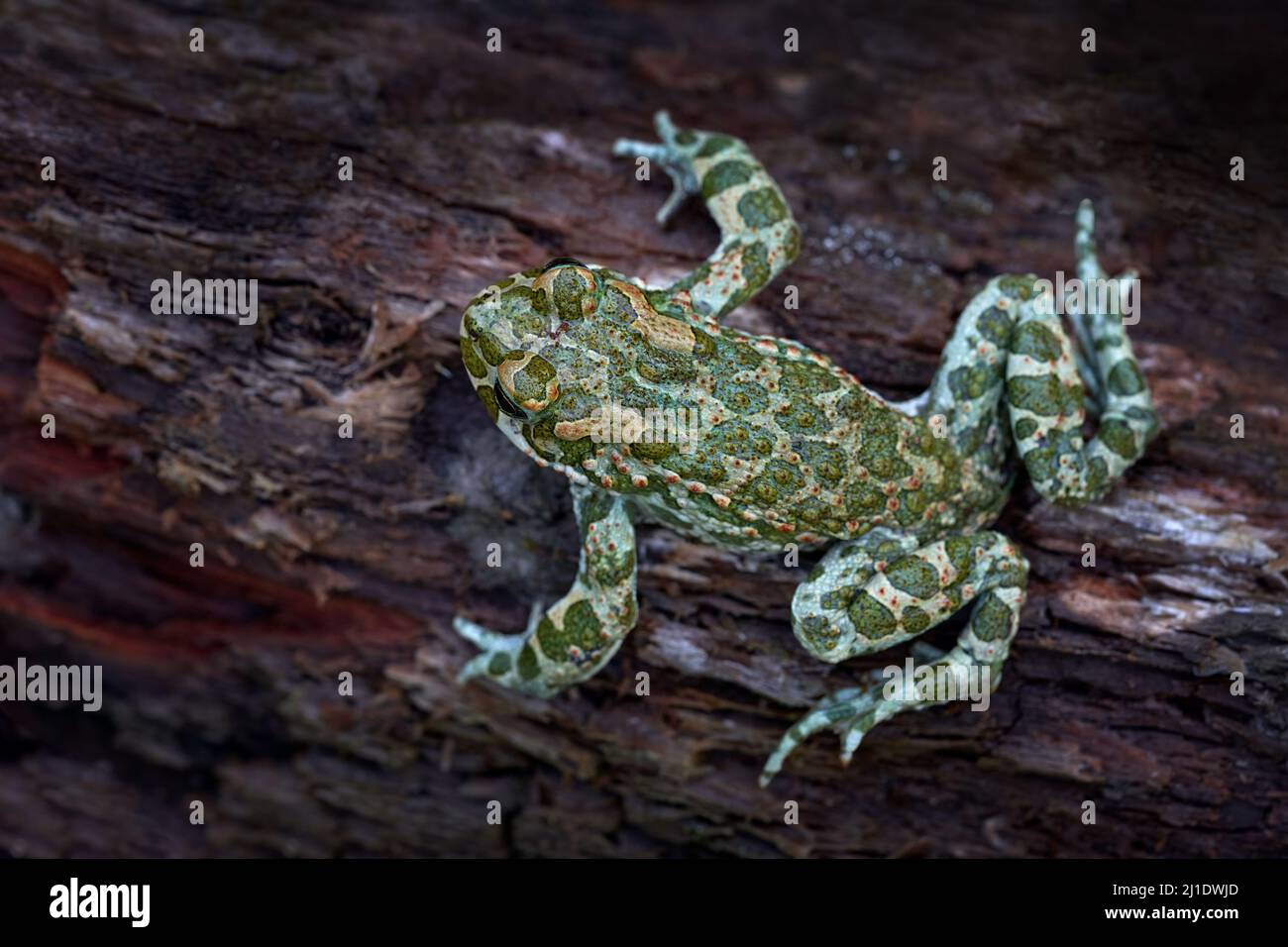
The Green Colour Of Bile In Frog Is Due To
Biliverdin is a green chemical produced from blood degradation that gives bruises a green color and, when further broken down, produces the yellow color seen in bile. "With a lot of extra biliverdin around, the frog takes on the characteristic bluish-green color," Fitak says. The Evolutionary Edge of Green Green coloration has become widespread and highly advantageous for many frog species due to natural selection.

Frogs with effective green camouflage are more likely to evade predators, successfully hunt, and survive long enough to reproduce. Hundreds of frog species around the world have green bones, muscles and skin caused by high concentrations of biliverdin, the first breakdown product of heme. We found that biliverdin - which normally is excreted - is kept at unusually high levels in green frogs by being bound to a serpin, a member of a group of proteins primarily known as protease inhibitors.

Notes on Digestive System of Frog (Labelled Diagrams) - Anatomy (Parts) & Physiology
The newly described protein. Green coloration of vertebrates is normally attributed to pigments and structural components inside skin chromatophores cells. However, these components do not account for the vivid blue.
Scientists have long grappled with the fact that many of these frogs contain very high levels of bile pigment called biliverdin that is a byproduct of breaking apart old red blood cells. This. 3.

Multiple origins of green coloration in frogs mediated by a novel biliverdin-binding serpin | PNAS
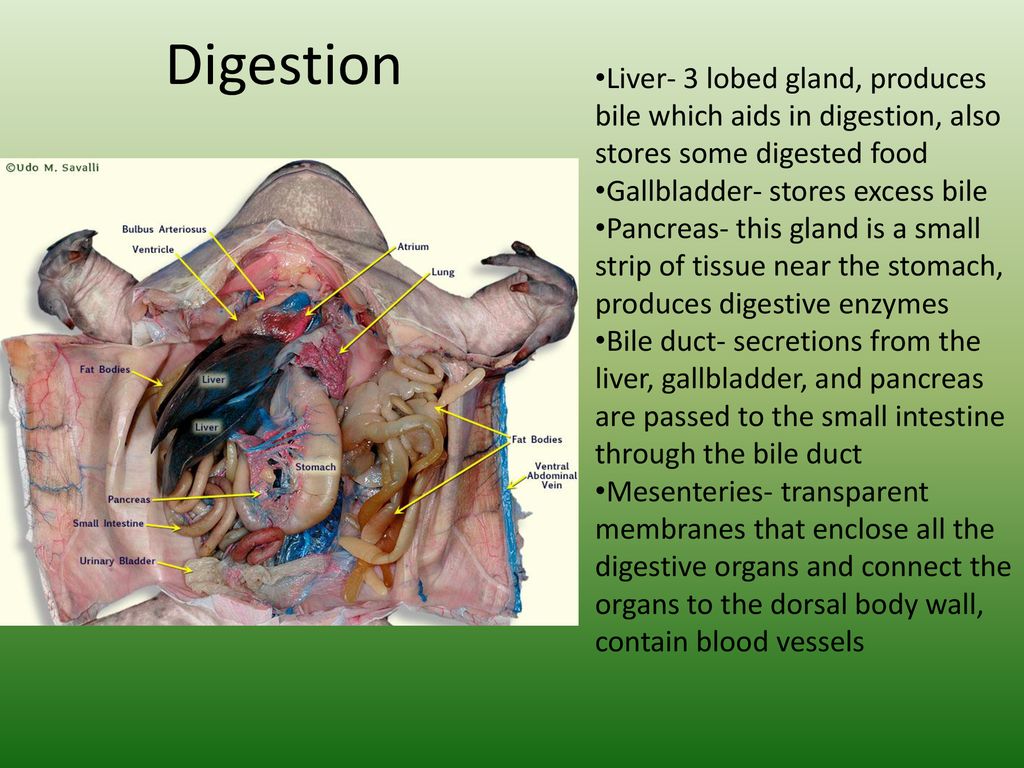
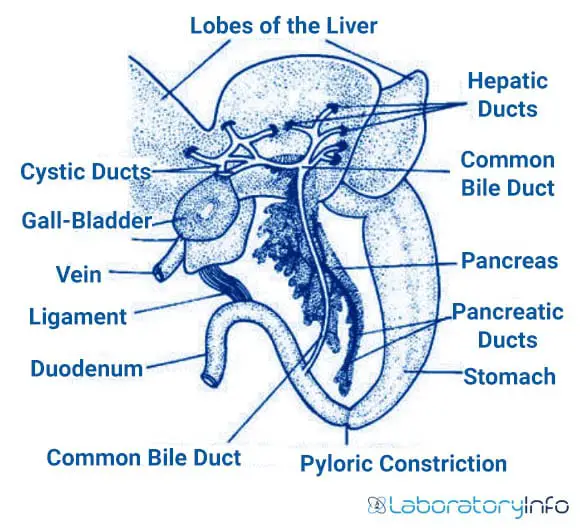
Tucked under the liver is the gall bladder, which stores bile that is produced by the liver. color the gall bladder green and the bile duct (3b) a darker green. 4.

The gall bladder connects to the duodenum of the small intestine. Color the duodenum light blue. 5.
College of Graduate Studies
The duodenum connects to the curly part of the small intestine known as the ileum. A: The green coloration in frogs is potentially due to the novel biliverdin-binding serpin. This biochemical agent binds with biliverdin, a green pigment, contributing significantly to the bright green fluorescence character seen in several frogs.
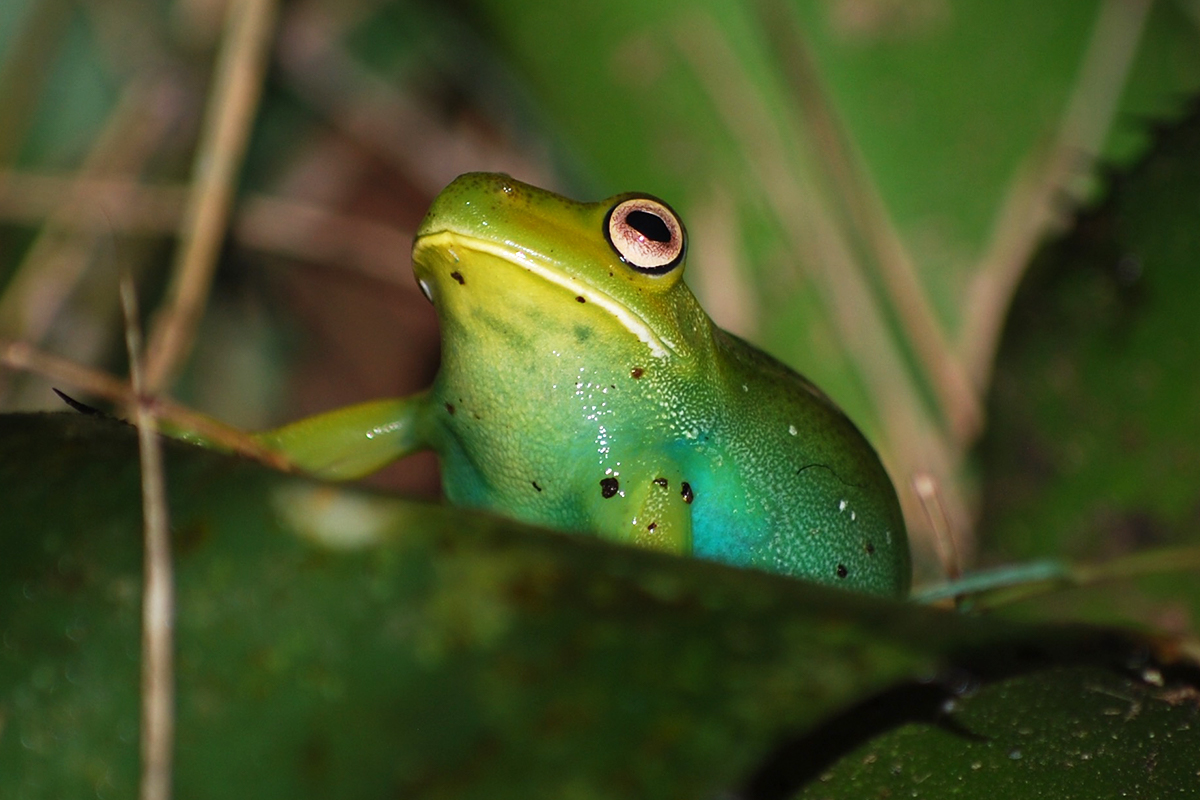

Why is frog liver blue? Biliverdin is a green chemical produced from blood degradation that gives bruises a green color and, when further broken down, produces the yellow color seen in bile. "With a lot of extra biliverdin around, the frog takes on the characteristic bluish-green color," Fitak says. Bile Production and Release Bile production begins in the frog's liver, its largest digestive gland.

Liver cells, known as hepatocytes, continuously synthesize bile components, secreting them into small bile ducts that merge to form larger hepatic ducts, which then transport the bile to the gallbladder. What colour is a frog's gallbladder? Tucked under the liver is the gall bladder, which stores bile that is produced by the liver. color the gall bladder green and the bile duct (3b) a darker green.