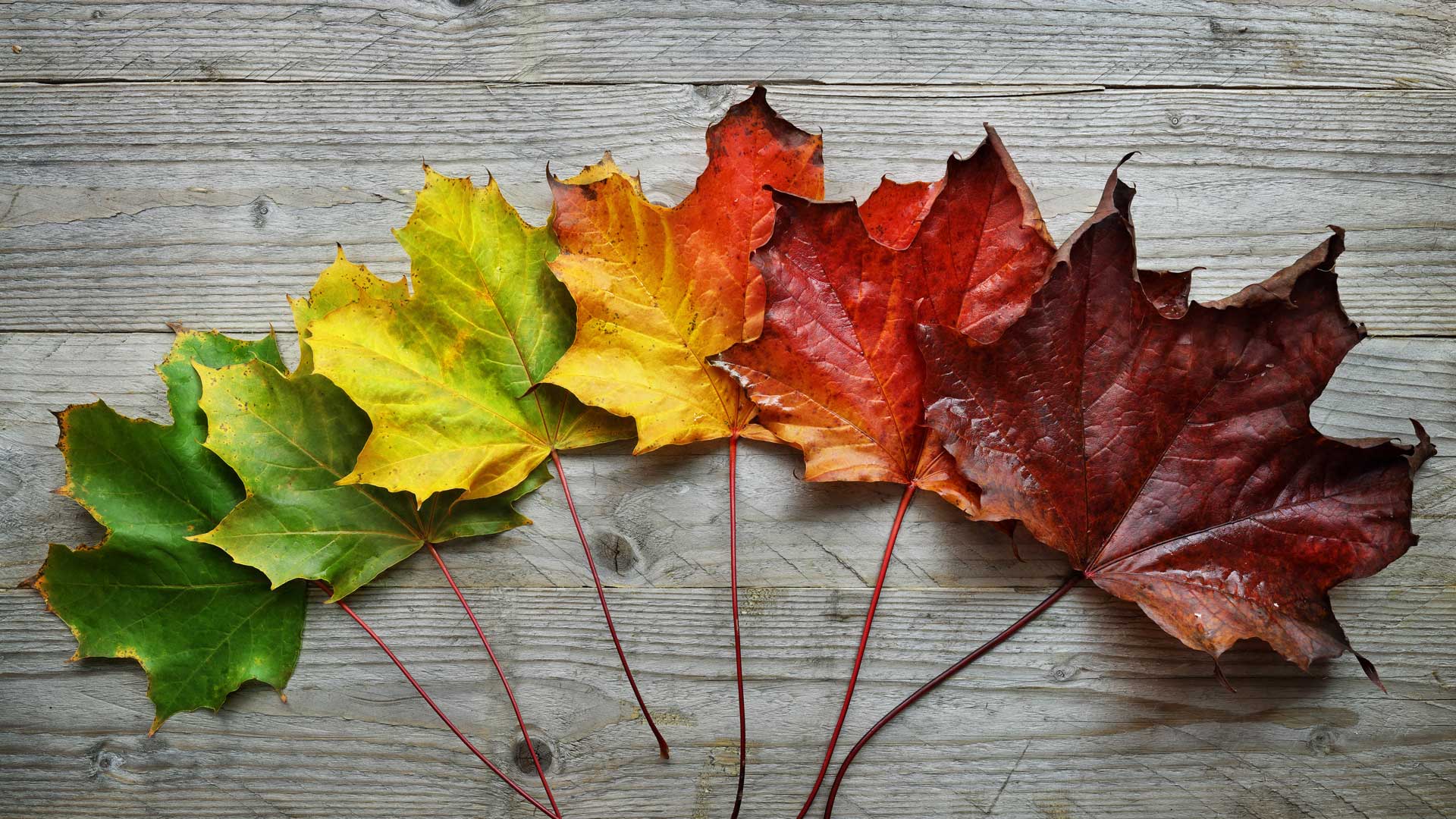

All leaves gradually lose chlorophyll during the growing season, and this loss accelerates before leaf fall. Under optimal conditions this process of chlorophyll loss is very orderly and allows the plants to resorb much of the nitrogen in the structure of the pigment. In many places around the world, autumn is marked by the slow, beautiful change of green foliage to vibrant reds, oranges, yellows, and purples.
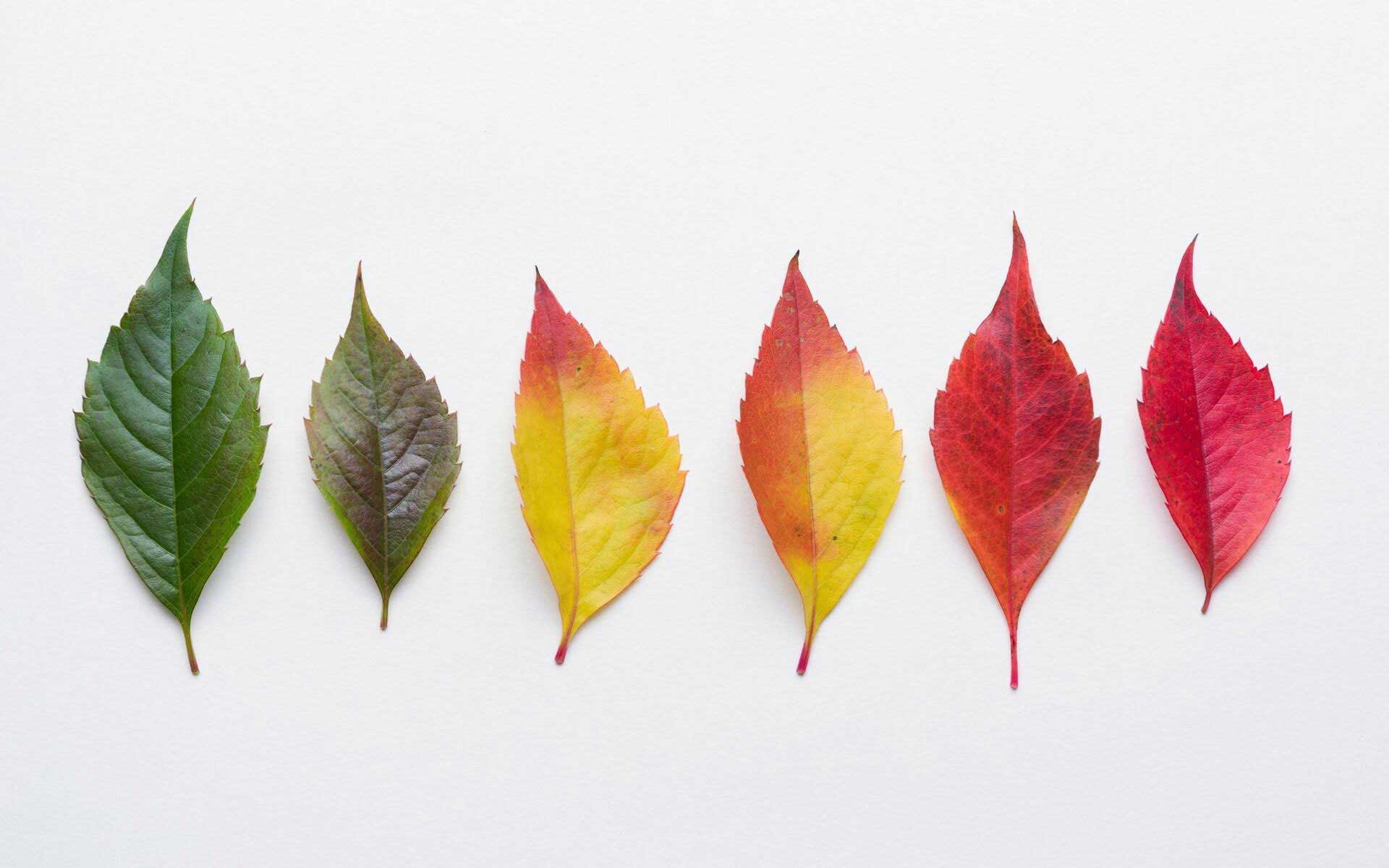

Why Do Leaves Change Colors in the Fall? | Britannica
Green leaves appear green because of the presence of the pigment chlorophyll, which is key to photosynthesis. The color change culminates in leaf abscission, the shedding of leaves from the tree. This protective mechanism allows deciduous trees to conserve water and energy during winter.

Admiring the vibrant red leaves that add so much color to Acadia's fall landscape. NPS Photo/Hadley Seymour When the temperature drops and there is less daylight, the tree begins to conserve the energy it generated in the spring and summer months. One way trees save energy for winter is by dropping their leaves.

As autumn progresses, a tree will send a substance to each leaf called an enzyme. Learn why leaves change color in the fall and see the chemistry of the pigment molecules responsible for different leaf colors.