Canine Skull Anatomy
Cross-sectional anatomy of the canine head on CT imaging (brain, face, skull, face, palate, hyoid apparatus, muscles, arteries and veins). Learn about the different bones, features and diagrams of dog skull anatomy. Find out the peculiar osteological characteristics, special structures and processes of each bone from the dog skull.
.jpeg/300px-Cranial_skull-_canine_(lateral_view).jpeg)
Learn about the anatomy and development of the canine and feline dentition, as well as the skull bones and sinuses. See radiographs and computed tomography images of the skull and teeth of different breeds and species. Explore the unique anatomy and variations of canine skulls, from breed.

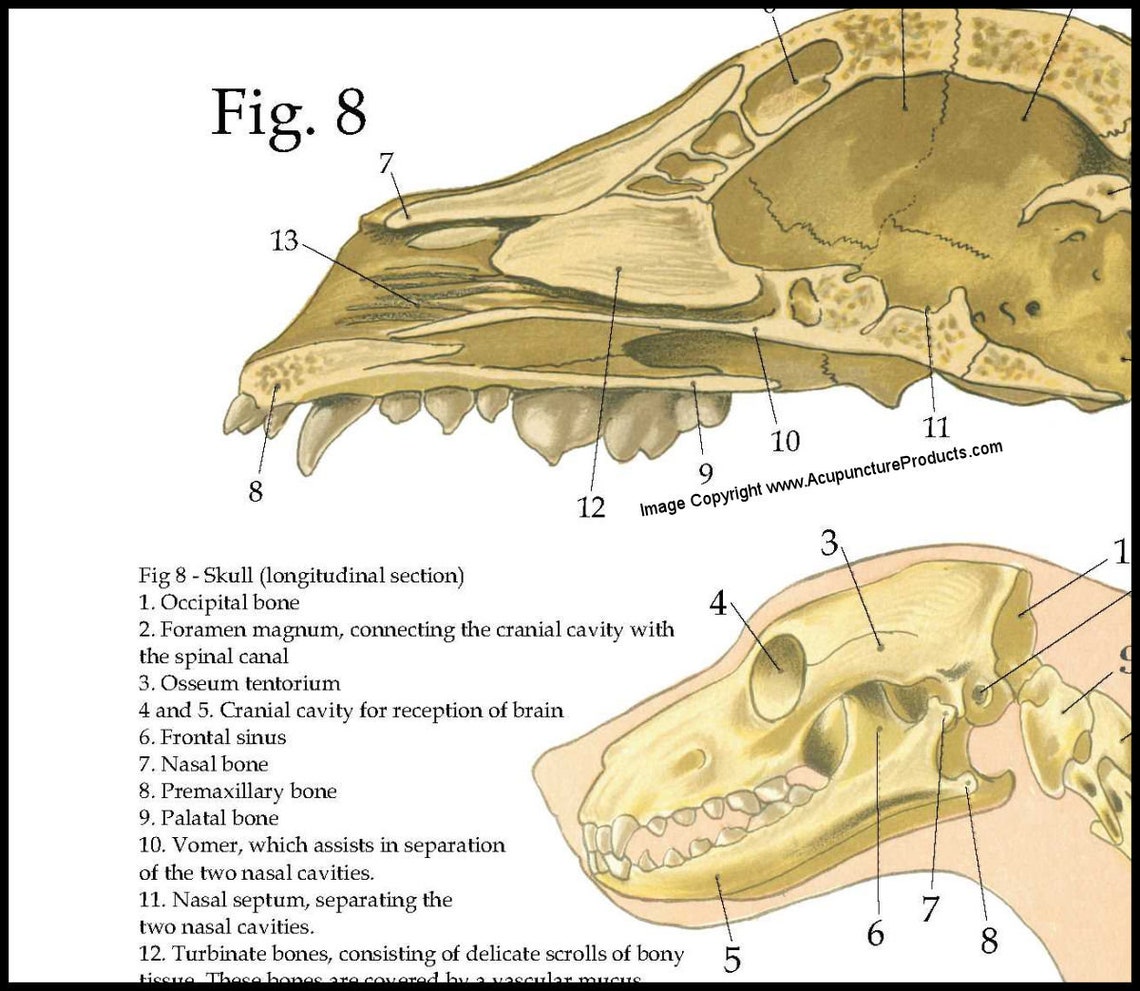
Sagittal section in canine skull - Veterinary Anatomy World
Canine Skull Example 1 The following radiographs are the right lateral view of the skull and neck as well as dorsoventral, dorsoventral right. Discover the fascinating anatomy of a dog's skull in this comprehensive article. Learn about the unique features that shape a dog's health, behavior, and breed characteristics.

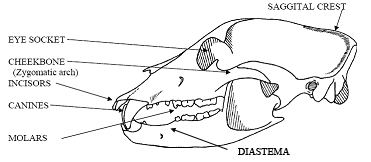
Explore the differences between dog skulls and those of other animals, gain insights into dental health, and understand the vital role of sensory organs. Uncover how evolution and selective breeding have influenced. Explore the intricacies of dog skull anatomy and uncover essential insights with our expert guide to understanding your canine's cranial structure.
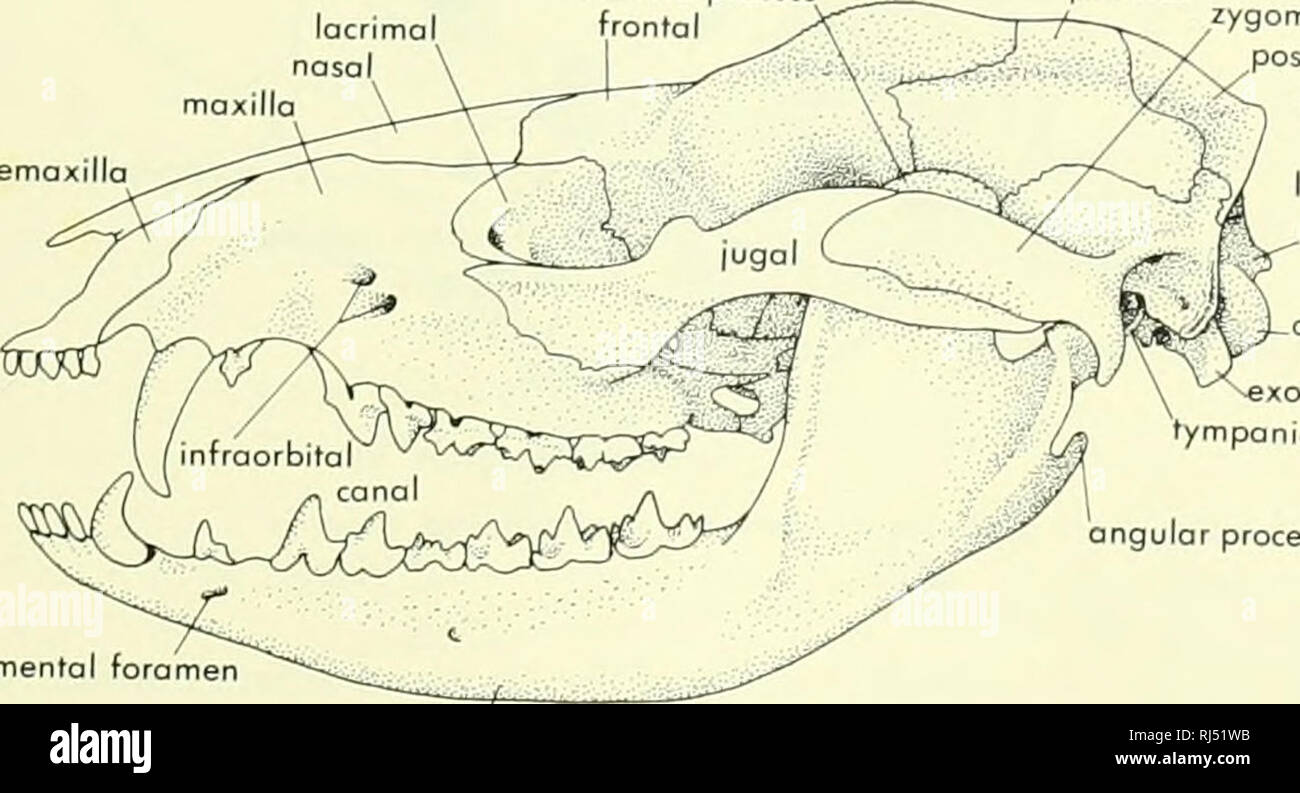
AP: Skull Anatomy Flashcards | Quizlet
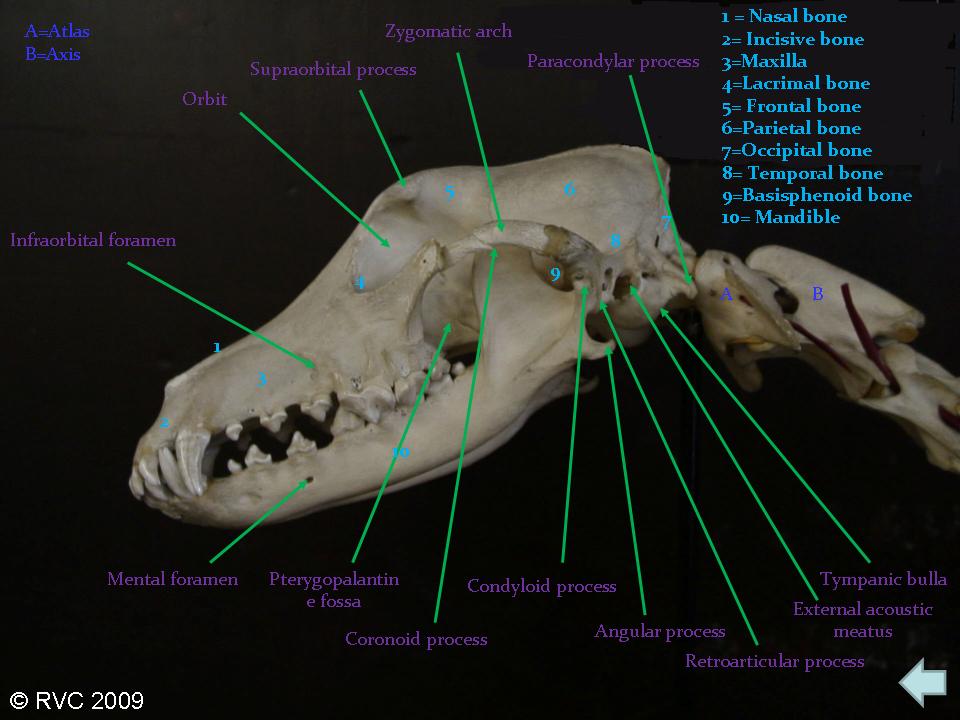
The maxilla contains the upper cheek teeth and canine, with infraorbital and palatine foramina for nerve and vessel passage. The incisive bone, nasal bone, and zygomatic bone are closely related to the maxilla in the skull's structure. Dogs have different skull lengths depending on breed.

Mesocephalic dogs have average conformation whilst dolichocephalic dogs have longer skull lengths and brachycephalic dogs have shorter skull lengths. The skull protects the brain and head against injury and supports the structures of the face. In dog skull anatomy, the pterygoid bone is small, thin, curved, and has four.