Moon Color From Earth
What Color Is the Moon? There is a very select group of people who have seen the Moon's true color albeit through the windows in spaceships, space stations and helmet visors. There are images taken from above Earth's surface of the Moon of course but photos can never really do justice. The color of the moon, as it is sometimes seen from Earth, can also vary substantially, from red and violet to white or yellow.
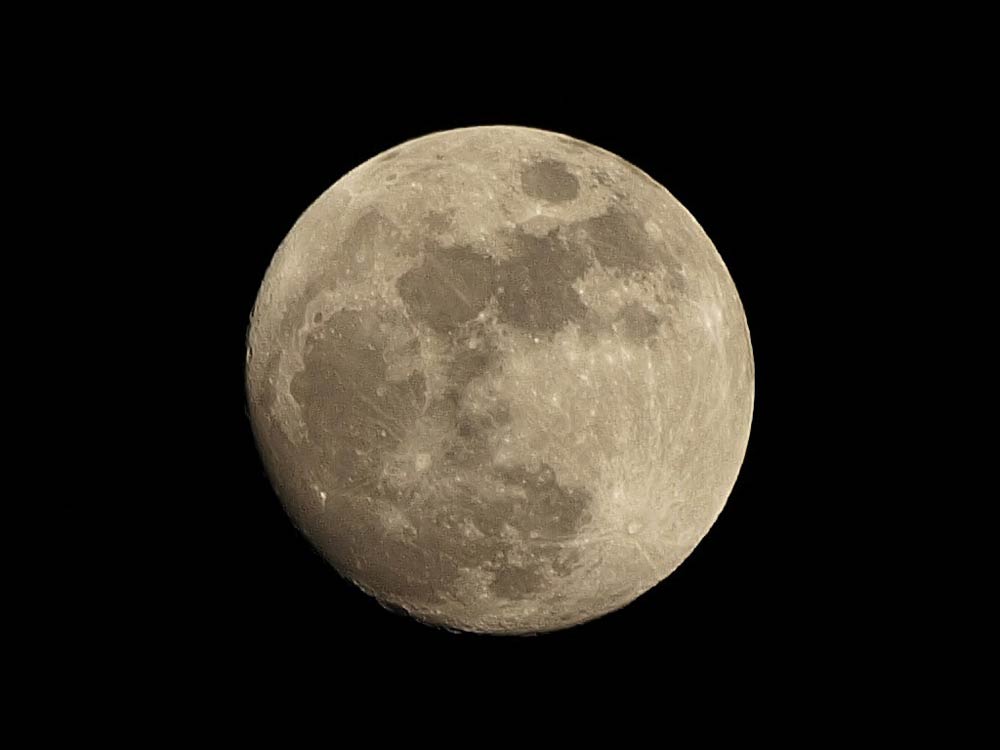
While Earth's atmosphere and the Moon's reflective properties significantly influence what we see, the lunar surface itself harbors a spectrum of subtle hues, revealing a complex geological story. The Moon's Apparent Color From Earth, the Moon typically looks off-white or light gray, sometimes tinged with yellow. The moon is Earth's only natural satellite and the fifth largest moon in our solar system.

Astronominsk
Moon's color appears to change depending on factors and viewing conditions. Moon's surface exhibits shades ranging from reddish to grayish hues. Learn about Moon's color variations, surface composition, and reflective properties.
Moon's color in space is gray. Astronauts observe. However, just because the moon can appear in so many colors doesn't mean it actually changes color.

A Colorful Moon
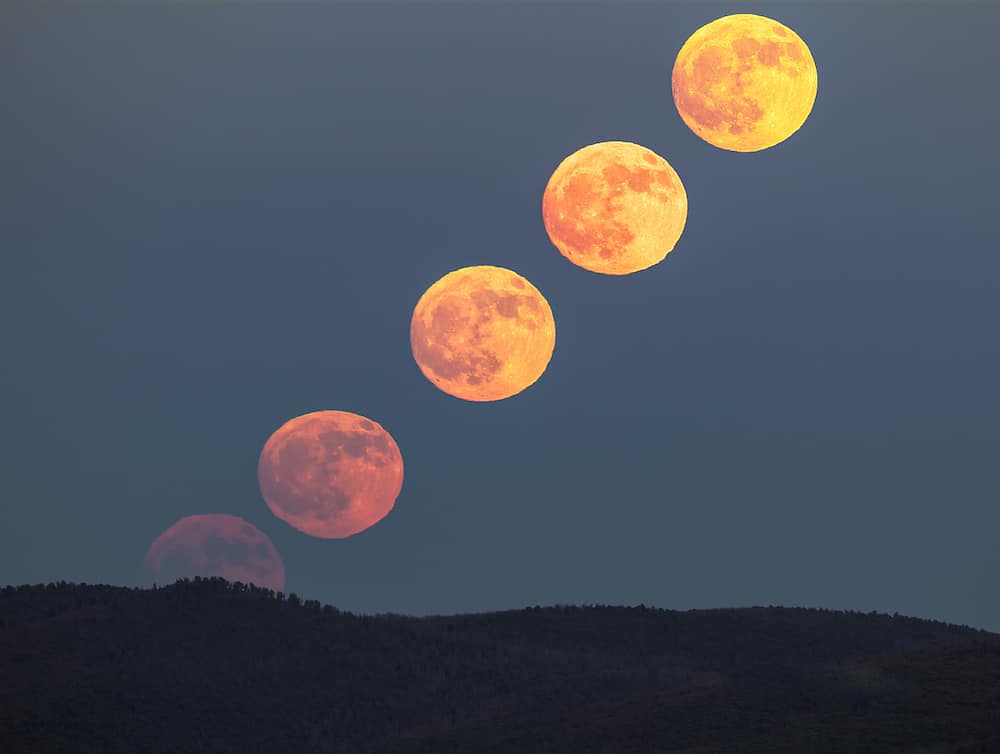
The dozens of hues are caused by many different factors, including the time of day, the moon's position, and the particles surrounding the moon. Let's take a look at why some of the unusual moon colors occur. White.

The Moon, our closest natural satellite, has always fascinated and intrigued humanity. Although we see it regularly from Earth, one recurring question remains: what colour is the Moon really? Depending on the time, the atmosphere and our perception, this mysterious star seems to vary its shades, and its real surface hides even more surprises. What is the real color of the Moon? Learn about Moon phases What Color is the Moon? From here on Earth, the sunlit part of the Moon usually looks bright, almost white.

Moon Color Visualizations
This is an illusion. The brightness of the Sun's reflected light makes it difficult to see the Moon's actual color from a distance. The Moon's natural color does not change, but how we perceive it in the sky does.

The perception of its color in our eyes is influenced by light viewed through the Earth's atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere significantly alters our perception of the Moon's color, causing it to appear in hues from white to yellow, orange, or red. This phenomenon is due to Rayleigh scattering, which explains why the sky appears blue.

The Moon often captivates observers with its changing hues, appearing white, yellow, orange, or even red at different times. This variability in color raises questions about the Moon's true appearance and the factors that influence how we perceive it from Earth. The answers involve both the inherent characteristics of our celestial neighbor and the atmospheric conditions on our own planet.






