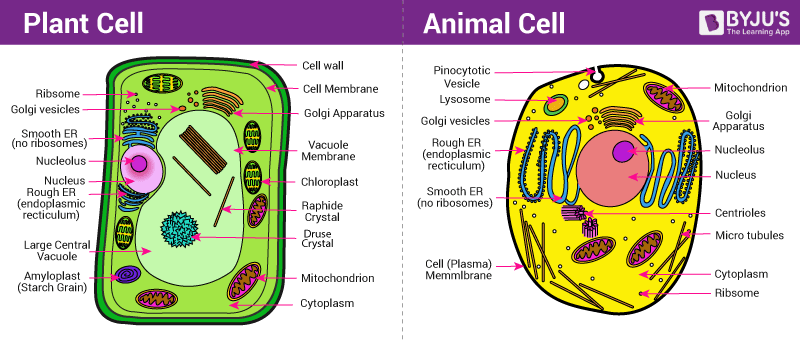
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Learn the difference between plant and animals cells. See the differences in structure and organelles for plant vs animal cells. Learn the similarities and differences between plant cells and animal cells, the basic units of life for plants and animals.
Compare their structures, functions, organelles, and examples with a table and diagrams. Learn the main differences and similarities between plant and animal cells, such as cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuoles, centrioles, and more. See comparison chart, pictures, and videos of plant and animal cells.
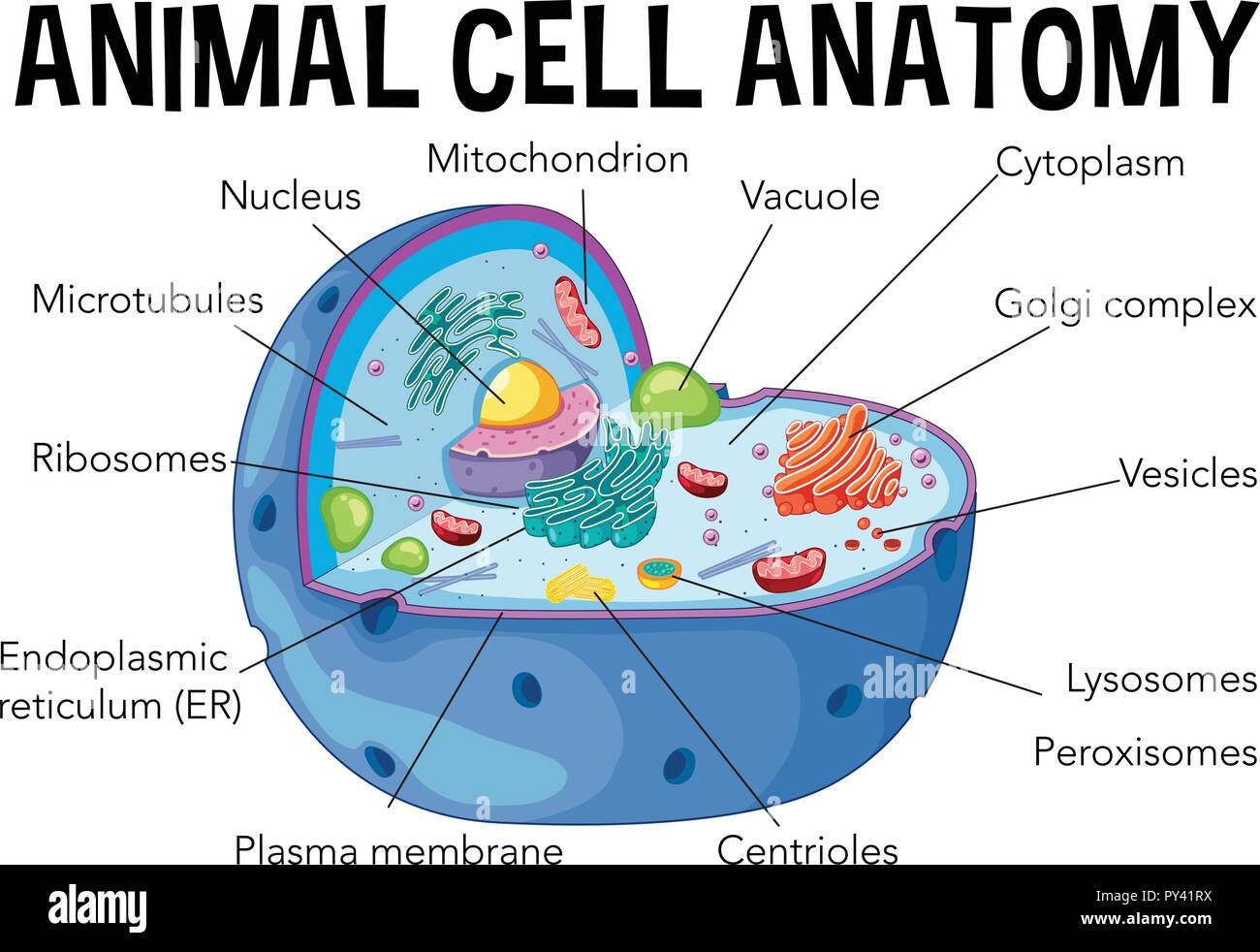
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)
Plant Cell And Animal Cell Liveworksheet
Learn how plant and animal cells are similar and different in terms of organelles, functions and evolution. See a chart that compares and contrasts the two types of cells and their features. Learn how plant and animal cells differ in their cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and more.

Explore how these differences reflect the evolution and adaptation of life on Earth. Learn how plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic, but have different sizes, shapes, structures, and functions. Compare and contrast the components, processes, and examples of these two types of cells.
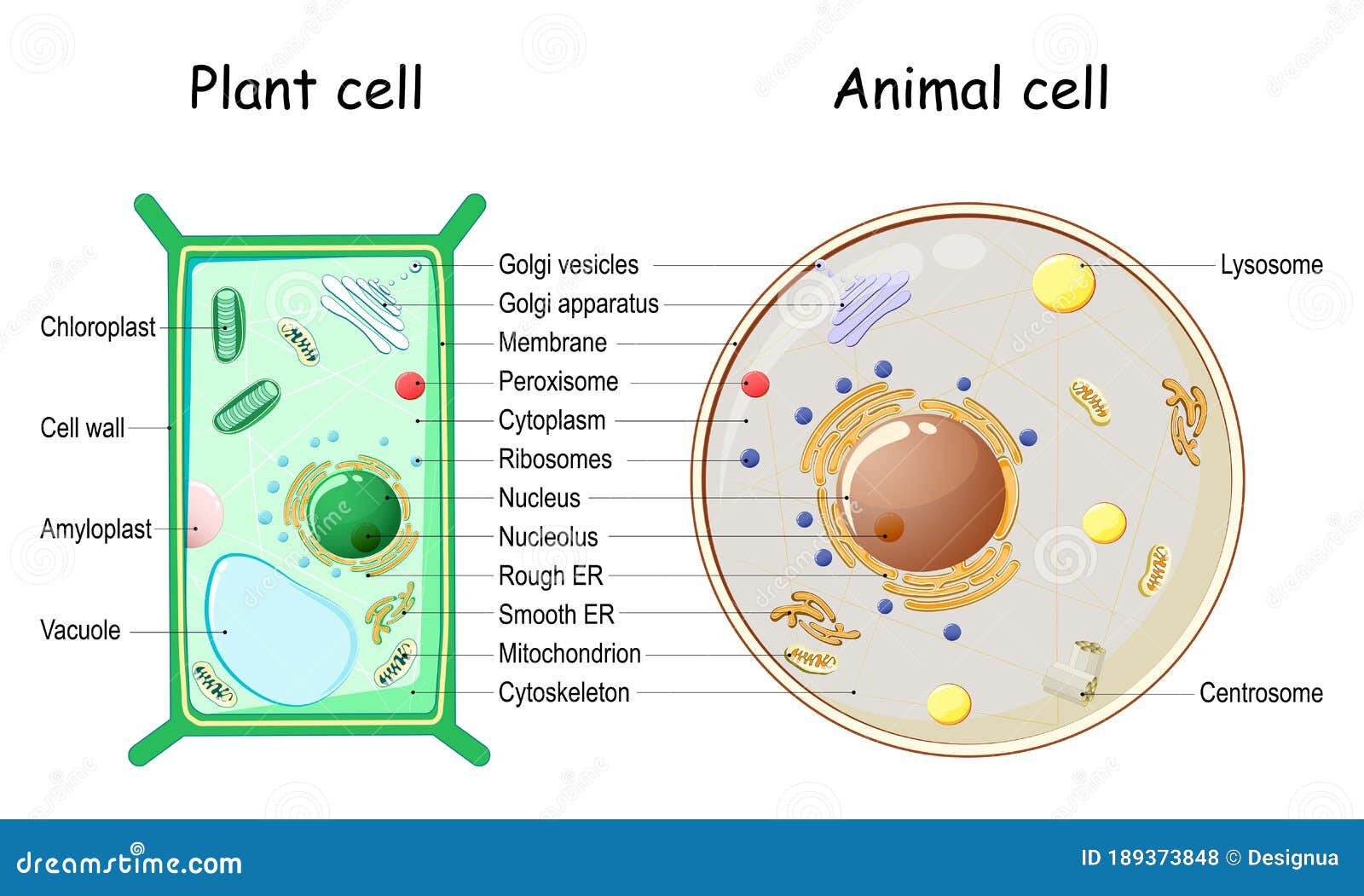
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_cell_vs_plant_cell-58b45d8f5f9b5860460ceb88.jpg)
Plant and Animal Cell 5th Grade Study Guide | Plant and animal cells ...
Learn how plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic, but have different features and functions. Compare cell walls, membranes, chloroplasts, vacuoles and more. Find out what animal and plant cells are and learn what the function of the cell wall and the nucleus is in this KS3 Bitesize biology article.

Cells are the fundamental units of all living organisms, carrying out essential life functions like growth, metabolism, and reproduction. While all cells share these processes, significant distinctions exist between plant and animal cells. Understanding these differences is central to comprehending the diverse forms and functions of living things.
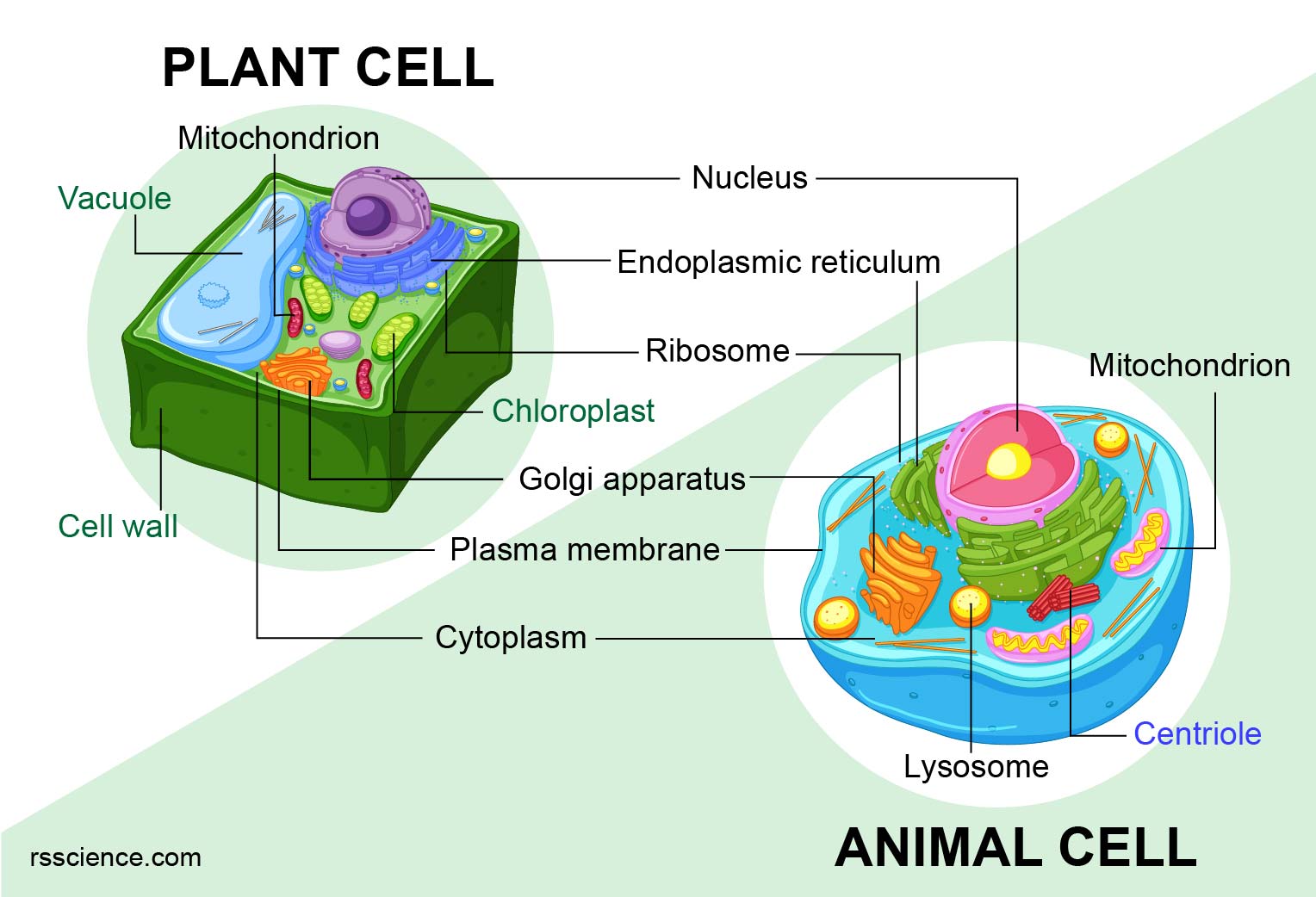
Plant Cell And Animal Cell Model
Structures Common to Both Cell Types Both. Although both animal and plant cells bear similarities, there are differences between plant and animal cells in shape, size, Organelles & functions. Explore plant cells vs animal cells from 17 cellular perspectives, such as shape, size, plasticity, vacuole, chloroplast, lysosome, centriole, food storage, and more.