Histograms Ppt
Histograms will be a completely new concept for sixth graders. However, students can apply their knowledge of bar graphs that they acquired in previous years to quickly gain an understanding of how to create and interpret histograms. By the end of this lesson, students should be able to both create and analyze histograms.
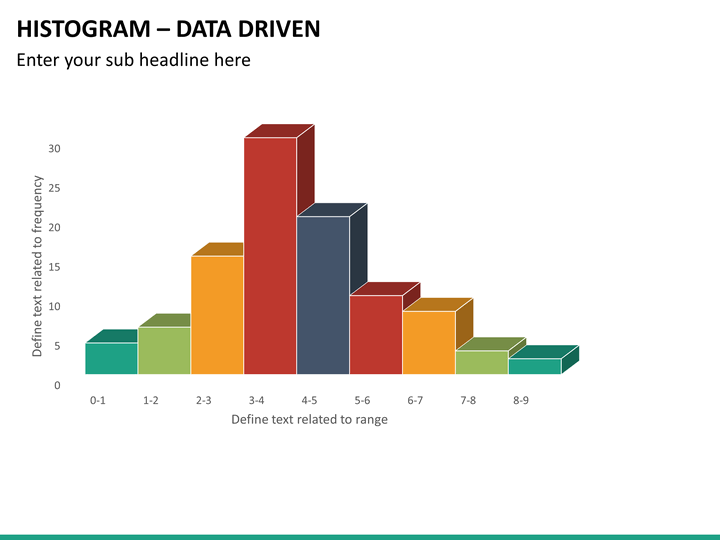
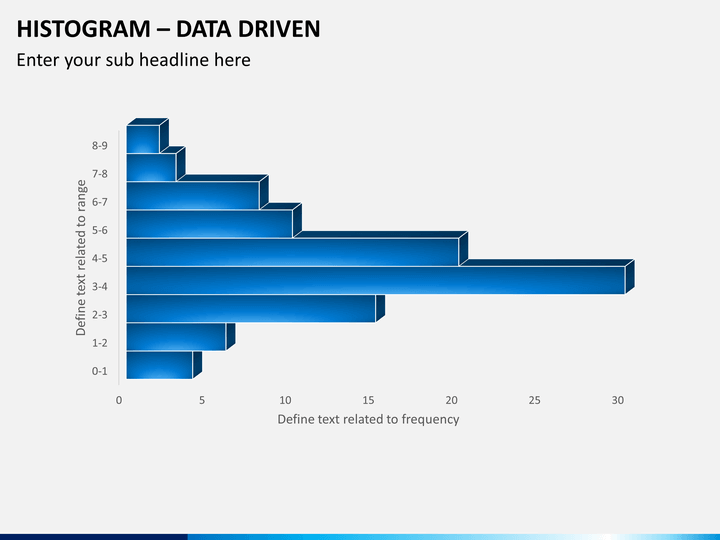
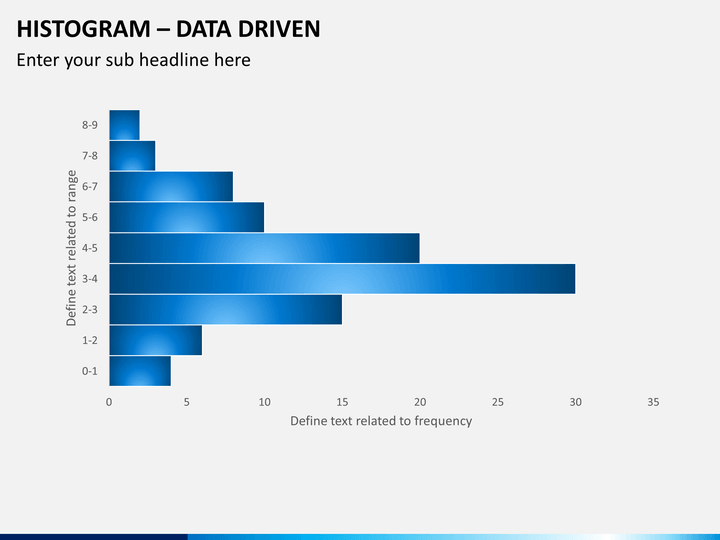
A histogram is a graphical representation of data using bars of different heights. It summarizes a data set by dividing it into bins and plotting the count of data points in each bin. The bins are usually consecutive, non.
PPT - Histograms PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2767452
Objectives: To understand why a histogram is useful for displaying data, and how to both draw and interpret a histogram. Powerpoints and Worksheets for 2 lessons on Histograms. One where the pupils learn to draw them and one with a recap of drawing as well as how to interpret some simple questions.

The histograms powerpoint features a range of questions, from simple to advanced, enhanced with illustrative examples. These materials help students construct and analyze histograms, supporting different learning rates and fostering a deep understanding of data distribution. Great resource! I used this to teach the Histograms maths skills for the AQA biology GCSE.

Histogram Chart for PowerPoint - PPT Slides
Clear and colourful PPT's for teaching. A histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights. It organizes and displays the distribution of data values or ranges of data.
The document discusses what a histogram is, why there is variation in data, how to construct a histogram, and key elements to study like location, spread, and shape of the data distribution. To construct a histogram, you need the minimum and. Histogram.

Histogram Chart for PowerPoint - PPT Slides
Differences from a bar chart: bars have equal width and always touch width of bars represents quantity heights of bars represent frequency. f. Measured quantity.
To construct a histogram from raw data:. Decide on the number of classes (5 to 15 is customary). Histograms Summary of column graphs so far A Bar Chart Sales of Paddling Pools per quarter A Frequency Diagram 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time taken to complete a Table Test Time in Minutes 1 2 3 4 5 6 Frequency Spot the differences from a bar chart to a frequency diagram: There are no gaps between the bars The horizontal axis has a continuous scale as it.
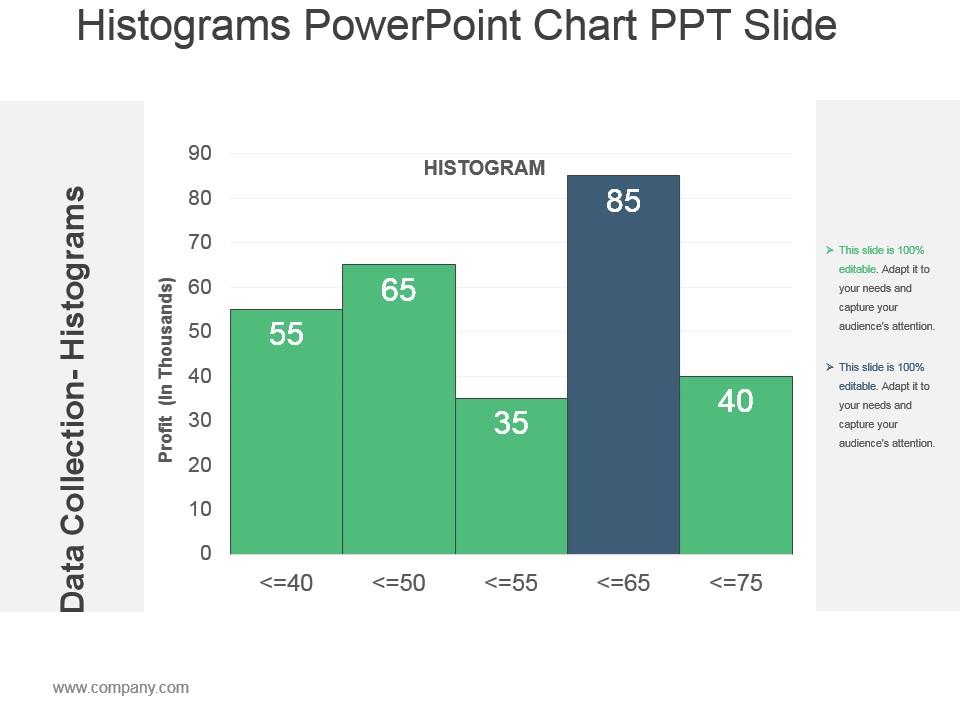
What proportion of students spend less than 5 minutes on their homework? What percentage of students spent more than 30 minutes on their homework? Draw a Frequency Table for this Histogram Draw a Cumulative Frequency Graph for this Histogram Estimate the mean time students spent on homework. What is the modal class?