Rainbow Color Formula
Newton Descartes understood roughly why the rainbow is located where it is, but he was fairly straightforward in declaring that he didn't understand why the rainbow showed different colors. In effect, he didn't know that different colors (which we now know to correspond to different wave lengths) of light have different refractive indices n. Keats complained that a mathematical explanation of rainbows robs them of their magic, conquering "all mysteries by rule and line".

But rainbow geometry is just as elegant as the rainbows themselves. The origin of colors in a rainbow was explained by Newton about 30 years after Descartes ex-plained the mechanism for forming rainbows. When experimenting with light transmission through prisms, Newton discovered that the re-fractive index n depends on the light wavelength: n = n().

Basic Math Formula Poster with Shapes and Rainbow Colors
A rainbow is just a distorted image of the sun. It results from raindrops which rearrange the sunlight via reflection and refraction. The Formation of a Rainbow Sir Isaac Newton found that white light is composed of all wavelengths of visible light.
White light is a mixture of all the colors of the spectrum, which are: Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet. If we break up white. The rainbow is a beautiful natural phenomenon that has fascinated people throughout history.

Primary Colors Of A Rainbow
It is formed when sunlight is refracted and dispersed by water droplets in the air, breaking white light into its full spectrum of color. But what exactly are the sequence of colors that make up a rainbow? Let's take a closer look at the 7 colors of the rainbow in order. The Rainbow - What Do You See? Table of Contents Introduction History of the Rainbow Geometric Optics.

The double rainbow occurs when the light undergoes two internal reflections before being refracted out to the viewer's eye. For every reflection and refraction, some of the light is lost, so the 2nd rainbow appears fainter than the main rainbow. It also appears higher in the sky: 50-53° above the sun's rays.
HTML Codes for Rainbow Colors
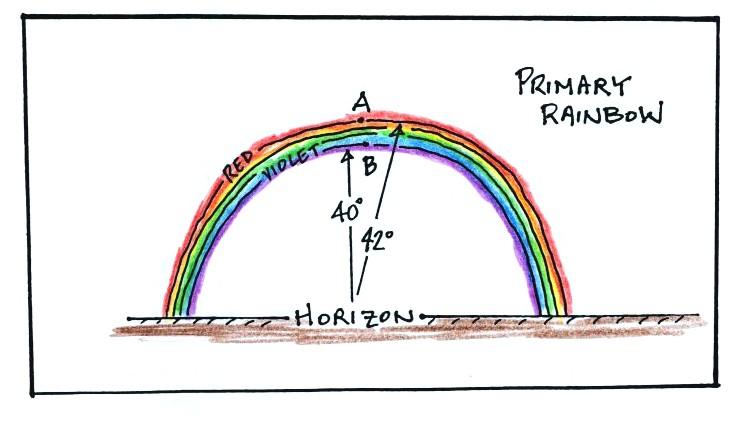
there is a second rainbow outside the first in which the colors go in the opposite direction! Figure \ (11.52\): Plot of \ (\theta_ {1}\) versus \ (\theta\) for red light and blue light. So what does this refraction do? The answer is almost nothing! The refracted ray is spread over a large range of angles, as shown in the graph in Figure. A rainbow can form when both sunshine and water droplets are in the sky.

Sunlight is white light, which is a mixture of all visible colors. As sunlight passes through the water droplets, it is bent and split into seven colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. You might be able to see a faint second rainbow above the main.

7 Colors of the Rainbow: A rainbow is a multi-colored curve that emerges in the heavens following rainfall. It materializes due to the interaction of sunlight and water droplets, involving both reflection and refraction. When sunlight traverses through raindrops or water particles, the light undergoes refraction, and the droplets reflect it from their surfaces.

Consequently, the light refracts.




